Abstract
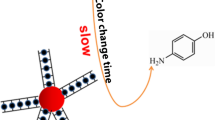
We describe a simple, highly sensitive, and selective colorimetric kinetic assay for the determination of potassium(I) by exploiting the specific recognition capability of an appropriate aptamer and catalytic signal amplification by gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Amplification is based on the reduction of 4-nitrophenol by borohydride which is catalyzed by AuNPs. This leads to a color change of the solution from yellow to colorless, and the color change can be recognized with bare eyes or via photometry. The K(I)-selective aptamer is placed on the AuNPs and forms a tightly bound G-quadruplex with K(I) which partially masks the surface of the AuNPs and prevents 4-nitrophenol to be reduced at the catalytically active surface of the AuNPs. Hence, the rate of decoloration is retarded. The assay displays high selectivity for K(I) over other cations, has a linear response in the 0.1 nM to 10 μM concentration range, and a detection limit as low as 0.06 nM. In addition, these findings pave the way to novel analytical methods based on the use of gold nanoparticle-catalyzed chemical reactions.

A simple, highly sensitive, and selective colorimetric kinetic assay for the determination of potassium(I) was represented.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gomes MTSR, Tavares KS, Oliveira JABP (2000) The quantification of potassium using a quartz crystal microbalance. Analyst 125:1983–1986
He HR, Mortellaro MA, Leiner MJP, Fraatz RJ, Tusa JK (2003) A fluorescent sensor with high selectivity and sensitivity for potassium in water. J Am Chem Soc 125:1468–1469
Kuo HC, Cheng CF, Clark RB, Lin JJC, Lin JLC, Hoshijima M, Nguyen-Tran VTB, Gu Y, Ikeda Y, Chu PH, Ross J Jr, Giles WR, Chien KR (2001) A defect in the Kv channel-interacting protein 2 (KChIP2) gene leads to a complete loss of I(to) and confers susceptibility to ventricular tachycardia. Cell 107:801–813
Yu SP, Canzoniero LMT, Choi DW (2001) Ion homeostasis and apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:405–411
Walz W (2000) Role of astrocytes in the clearance of excess extracellular potassium. Neurochem Int 36:291–300
Michaud GF, Strickberger SA (2001) Should an abnormal serum potassium concentration be considered a correctable cause of cardiac arrest. J Am Coll Cardiol 38:1224–1225
Modesto KM, Møller JE, Freeman WK, Shub C, Bailey KR, Pellikka PA (2006) Natural history of cardiac rhabdomyoma in infancy and childhood. Am J Cardiol 97:1247–1249
Ueyama H, Takagi M, Takenaka S (2002) A novel potassium sensing in aqueous media with a synthetic oligonucleotide derivative. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer associated with guanine quartet-potassium ion complex formation. J Am Chem Soc 124:14286–14287
Nagatoishi S, Nojima T, Juskowiak B, Takenaka S (2005) Pyrene-labeled G-quadruplex oligonucleotide as a fluorescence probe for potassium ions detection in biological applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:5067–5070
Wu ZS, Chen CR, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2008) Reversible electronic nanoswitch based on DNA G-quadruplex conformation: a platform for single-step, reagentless potassium detection. Biomaterials 29:2689–2696
Kim J, McQuade DT, McHugh SK, Swager TM (2000) Ion-specific aggregation in conjugated polymers: highly sensitive and selective fluorescent ion chemosensors. Angew Chem Int Ed 39:3868–3872
He F, Tang LY, Wang S, Li YL, Zhu DB (2005) Fluorescent amplifying recognition for DNA G-quadruplex folding with a cationic conjugated polymer: a platform for homogeneous potassium detection. J Am Chem Soc 127:12343–12346
Lee J, Kim HJ, Kim J (2008) Polydiacetylene liposome arrays for selective potassium detection. J Am Chem Soc 130:5010–5011
Qin H, Ren J, Wang J, Luedtke NW, Wang E (2010) G-quadruplex-modulated fluorescence detection of potassium in the presence of a 3500-fold excess of sodium ions. Anal Chem 82:8356–8360
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–822
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249:505–510
Stoltenburg R, Reinemann C, Strehlitz B (2007) SELEX-a (r)evolutionary method to generate high-affinity nucleic acid ligands. Biomol Eng 24:381–403
Stoltenburg R, Reinemann C, Strehlitz B (2005) FluMag-SELEX as an advantageous method for DNA aptamer selection. Anal Bioanal Chem 383:83–91
Liang HR, Hu GQ, Xue XH, Li L, Zheng XX, Gao YW, Yang ST, Xia XZ (2014) Selection of an aptamer against rabies virus: a new class of molecules with antiviral activity. Virus Res 184:7–13
Cunningham JC, Brenes NJ, Crooks RM (2014) Paper electrochemical device for detection of DNA and thrombin by target-induced conformational switching. Anal Chem 86:6166–6170
Mann D, Reinemann C, Stoltenburg R, Strehlitz B (2005) In vitro selection of DNA aptamers binding ethanolamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:1928–1934
Reinemann C, Stoltenburg R, Strehlitz B (2009) Investigations on the specificity of DNA aptamers binding to ethanolamine. Anal Chem 81:3973–3978
Ng A, Chinnappan R, Eissa S, Liu H, Tlili C, Zourob M (2012) Selection, characterization, and biosensing application of high affinity congener-specific microcystin-targeting aptamers. Environ Sci Technol 46:10697–10703
Eissa S, Ng A, Siaj M, Tavares AC, Zourob M (2013) Selection and identification of DNA aptamers against okadaic acid for biosensing application. Anal Chem 85:11794–11801
Kim B, Jung IH, Kang M, Shim HK, Woo HY (2012) Cationic conjugated polyelectrolytes-triggered conformational change of molecular beacon aptamer for highly sensitive and selective potassium ion detection. J Am Chem Soc 134:3133–3138
Alkilany AM, Lohse SE, Murphy CJ (2013) The gold standard: gold nanoparticle libraries to understand the nano-bio interface. Acc Chem Res 46:650–661
Dreaden EC, Alkilany AM, Huang XH, Murphy CJ, ElSayed MA (2012) The golden age: gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev 41:2740–2779
Storhoff JJ, Lazarides AA, Mucic RC, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL, Schatz GC (2000) What controls the optical properties of DNA-linked gold nanoparticle assemblies? J Am Chem Soc 122:4640–4650
Storhoff JJ, Elghanian R, Mucic RC, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL (1998) One-pot colorimetric differentiation of polynucleotides with single base imperfections using gold nanoparticle probes. J Am Chem Soc 120:1959–1964
Jin RC, Wu GS, Li Z, Mirkin CA, Schatz GC (2003) What controls the melting properties of DNA-linked gold nanoparticle assemblies? J Am Chem Soc 125:1643–1654
Verdian-Doghaei A, Housaindokht MR, Abnous K (2014) A fluorescent aptasensor for potassium ion detection-based triple-helix molecular switch. Anal Biochem 466:72–75
Yuanboonlim W, Siripornnoppakhun W, Niamnont N, Rashatasakhon P, Vilaivan T, Sukwattanasinitt M (2012) Phenylene-ethynylene trication as an efficient fluorescent signal transducer in an aptasensor for potassium ion. Biosens Bioelectron 33:17–22
Fan XY, Li HT, Zhao J, Lin FB, Zhang LL, Zhang YY, Yao SZ (2012) A novel label-free fluorescent sensor for the detection of potassium ion based on DNAzyme. Talanta 89:57–62
Sun HJ, Li XH, Li YC, Fan LZ, Kraatz HB (2013) A novel colorimetric potassium sensor based on the substitution of lead from G-quadruplex. Analyst 138:856–862
Chen ZB, Huang YQ, Li XX, Zhou T, Ma H, Qiang H, Liu YF (2013) Colorimetric detection of potassium ions using aptamer-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 787:189–192
Chen ZB, Guo JX, Ma H, Zhou T, Li XX (2014) A simple colorimetric sensor for potassium ion based on DNA G-quadruplex conformation and salt-induced gold nanoparticles aggregation. Anal Methods 6:8018–8021
Acknowledgments
All authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of key scientific and technological project of Henan Province (122102210406).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1.31 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Li, W. Colorimetric kinetic determination of potassium ions based on the use of a specific aptamer and catalytically active gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182, 2307–2312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1581-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1581-x