Abstract
Purposes
Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a key target for the treatment of several malignancies. The present study was conducted to clarify the role of serum PD-L1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
Serum PD-L1 (sPD-L1) was examined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 153 patients with HCC who underwent curative hepatectomy at Kumamoto University in 2011–2016. The expression of PD-L1 in tissue (tPD-L1) was investigated by immunohistochemistry. The clinical roles of the PD-L1 expression in both serum and tissue were examined.
Results
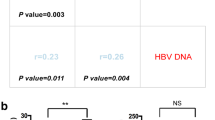
The sPD-L1 was significantly elevated in HCC patients compared to patients without any malignant or inflammatory disease (234 vs. 93 pg/mL, p < 0.0001). The percentage of the tPD-L1-positive area (%tPD-L1) in the background liver was significantly higher than in the tumor (1.52% vs. 0.48%, p < 0.0001). The %tPD-L1 in the background liver but not in the tumor was significantly correlated with the sPD-L1 level (p = 0.0079). The sPD-L1, %tPD-L1 in the tumor, and %tPD-L1 in the background liver were not correlated with the overall survival after surgery.
Conclusion
PD-L1-expressing cells in the background liver, but not in the tumor tissue, appeared to contribute to the sPD-L1 level. The sPD-L1 level may thus not indicate the tumor burden in patients with HCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang H, Liddell CA, Coates MM, Mooney MD, Levitz CE, Schumacher AE, et al. Global, regional, and national levels of neonatal, infant, and under-5 mortality during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384:957–79.
Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–55.
Steel JL, Geller DA, Gamblin TC, Olek MC, Carr BI. Depression, immunity, and survival in patients with hepatobiliary carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2397–405.
Binnewies M, Roberts EW, Kersten K, Chan V, Fearon DF, Merad M, et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nature Med. 2018;24:541–50.
Sznol M, Chen L. Antagonist antibodies to PD-1 and B7–H1 (PD-L1) in the treatment of advanced human cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:1021–34.
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. New Engl J Med. 2010;363:711–23.
Gao Q, Wang XY, Qiu SJ, Yamato I, Sho M, Nakajima Y, et al. Overexpression of PD-L1 significantly associates with tumor aggressiveness and postoperative recurrence in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:971–9.
Calderaro J, Rousseau B, Amaddeo G, Mercey M, Charpy C, Costentin C, et al. Programmed death ligand 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: relationship with clinical and pathological features. Hepatology. 2016;64:2038–46.
Xie QK, Zhao YJ, Pan T, Lyu N, Mu LW, Li SL, et al. Programmed death ligand 1 as an indicator of pre-existing adaptive immune responses in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5:e1181252.
El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi TS, Kudo M, Hsu C, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2492–502.
Chen Y, Wang Q, Shi B, Xu P, Hu Z, Bai L, et al. Development of a sandwich ELISA for evaluating soluble PD-L1 (CD274) in human sera of different ages as well as supernatants of PD-L1+ cell lines. Cytokine. 2011;56:231–8.
Finkelmeier F, Canli O, Tal A, Pleli T, Trojan J, Schmidt M, et al. High levels of the soluble programmed death-ligand (sPD-L1) identify hepatocellular carcinoma patients with a poor prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 2016;59:152–9.
Han X, Gu YK, Li SL, Chen H, Chen MS, Cai QQ, et al. Pre-treatment serum levels of soluble programmed cell death-ligand 1 predict prognosis in patients with hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019;145:303–12.
Okabe H, Yoshizumi T, Yamashita YI, Imai K, Hayashi H, Nakagawa S, et al. Histological architectural classification determines recurrence pattern and prognosis after curative hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0203856.
Okabe H, Delgado E, Lee JM, Yang J, Kinoshita H, Hayashi H, et al. Role of leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 as a biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e98817.
Ichida FTT, Omata M, Ichida T, Inoue K, Kamimura T, Yamada G, Hino K, Yokosuka O, Suzuki H. New Inuyama classification; new criteria for histological assessment of chronic hepatitis. Int Hepatol Commun. 1996;6:112–9.
Okabe H, Beppu T, Hayashi H, Horino K, Masuda T, Komori H, et al. Hepatic stellate cells may relate to progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:2555–644.
Takahashi N, Iwasa S, Sasaki Y, Shoji H, Honma Y, Takashima A, et al. Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 as a prognostic factor on the first-line treatment of metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016;142:1727–38.
El-Ghammaz AMS, Gadallah HA, Kamal G, Maher MM, Mohamad MA. Impact of serum soluble programed death ligand 1 on end of treatment metabolic response of diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients. Clin Exp Med. 2018;18:505–12.
Akutsu Y, Murakami K, Kano M, Toyozumi T, Matsumoto Y, Takahashi M, et al. The concentration of programmed cell death-ligand 1 in the peripheral blood is a useful biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus. 2018;15:103–8.
Chang B, Huang T, Wei H, Shen L, Zhu D, He W, et al. The correlation and prognostic value of serum levels of soluble programmed death protein 1 (sPD-1) and soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019;68:353–63.
Mataki N, Kikuchi K, Kawai T, Higashiyama M, Okada Y, Kurihara C, et al. Expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in the liver in autoimmune liver diseases. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:302–12.
Yamagiwa S, Ishikawa T, Waguri N, Sugitani S, Kamimura K, Tsuchiya A, et al. Increase of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Int J Med Sci. 2017;14:403–11.
Muhlbauer M, Fleck M, Schutz C, Weiss T, Froh M, Blank C, et al. PD-L1 is induced in hepatocytes by viral infection and by interferon-alpha and -gamma and mediates T cell apoptosis. J Hepatol. 2006;45:520–8.
Yanaba K, Hayashi M, Yoshihara Y, Nakagawa H. Serum levels of soluble programmed death-1 and programmed death ligand-1 in systemic sclerosis: association with extent of skin sclerosis. J Dermatol. 2016;43:954–7.
Shi B, Du X, Wang Q, Chen Y, Zhang X. Increased PD-1 on CD4(+)CD28(-) T cell and soluble PD-1 ligand-1 in patients with T2DM: association with atherosclerotic macrovascular diseases. Metabolism. 2013;62:778–85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elmezayen, H.A., Okabe, H., Baba, Y. et al. Clinical role of serum programmed death ligand 1 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Where does it come from?. Surg Today 50, 569–576 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-019-01920-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-019-01920-8