Abstract
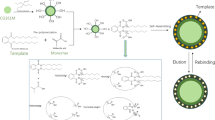
Fragment-imprinted microspheres (FIMs) were synthesized by suspension polymerization of 4-sulfa-6-chloropyrimidine (the template), methacrylic acid and styrene (the mixed functional monomers), divinylbenzene (the crosslinker), and azobisisobutyronitrile (the initiator). The optimum conditions were obtained by an orthogonal experiment. After removal of the templates, the microspheres serve as a material to fairly specifically bind sulfonamides, the absorption capacity being 6.32 mg g–1, whereas the absorption by non-imprinted microspheres is 1.68 mg g−1. A method was worked out for the simultaneous determination of five sulfonamides by solid phase extraction (using the FIMs) coupled to HPLC, and applied to analyze milk samples. The recoveries are within 87.6 and 96.5 %, with relative standard deviations between 1.25 and 2.89 %.

Graphical abstract showed that fragment imprinted-solid phase extraction had the best selective adsorption performance of the five sulfonamide antibiotics compare with C18, Silica and Florisil column. It was satisfactory by using fragment imprinted microspheres as sorbents of solid phase extraction for enriching and separating target compounds from complex matrices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curini R, Bogialli S, Corcia AD, Laganà A, Rizzuti G (2006) A rapid confirmatory method for analyzing tetracycline antibiotics in bovine, swine, and poultry muscle tissues: Matrix solid-phase dispersion with heated water as extractant followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Agr Food Chem 54:1564–1570
Koesukwiwat U, Jayanta S, Leepipatpiboon N (2007) Solid-phase extraction for multiresidue determination of sulfonamides, tetracyclines, and pyrimethamine in Bovine’s milk. J Chromatogr A 1149:102–111
Díaz-Cruz MS, García-Galán MJ, Barceló D (2008) Highly sensitive simultaneous determination of sulfonamide antibiotics and one metabolite in environmental waters by liquid chromatography–quadrupole linear ion trap–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1193:50–59
García-Galán MJ, Garrido T, Fraile J, Ginebreda A, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2011) Application of fully automated online solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of sulfonamides and their acetylated metabolites in groundwater. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:795–806
Nebot C, Regal P, Miranda J, Cepeda A, Fente C (2012) Simultaneous determination of sulfonamides, penicillins and coccidiostats in pork by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr Sci 50:414–425
Tso J, Dutta S, Inamdar S, Aga DS (2011) Simultaneous analysis of free and conjugated estrogens, sulfonamides, and tetracyclines in runoff water and soils using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography—tandem mass spectrometry. J Agr Food Chem 59:2213–2222
Su SF, Zhang M, Li BL, Zhang HY, Dong XC (2008) HPLC determination of sulfamethazine in milk using surface-imprinted silica synthesized with iniferter technique. Talanta 76:1141–1146
He J, Lv RH, Zhu J, Lu K (2010) Selective solid-phase extraction of dibutyl phthalate from soybean milk using molecular imprinted polymers. Anal Chim Acta 661:215–221
Xu WJ, Su SF, Jiang P, Wang HS, Dong XC, Zhang M (2010) Determination of sulfonamides in bovine milk with column-switching high performance liquid chromatography using surface imprinted silica with hydrophilic external layer as restricted access and selective extraction material. J Chromatogr A 1217:7198–7207
Xu ZG, Song CY, Hu YL, Li GK (2011) Molecularly imprinted stir bar sorptive extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for trace analysis of sulfa drugs in complex samples. Talanta 85(97):103
He J, Chen S, Jiang YL, Shen YZ, Zhu J, Wei HL, Zhang HX, Lu K (2012) Preparation and selective recognition of a novel solid-phase microextraction fiber combined with molecularly imprinted polymers for the extraction of parabens in soy sample. J Sep Sci 35:308–314
Varanasi VK (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymers: The Way forward. Org Chem Curr Res 1:1–2
Shi XZ, Meng Y, Liu JH, Sun AL, Li DX, Yao CX, Lu Y, Chen J (2011) Group-selective molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction for the simultaneous determination of six sulfonamides in aquaculture products. J Chromatogr B 879(1071):1076
Quesada-Molina C, Claude B, García-Campaña AM, Olmo-Iruela MD, Morin P (2012) Convenient solid phase extraction of cephalosporins in milk using a molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem 135:775–779
Sun N, Wu SL, Chen HX, Zheng DJ, Xu JW, Ye Y (2012) Determination of sulfamethoxazole in milk using molecularly imprinted polymer monolith microextraction coupled to HPLC. Microchim Acta 179:33–40
Chen C, Zhang XF, Long Z, Zhang JY, Zheng CB (2012) Molecularly imprinted dispersive solid-phase microextraction for determination of sulfamethazine by capillary electrophoresis. Microchim Acta 178:293–299
Kubo T, Hosoya K, Watabe Y, Ikegami T, Tanaka N, Sano T, Kaya K (2004) Polymer-based adsorption medium prepared using a fragment imprinting technique for homologues of chlorinated bisphenol A produced in the environment. J Chromatogr A 1029:37–41
Theodoridis G, Kantifes A, Manesiotis P, Raikos N, Tsoukali-Papadopoulou H (2003) Preparation of a molecularly imprinted polymer for the solid-phase extraction of scopolamine with hyoscyamine as a dummy template molecule. J Chromatogr A 987:103–109
Kubo T, Nomachi M, Nemoto K, Sano T, Hosoya K, Tanaka N, Kaya K (2006) Chromatographic separation for domoic acid using a fragment imprinted polymer. Anal Chim Acta 577:1–7
Kubo T (2008) Development and applications of fragment imprinting technique. Chromatogr 29:9–17
Bossi AM, Sharma PS, Montana L, Zoccatelli G, Laub O, Levi R (2012) Fingerprint-imprinted polymer: Rational selection of peptide epitope templates for the determination of proteins by molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chem 84:4036–4041
ZhangZ M, Tan W, Hu YL, Li GK, Zan S (2012) Microwave synthesis of gibberellinacid 3 magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads for the trace analysis ofgibberellin acids in plant samples by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometrydetection. Analyst 137:968–977
Yan HY, Wang F, Han DD, Yang GL (2012) Simultaneous determination of four plant hormones inbananas by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with highperformance liquid chromatography. Analyst 137:2884–2890
Haginaka J, Tabo H, Matsunaga H (2012) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers for organophosphates and their application to the recognition of organophosphorus compounds and phosphopeptides. Anal Chim Acta 748:1–8
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully appreciate the financial support from the following research funds: Key Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Province (112102310030), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in the Education Department of Henan Province (2010A150006), Plan of Nature Science Fundamental Research in Henan University of Technology and Education Innovation Foundation for the Postgraduate of Henan University of Technology (11YJCX08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Tang, H., You, L. et al. Fragment-imprinted microspheres for the extraction of sulfonamides. Microchim Acta 180, 903–910 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1011-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1011-x