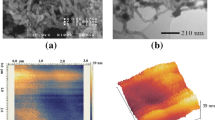
Abstract
The paper describes a sensitive method for simultaneous sensing of morphine (MOR) and diclofenac (DCF). The surface of a MgFe2O4/graphite paste electrode was modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes, and the resulting sensor was characterized by cyclic voltammetry, differential pulse voltammetry, chronoamperometry, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The electrode showed an efficient synergistic effect in term of oxidation of DCF and MOR, with sharp oxidation peaks occurring at +0.370 and 0.540 V (vs Ag/AgCl) at pH 7.0. The calibration plot for MOR is linear in the 50 nM to 920 μM concentration range, and the detection limit is 10 nM (at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3). The respective data for DCF are 100 nM to 580 μM, with a 60 nM LOD. The sensor was applied to the determination of MOR and DCF in spiked serum and urine samples, with recoveries ranging between 91.4 and 100.7 %.

A sensitive method for simultaneous sensing of morphine (MOR) and diclofenac (DCF) is described. The surface of MgFe2O4/graphite paste electrode was modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes, and the resulting sensor showed an efficient synergistic effect in terms of oxidation of DCF and MOR. The calibration plot for MOR is linear in the 50 nM to 920 μM concentration range, and the detection limit is 10 nM. The respective data for DCF are 100 nM to 580 μM, with a 60 nM LOD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Enna SJ, Bylund DB (2008) The comprehensive pharmacology reference. Elsevier Inc
Miranda HF, Silva E, Pinardi G (2004) Synergy between the antinociceptive effects of morphine and NSAIDs. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 82:331–337
Sun HL, Wu CC, Lin MS, Chang CF (1993) Effects of epidural morphine and intramuscular diclofenac combination in Postcesarean analgesia: a dose-range study. Anesth Analg 76:284–288
Ensafi AA, Izadi M, Karimi-Maleh H (2013) Sensitive voltammetric determination of diclofenac using room-temperature ionic liquid-modified carbon nanotubes paste electrode. Ionics 19:137–144
Talemi RP, Mashhadizadeh MH (2015) A novel morphine electrochemical biosensor based on intercalative and electrostatic interaction of morphine with double strand DNA immobilized onto a modified Au electrode. Talanta 131:460–466
Nigović B, Sadiković M, Sertić M (2014) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes/Nafion composite film modified electrode as a sensor for simultaneous determination of ondansetron and morphine. Talanta 122:187–194
Ahmar H, Tabani H, Koruni MH, Davarani SSH, Fakhari AR (2014) A new platform for sensing urinary morphine based on carrier assisted electromembrane extraction followed by adsorptive stripping voltammetric detection on screen-printed electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 54:189–194
Pournaghi-Azar MH, Saadatirad A (2008) Simultaneous voltammetric and amperometric determination of morphine and codeine using a chemically modified-palladized aluminum electrode. J Electroanal Chem 624:293–298
Sanati AL, Karimi-Maleh H, Badiei A, Biparva P, Ensafi AA (2014) A voltammetric sensor based on NiO/CNTs ionic liquid carbon paste electrode for determination of morphine in the presence of diclofenac. Mater Sci Eng C 35:379–385
Fei W, Chen F, Sun L, Li Q, Yang J, Wu Y (2014) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescent immunoassay for morphine using a gold electrode modified with CdS quantum dots, polyamidoamine, and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181:419–425
Mokhtari A, Karimi-Maleh H, Ensafi AA, Beitollahi H (2012) Application of modified multiwall carbon nanotubes paste electrode for simultaneous voltammetric determination of morphine and diclofenac in biological and pharmaceutical samples. Sensors Actuators B 169:96–105
Ensafi AA, Abarghoui MM, Rezaei B (2015) Simultaneous determination of morphine and codeine using Ptnanoparticles supported on porous silicon flour modified ionic liquid carbon paste electrode. Sensors Actuators B 219:1–9
Afkham A, Bahiraei A, Madrakian T (2016) Gold nanoparticle/multi-walled carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode as a sensitive voltammetric sensor for the determination of diclofenac sodium. Mater Sci Eng C 59:168–176
Taei M, Hadadzadeh H, Hasanpour F, Tavakkoli N, Dolatabadi MH (2015) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, epinephrine, and uric acid using a polymer film-modified electrode based on Au nanoparticles/poly(3,3′,5,5′-tetrabromo-m-cresolsulfonphthalein). Ionics 21:3267–3278
Sanghavi BJ, Wolfbeis OS, Hirsch T, Swami NS (2015) Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensing of neurological drugs and neurotransmitters. Microchim Acta 182:1–41
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354:56–58
Li WZ, Xie SS, Qian LX, Chang BH, Zou BS, Zhou WY, Zhao RA, Wang G (1996) Large-scale synthesis of aligned carbon nanotubes. Science 274:1701–1703
Treachy MM, Ebbesen TW, Gibson JM (1996) Exceptionally high Young’s modulus observed for individual carbon nanotubes. Nature 381:678–680
Ensafi AA, Karimi-Maleh H (2010) Modified multiwall carbon nanotubes paste electrode as a sensor for simultaneous determination of 6-thioguanine and folic acid using ferrocenedicarboxylic acid as a mediator. J Electroanal Chem 640:75–83
Xu Q, Wang SF (2005) Electrocatalytic oxidation and direct determination of L-tyrosine by square wave voltammetry at multi-wall carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrodes. Microchim Acta 151:47–52
Sun Y, Fei J, Hou J, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Hu B (2009) Simultaneous determination of dopamine and serotonin using a carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid gel modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim Acta 165:373–379
Zhang Y, Kang TF, Wan YW, Chen SY (2009) Gold nanoparticles-carbon nanotubes modified sensor for electrochemical determination of organophosphate pesticides. Microchim Acta 165:307–311
Wei S, Zhao F, Xu Z, Zeng B (2006) Voltammetric determination of folic acid with a multi-walled carbon nanotube-modified gold electrode. Microchim Acta 152:285–290
Wu FH, Zhao GC, Wei XW, Yang ZS (2004) Electrocatalysis of tryptophan at multi-walled carbon nanotube modified electrode. Microchim Acta 144:243–247
Shakir I, Sarfraza M, Ali Z, Aboud MFA, Agboola PO (2016) Magnetically separable and recyclable graphene-MgFe2O4 nanocomposites for enhanced photocatalytic applications. J Alloys Compd 660:450–455
Rai AK, Thi TV, Gim J, Kim J (2014) Combustion synthesis of MgFe2O4/graphene nanocomposite as a high-performance negative electrode for lithium ion batteries. Mater Charact 95:259–265
Chen Q, Rondinone AJ, Chakoumakos BC, Zhang ZJ (1999) Synthesis of superparamagnetic MgFe2O4 nanoparticles by coprecipitation. J Magn Magn Mater 194:1–7
Hackett LP, Dusci LJ, Ilett KF, Chiswell GM (2002) Optimizing the hydrolysis of codeine and morphine glucuronides in urine. Therap Drug Monit 24:652–657
Chen T, Dai L (2013) Carbon nanomaterials for highperformance supercapacitors. Mater Today 16:272–280
Ensafi AA, Arashpour B, Rezaei B, Allafchian AR (2014) Voltammetric behavior of dopamine at a glassy carbon electrode modified with NiFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles decorated withmultiwall carbon nanotubes. Mater Sci Eng C 39:78–85
Khot VM, Salunkhe AB, Thorat ND, Ningthoujam RS, Pawar SH (2013) Induction heating studies of dextran coated MgFe2O4 nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. Dalton Trans 42:1249–1258
Dehdashtian S, Gholivand MB, Shamsipur M, Kariminia S (2016) Construction of a sensitive and selective sensor for morphine using chitosan coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle as a modifier. Mater Sci Eng C 58:53–59
Goodarzian M, Khalilzade MA, Karimi F, Gupta VK, Keyvanfard M, Bagheri H, Fouladgar M (2014) Square wave voltammetric determination of diclofenac in liquid phase using a novel ionic liquid multiwall carbon nanotubes paste electrode. J Mol Liq 197:114–119
Sarwar M, Aman T (1984) Spectrophotometric determination of morphine. Microchem J 30:304–309
Khaskheli AR, Sarajuddin S, Abro K, Sherazi STH, Afridi HI, Mahesar SA, Saeed M (2009) Simpler and faster spectrophotometric determination of diclofenac sodium in tablets, serum and urine samples. Pak J Anal Environ Chem 10:53–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 548 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basiri, F., Taei, M. Application of spinel-structured MgFe2O4 nanoparticles for simultaneous electrochemical determination diclofenac and morphine. Microchim Acta 184, 155–162 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1995-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1995-0