Abstract
Purpose
Immune checkpoint molecules are key targets for the treatment of various malignancies. Due to the heterogeneity of advanced gastric cancer (GC), the role of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression as a tumor biomarker remains controversial. In this study, the prognostic value of soluble PD-L1 (sPD-L1) levels in serum samples was assessed in patients with metastatic GC.
Methods
All patients received first-line treatment with fluoropyrimidine and platinum chemotherapy, and trastuzumab was added for HER2-positive patients. Serum levels of sPD-L1 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results
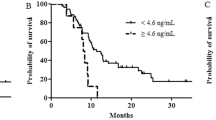
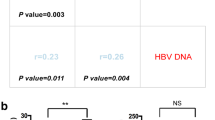
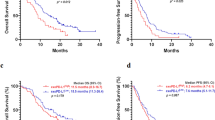
Among 75 metastatic GC patients, the median serum sPD-L1 level was 0.704 ng/ml (range <0.156–3.214). Serum sPD-L1 was significantly higher in patients with a high versus a low white blood cell count at baseline. When the cutoff value was set as the median, multivariate analyses showed that high sPD-L1 levels were associated with worse overall survival compared with low sPD-L1 levels (HR 2.218, 95 % CI 1.139–4.320, P = 0.019). Regardless of HER2 status, overall survival tended to be shorter in patients with high sPD-L1 compared with low sPD-L1. There was no significant association between sPD-L1 level and progression-free survival on the first-line treatment of metastatic GC.
Conclusions
High serum levels of sPD-L1 correlated with worse overall survival on the first-line chemotherapy in metastatic GC patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T (2010) Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376:687–697
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR, Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, Barlesi F, Kohlhäufl M, Arrieta O, Burgio MA, Fayette J, Lena H, Poddubskaya E, Gerber DE, Gettinger SN, Rudin CM, Rizvi N, Crinò L, Blumenschein GR Jr, Antonia SJ, Dorange C, Harbison CT, Graf Finckenstein F, Brahmer JR (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373:1627–1639
Callea M, Albiges L, Gupta M, Cheng SC, Genega EM, Fay AP, Song J, Carvo I, Bhatt RS, Atkins MB, Hodi FS, Choueiri TK, McDermott DF, Freeman GJ, Signoretti S (2015) Differential expression of PD-L1 between primary and metastatic sites in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res 3:1158–1164
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2014) Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature 513:202–209
Chen Y, Wang Q, Shi B, Xu P, Hu Z, Bai L, Zhang X (2011) Development of a sandwich ELISA for evaluating soluble PD-L1 (CD274) in human sera of different ages as well as supernatants of PD-L1+ cell lines. Cytokine 56:231–238
Cheng S, Zheng J, Zhu J, Xie C, Zhang X, Han X, Song B, Ma Y, Liu J (2015) PD-L1 gene polymorphism and high level of plasma soluble PD-L1 protein may be associated with non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Biol Markers 30:e364–e368
Cierna Z, Mego M, Miskovska V, Machalekova K, Chovanec M, Svetlovska D, Hainova K, Rejlekova K, Macak D, Spanik S, Ondrus D, Kajo K, Mardiak J, Babal P (2016) Prognostic value of programmed-death-1 receptor (PD-1) and its ligand 1 (PD-L1) in testicular germ cell tumors. Ann Oncol 27:300–305
Crane CA, Panner A, Murray JC, Wilson SP, Xu H, Chen L, Simko JP, Waldman FM, Pieper RO, Parsa AT (2009) PI(3) kinase is associated with a mechanism of immunoresistance in breast and prostate cancer. Oncogene 28:306–312
de Guillebon E, Roussille P, Frouin E, Tougeron D (2015) Anti program death-1/anti program death-ligand 1 in digestive cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 7:95–101
Dronca RS, Markovic SN, Kottschade LA, Nevala W, Dong H (2015) Bim as a predictive T cell biomarker for response to anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma (MM). CRI-CIMT-EATI-AACR; September 16–19, New York, NY, Abstract A007
Frigola X, Inman BA, Lohse CM, Krco CJ, Cheville JC, Thompson RH, Leibovich B, Blute ML, Dong H, Kwon ED (2011) Identification of a soluble form of B7-H1 that retains immunosuppressive activity and is associated with aggressive renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 17:1915–1923
Frigola X, Inman BA, Krco CJ, Liu X, Harrington SM, Bulur PA, Dietz AB, Dong H, Kwon ED (2012) Soluble B7-H1: differences in production between dendritic cells and T cells. Immunol Lett 142:78–82
Fuchs CS, Tomasek J, Yong CJ, Dumitru F, Passalacqua R, Goswami C, Safran H, dos Santos LV, Aprile G, Ferry DR, Melichar B, Tehfe M, Topuzov E, Zalcberg JR, Chau I, Campbell W, Sivanandan C, Pikiel J, Koshiji M, Hsu Y, Liepa AM, Gao L, Schwartz JD, Tabernero J, Trial Investigators REGARD (2014) Ramucirumab monotherapy for previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (REGARD): an international, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 383:31–39
Geng Y, Wang H, Lu C, Li Q, Xu B, Jiang J, Wu C (2014) Expression of costimulatory molecules B7-H1, B7-H4 and Foxp3+ Tregs in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Int J Clin Oncol 20:273–281
Grenader T, Waddell T, Peckitt C, Oates J, Starling N, Cunningham D, Bridgewater J (2016) Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in advanced oesophago-gastric cancer: exploratory analysis of the REAL-2 trial. Ann Oncol 2016(27):687–692
Hanahan D, Coussens LM (2012) Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 21:309–322
Hou J, Yu Z, Xiang R, Li C, Wang L, Chen S, Li Q, Chen M, Wang L (2014) Correlation between infiltration of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells and expression of B7-H1 in the tumor tissues of gastric cancer. Exp Mol Pathol 96:284–291
Huang B, Chen L, Bao C, Sun C, Li J, Wang L, Zhang X (2015) The expression status and prognostic significance of programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 in gastrointestinal tract cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther 8:2617–2625
Jiang D, Xu YY, Li F, Xu B, Zhang XG (2014) The role of B7-H1 in gastric carcinoma: clinical significance and related mechanism. Med Oncol 31:268
Joyce JA, Pollard JW (2009) Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 9:239–252
Kerr KM, Tsao MS, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Wistuba II, Hirsch FR, Pathology Committee IASLC (2015) Programmed death-ligand 1 immunohistochemistry in lung cancer: In what state is this art? J Thorac Oncol 10:985–989
Kim GM, Jeung HC, Rha SY, Kim HS, Jung I, Nam BH, Lee KH, Chung HC (2012) A randomized phase II trial of S-1-oxaliplatin versus capecitabine-oxaliplatin in advanced gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer 48:518–526
Kim JR, Moon YJ, Kwon KS, Bae JS, Wagle S, Kim KM, Park HS, Lee H, Moon WS, Chung MJ, Kang MJ, Jang KY (2013) Tumor infiltrating PD1-positive lymphocytes and the expression of PD-L1 predict poor prognosis of soft tissue sarcomas. PLoS One 8:e82870
Kim JW, Nam KH, Ahn SH, Park do J, Kim HH, Kim SH, Chang H, Lee JO, Kim YJ, Lee HS, Kim JH, Bang SM, Lee JS, Lee KW (2016) Prognostic implications of immunosuppressive protein expression in tumors as well as immune cell infiltration within the tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 19:42–52
Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T, Takagane A, Akiya T, Takagi M, Miyashita K, Nishizaki T, Kobayashi O, Takiyama W, Toh Y, Nagaie T, Takagi S, Yamamura Y, Yanaoka K, Orita H, Takeuchi M (2008) S-1 plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): a phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 9:215–221
Koizumi W, Nakayama N, Tanabe S, Sasaki T, Higuchi K, Nishimura K, Takagi S, Azuma M, Ae T, Ishido K, Nakatani K, Naruke A, Katada C (2012) A multicenter phase II study of combined chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and S-1 in patients with unresectable or recurrent gastric cancer (KDOG 0601). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69:407–413
Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Kemberling H, Eyring AD, Skora AD, Luber BS, Azad NS, Laheru D, Biedrzycki B, Donehower RC, Zaheer A, Fisher GA, Crocenzi TS, Lee JJ, Duffy SM, Goldberg RM, de la Chapelle A, Koshiji M, Bhaijee F, Huebner T, Hruban RH, Wood LD, Cuka N, Pardoll DM, Papadopoulos N, Kinzler KW, Zhou S, Cornish TC, Taube JM, Anders RA, Eshleman JR, Vogelstein B, Diaz LA Jr (2015) PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency. N Engl J Med 372:2509–2520
Llosa NJ, Cruise M, Tam A, Wicks EC, Hechenbleikner EM, Taube JM, Blosser RL, Fan H, Wang H, Luber BS, Zhang M, Papadopoulos N, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Sears CL, Anders RA, Pardoll DM, Housseau F (2015) The vigorous immune microenvironment of microsatellite instable colon cancer is balanced by multiple counter-inhibitory checkpoints. Cancer Discov 5:43–51
Lote H, Cafferkey C, Chau I (2015) PD-1 and PD-L1 blockade in gastrointestinal malignancies. Cancer Treat Rev 41:893–903
Madore J, Vilain RE, Menzies AM, Kakavand H, Wilmott JS, Hyman J, Yearley JH, Kefford RF, Thompson JF, Long GV, Hersey P, Scolyer RA (2015) PD-L1 expression in melanoma shows marked heterogeneity within and between patients: implications for anti-PD-1/PD-L1 clinical trials. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 28:245–253
McLaughlin J, Han G, Schalper KA, Carvajal-Hausdorf D, Pelekanou V, Rehman J, Velcheti V, Herbst R, LoRusso P, Rimm DL (2016) Quantitative assessment of the heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol 2:46–54
Meng X, Huang Z, Teng F, Xing L, Yu J (2015) Predictive biomarkers in PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev 41:868–876
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, Tykodi SS, Sosman JA, Procopio G, Plimack ER, Castellano D, Choueiri TK, Gurney H, Donskov F, Bono P, Wagstaff J, Gauler TC, Ueda T, Tomita Y, Schutz FA, Kollmannsberger C, Larkin J, Ravaud A, Simon JS, Xu LA, Waxman IM, Sharma P, CheckMate 025 Investigators (2015) Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 373:1803–1813
Muenst S, Schaerli AR, Gao F, Däster S, Trella E, Droeser RA, Muraro MG, Zajac P, Zanetti R, Gillanders WE, Weber WP, Soysal SD (2014) Expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 146:15–24
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB, Lewis CE (2008) The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 8:618–631
Muro K, Bang YJ, Shankaran V, Geva R, Catenacci DVT, Gupta S, Eder JP, Berger R, Gonzalez EJ, Ray A, Dolled-Filhart M, Emancipator K, Pathiraja K, Lunceford JK, Cheng JD, Koshiji M, Chung HC (2014) Relationship between PD-L1 expression and clinical outcomes in patients (Pts) with advanced gastric cancer treated with the anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody pembrolizumab (Pembro; MK-3475) in KEYNOTE-012. Ann Oncol 25:1–41
Nomi T, Sho M, Akahori T, Hamada K, Kubo A, Kanehiro H, Nakamura S, Enomoto K, Yagita H, Azuma M, Nakajima Y (2007) Clinical significance and therapeutic potential of the programmed death-1 ligand/programmed death-1 pathway in human pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:2151–2157
Ock CY, Nam AR, Lee J, Bang JH, Lee KH, Han SW, Kim TY, Im SA, Kim TY, Bang YJ, Oh DY (2016) Prognostic implication of antitumor immunity measured by the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and serum cytokines and angiogenic factors in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. Epub ahead of print
Paydas S, Bağır E, Seydaoglu G, Ercolak V, Ergin M (2015) Programmed death-1 (PD-1), programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), and EBV-encoded RNA (EBER) expression in hodgkin lymphoma. Ann Hematol 94:1545–1552
Qian Y, Deng J, Geng L, Xie H, Jiang G, Zhou L, Wang Y, Yin S, Feng X, Liu J, Ye Z, Zheng S (2008) TLR4 signaling induces B7-H1 expression through MAPK pathways in bladder cancer cells. Cancer Investig 26:816–821
Qing Y, Li Q, Ren T, Xia W, Peng Y, Liu GL, Luo H, Yang YX, Dai XY, Zhou SF, Wang D (2015) Upregulation of PD-L1 and APE1 is associated with tumorigenesis and poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:901–909
Robert C, Long GV, Brady B, Dutriaux C, Maio M, Mortier L, Hassel JC, Rutkowski P, McNeil C, Kalinka-Warzocha E, Savage KJ, Hernberg MM, Lebbé C, Charles J, Mihalcioiu C, Chiarion-Sileni V, Mauch C, Cognetti F, Arance A, Schmidt H, Schadendorf D, Gogas H, Lundgren-Eriksson L, Horak C, Sharkey B, Waxman IM, Atkinson V, Ascierto PA (2015) Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med 372:320–330
Rossille D, Gressier M, Damotte D, Maucort-Boulch D, Pangault C, Semana G, Le Gouill S, Haioun C, Tarte K, Lamy T, Milpied N, Fest T, Groupe Ouest-Est des Leucémies et Autres Maladies du Sang; Groupe Ouest-Est des Leucémies et Autres Maladies du Sang (2014) High level of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 in blood impacts overall survival in aggressive diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma: results from a French multicenter clinical trial. Leukemia 28:2367–2375
Simon I, Zhuo S, Corral L, Diamandis EP, Sarno MJ, Wolfert RL, Kim NW (2006) B7-h4 is a novel membrane-bound protein and a candidate serum and tissue biomarker for ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 66:1570–1575
Simon I, Liu Y, Krall KL, Urban N, Wolfert RL, Kim NW, McIntosh MW (2007) Evaluation of the novel serum markers B7-H4, Spondin 2, and DcR3 for diagnosis and early detection of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 106:112–118
Thompson RH, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Dong H, Lohse CM, Webster WS, Sengupta S, Frank I, Parker AS, Zincke H, Blute ML, Sebo TJ, Cheville JC, Kwon ED (2006) Tumor B7-H1 is associated with poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma patients with long-term follow-up. Cancer Res 66:3381–3385
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2012) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108
Wang L, Chang EW, Wong SC, Ong SM, Chong DQ, Ling KL (2013) Increased myeloid-derived suppressor cells in gastric cancer correlate with cancer stage and plasma S100A8/A9 proinflammatory proteins. J Immunol 190:794–804
Wang A, Wang HY, Liu Y, Zhao MC, Zhang HJ, Lu ZY, Fang YC, Chen XF, Liu GT (2015a) The prognostic value of PD-L1 expression for non-small cell lung cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol 41:450–456
Wang L, Wang H, Chen H, Wang WD, Chen XQ, Geng QR, Xia ZJ, Lu Y (2015b) Serum levels of soluble programmed death ligand 1 predict treatment response and progression free survival in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 6:41228–41236
Wilke H, Muro K, Van Cutsem E, Oh SC, Bodoky G, Shimada Y, Hironaka S, Sugimoto N, Lipatov O, Kim TY, Cunningham D, Rougier P, Komatsu Y, Ajani J, Emig M, Carlesi R, Ferry D, Chandrawansa K, Schwartz JD, Ohtsu A, RAINBOW Study Group (2014) Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (RAINBOW): a double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 15:1224–1235
Wu C, Zhu Y, Jiang J, Zhao J, Zhang XG, Xu N (2006) Immunohistochemical localization of programmed death-1 ligand-1 (PD-L1) in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Acta Histochem 108:19–24
Wu P, Wu D, Li L, Chai Y, Huang J (2015) PD-L1 and survival in solid tumors: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 10:e0131403
Yamada Y, Higuchi K, Nishikawa K, Gotoh M, Fuse N, Sugimoto N, Nishina T, Amagai K, Chin K, Niwa Y, Tsuji A, Imamura H, Tsuda M, Yasui H, Fujii H, Yamaguchi K, Yasui H, Hironaka S, Shimada K, Miwa H, Hamada C, Hyodo I (2015) Phase III study comparing oxaliplatin plus S-1 with cisplatin plus S-1 in chemotherapy-naïve patients with advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol 26:141–148
Yang L, Huang J, Ren X, Gorska AE, Chytil A, Aakre M, Carbone DP, Matrisian LM, Richmond A, Lin PC, Moses HL (2008) Abrogation of TGF beta signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits Gr-1+ CD11b+ myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 13:23–35
Zheng Z, Bu Z, Liu X, Zhang L, Li Z, Wu A, Wu X, Cheng X, Xing X, Du H, Wang X, Hu Y, Ji (2014) Level of circulating PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced gastric cancer and its clinical implications. Chin J Cancer Res 26:104–111
Acknowledgments
We gratefully appreciate the participation of the patients and their families in this study, and we would like to thank all co-investigators for their contributions: Ms. Hideko Morita and Mrs. Noriko Abe (serum sample preparation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the national regulations and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent of Biobank of National Cancer Center and using the clinical data was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2016_2184_MOESM2_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 2. Prognostic analyses of progression-free survival by uni- and multivariate analyses (DOCX 20 kb)
432_2016_2184_MOESM3_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 3. Difference in patient characteristics by serum sPD-L1 levels using the median as the cutoff value (DOCX 22 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, N., Iwasa, S., Sasaki, Y. et al. Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 as a prognostic factor on the first-line treatment of metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 1727–1738 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2184-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2184-6