Abstract
Purpose
Percutaneous thermal ablation is used for treating hepatic tumors. Recent advances in laparoscopy and imaging modalities have led to the development of a novel image-guided minimally invasive loco-regional treatment. The aim of this trial was to apply laparoscopic assistance to magnetic resonance (MR) image-guided thermoablation instead of ultrasonography, because of its various advantages.
Methods
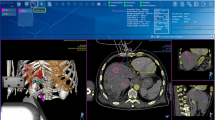
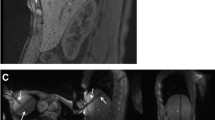
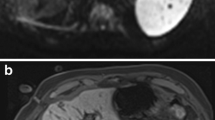
Patients with hepatic tumors and liver cirrhosis underwent magnetic resonance (MR) image-guided laparoscopic microwave coagulation therapy using a borescope and endoscopic forceps. Six cases of laparoscopic microwave coagulation treatment using MR image guidance were successfully performed between January 2000 and December 2008. Tumors were detected, punctured, and ablated in an open-configured MR scanner. A total of nine hepatocellular carcinoma nodules were preoperatively identified in S3, S5 and S6 (mean diameter = 20.8 ± 5.4 mm).
Results
MR-guided microwave coagulation was laparoscopically achieved in all patients without any significant complications that required invasive treatment. The mean length of the operation was 275.3 ± 60.5 min, and the mean postsurgical hospital stay was 10.0 ± 2.3 days. Postoperative confirmation scanning was performed without moving the patients.
Conclusion
MR-guided laparoscopic microwave coagulation therapy is an effective treatment for hepatic tumors adjacent to other organs, as it allows for more accurate detection of lesions and for tumors to be treated safely while avoiding adjacent organs. It is less invasive than conventional procedures, because the MR real-time guidance enabled continuous monitoring throughout the procedure.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seifert JK, Junginger T, Morris Dl. A collective review of the world literature on hepatic cryotherapy. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1998;43:141–54.
Gilbert JC. Current advances in interventional MRI guided cryosurgery. Eur Radiol. 1997;7:1165.
Mack MG, Straub R, Eichler K, Engelmann K, Zangos S, Roggan A, et al. Percutaneous MR imaging-guided laser-induced thermotherapy of hepatic metastases. Abdom Imaging. 2001;26:369–74.
Rossi S, Di Stasi M, Buscarini E, Cavanna L, Quaretti P, Squassante E, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency interstitial thermal ablation in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer J Sci Am. 1995;1(1):73–81.
Poon RT, Fan ST, Tsang FH, Wong J. Locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: a critical review from the surgeon’s perspective. Ann Surg. 2002;235:466–86.
Ido K, Isoda N, Sugano K. Microwave coagulation therapy for liver cancer: laparoscopic microwave coagulation. J Gastroenterol. 2001;36:145–52.
Stattner S, Primavesi F, Yip VS, Jones RP, Ofner D, Malik HZ, et al. Evolution of surgical microwave ablation for the treatment of colorectal cancer liver metastasis: review of the literature and a single centre experience. Surg Today 2014 (Online First).
Head HW, Dodd GD III. Thermal ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:167–78.
Ng KK, Poon RT. Radiofrequency ablation for malignant liver tumor. Surg Oncol. 2005;14:41–52.
Cillio U, Vitale A, Dupuis D, Corso S, Neri D, Damico, et al. Laparoscopic ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients unsuitable for liver resection or percutaneous treatment: A cohort study. PLoS One 2013;8(2):1–8.
Santambrogio R, Opocher E, Montorsi M. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: a critical review from the surgeon’s perspective. J Ultrasound. 2008;11:1–7.
Seki S, Sakaguchi H, Iwai S, Kadoya H, Kabayashi S, Kitada T, et al. Five-year survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with laparoscopic microwave coagulation therapy. Endoscopy. 2005;37(12):1220–5.
Imura S, Shimada M, Utsunomiya T, Morine Y, Wakabayashi G, Kaneko H. Current status of laparoscopic liver surgery in Japan: results of a multicenter Japanese experience. Surg Today. 2014;44(7):1214–9.
Jolesz FA, Morrison PR, Koran SJ, Kelley RJ, Hushek SG, Newman RW, et al. Compatible instrumentation for intraoperative MRI: expanding resources. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1998;8(1):8–11.
Moscatel MA, Shellock FG, Morisoli SM. Biopsy needles and devices: assessment of ferromagnetism and artifacts during exposure to a 1.5-T MR system. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1995;5(3):369–72.
Morikawa S, Inubushi T, Kurumi Y, Naka S, Sato K, Tani T, et al. MR-guided microwave thermocoagulation therapy of liver tumors: initial clinical experiences using a.5 T open MR system. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;16:576–83.
Sato K, Morikawa S, Inubushi T, Kurumi Y, Naka S, Haque HA, et al. Alternate biplanar MR navi- gation for microwave ablation of liver tumors. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2005;4:89–94.
Morikawa S, Inubushi T, Kurumi Y, Naka S, Sato K, Demura K, et al. Feasibility of respiratory triggering for MR-guided microwave ablation of liver tumors under general anesthesia. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2004;27:370–3.
Morikawa S, Inubushi T, Kurumi Y, Naka S, Sato K, Tani T, et al. New assistive devices for MR-guided microwave thermocoagulation of liver tumors. Acad Radiol. 2003;10:180–8.
Morikawa S, Inubushi T, Kurumi Y, Naka S, Sato K, Demura K, et al. Advanced computer assistance for magnetic resonance-guided microwave thermocoagulation of liver tumors. Acad Radiol. 2003;10:1442–9.
Kurumi Y, Tani T, Naka S, Shiomi H, Shimizu T, Abe H, et al. MR-guided microwave ablation for malignancies. Int J Clin Oncol. 2007;12:85–93.
Tabuse K. A new operative procedure of hepatic surgery using a microwave tissue coagulator. Nippon Geka Hokan. 1979;48:160–72.
Murakami R, Yoshimatsu S, Yamashita Y, Matsukawa T, Takahashi M, Sagara K. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: value of percutaneous microwave coagulation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995;164(5):1159–64.
Laeseke PF, Lee FT, Sampson LA, van der Weide DW, Brace CL. Microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation in the kidney: high-power triaxial antennas create larger ablation zones than similarly sized internally cooled electrodes. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20(9):1224–9.
Okamoto T, Onda S, Yanaga K, Suzuki N, Hattori A. Clinical application of navigation surgery using augmented reality in the abdominal field. Surg Today 2014 (Online First).
Shiomi H, Naka S, Sato K, Demura K, Murakami K, Shimizu T, et al. Thoracoscopy-assisted magnetic resonance guided microwave coagulation therapy for hepatic tumors. Am J Surg. 2008;195(6):854–60.
Brace CL. Microwave tissue ablation: biophysics, technology and applications. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;38(1):65–78.
Mukaisho K, Kurumi Y, Sugihara H, Naka S, Kamitani S, Tsubosa Y, et al. Enzyme histochemistry is useful to assess viability of tumor tissue after microwave coagulation therapy (MCT): metastatic adenocarcinoma treated by lateral segmentectomy after MCT. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47(11):2441–5.
Yamaguchi T, Mukaisho K, Yamamoto H, Shiomi H, Kurumi Y, Sugihara H, et al. Disruption of erythrocytes distinguishes fixed cells/tissues from viable cells/tissues following microwave coagulation therapy. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:1347–55.
Murakami K, Morikawa S, Naka S, Demura K, Sato K, Shiomi H, et al. Correlation between high field MR images and histopathological findings of rat transplanted cancer immediately after partial microwave coagulation. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2008;7(3):105–12.
Morikawa S, Inubushi T, Kurumi Y, Naka S, Sato K, Demura K, et al. Advanced computer assistance for magnetic resonance-guided microwave thermocoagulation of liver tumors. Acad Radiol. 2013;10(12):1442–9.
Simo KA, Sereika SE, Newton KN, Gerber DA. Laparoscopic-assisted microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: safety and efficacy in comparison with radiofrequency ablation. J Surg Oncl. 2011;104:822–9.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Conflict of interest
Koichiro Murakami and co-authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, K., Naka, S., Shiomi, H. et al. Initial experiences with MR Image-guided laparoscopic microwave coagulation therapy for hepatic tumors. Surg Today 45, 1173–1178 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-014-1042-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-014-1042-x