Abstract
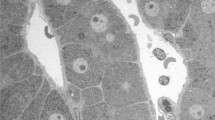
Microwave coagulation therapy (MCT) has recently been applied to treat hepatic tumors. However, the histological changes in the liver following MCT have not been fully elucidated. A type of cell death known as microwave fixation has been reported in areas adjacent to the microwave irradiator electrodes, and these areas are without acid phosphatase (AcP) activity. Diagnosis of microwave-fixed tissue by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining is very difficult because morphology is well maintained for months. In an effort to clarify the histological changes and the mechanisms of microwave fixation, we performed HE staining, enzyme histochemistry for AcP, and electron microscopy in both rat and human liver samples after MCT. Although the microwave-fixed tissues maintained their structure on HE staining, membranes of microwave-fixed cells were seriously damaged and there were no apparent organelle structures in these cells on electron microscopy. Erythrocytes were also damaged in these tissues on both light and electron microscopy. The cause of microwave fixation is thought to be injury of the membrane, which is similar to coagulative necrosis. In conclusion, microwave fixation can be considered a type of coagulative necrosis without enzyme digestion. Disruption of erythrocytes on HE staining is an interesting and important diagnostic clue in distinguishing nonviable fixed tissues from viable tissues following MCT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seki T, Wakabayashi M, Nakagawa T, Itho T, Shiro T, Kunieda K, Sato M, Uchiyama S, Inoue K: Ultrasonically guided percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 74:817–825, 1994
Murakami R, Yoshimatsu S, Yamashita Y, Matsukawa T, Takahashi M, Segara K: Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: value of percutaneous microwave coagulation. AJR 164:1159–1164, 1995
Matsukawa T, Yamashita Y, Arakawa A, Nishiharu T, Urata J, Murakami R, Takahashi M, Yoshimatu S: Percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy in liver tumors. A 3-year experience. Acta Radiol 38:410–415, 1997
Shibata T, Niinobu T, Ogata N, Takami M: Microwave coagulation therapy for multiple hepatic metastases from colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 89:276–284, 2000
Dong B, Liang P, Yu X, Su L, Yu D, Cheng Z, Zhang J: Percutaneus sonographically guided microwave coagulation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: results in 234 patients. AJR 180:1547–1555, 2003
Watanabe Y, Sato M, Abe Y, Horiuchi S, Kito K, Kimura K, Kimura S: Laparoscopic microwave coagulo-necrotic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a feasible study of an alternative option for poor–risk patients. J Laparoendosc Surg 5:169–175, 1995
Yamanaka N, Okamoto E, Tanaka T, Oriyama T, Fujimoto J, Furukawa K, Kawamura E: Laparoscopic microwave coagulonecrotic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Laparosc Endosc 5:444–449, 1995
Ido K, Isoda N, Kawamoto C, Hozumi M, Suzuki T, Nagamine N, Nakazawa Y, Ono K, Hirota N, Hyodoh H, Kimura K: Laparoscopic microwave coagulation therapy for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma performed under lapaloscopic ultrasonography. Gastrointest Endosc 45:415–420, 1997
Abe T, Shinzawa H, Watabayashi H, Aoki M, Sugahara K. Iwaba A, Haga H, Miyano S, Terui Y, Mitsuhashi H, Watanabe H, Matsuo T, Saito K, Saito T, Togashi H, Takahashi T: Value of laparoscopic microwave coagulation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in relation to tumor size and location. Endoscopy 32:598–603, 2000
Ishikawa T, Kohno T, Shibayama T, Fukushima Y, Obi S, Teratani T, Shiina S, Shiratori Y, Omata M: Thoracoscopic thermal ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma located beneath the diaphragm. Endoscopy 33:697–702, 2001
Sato M, Watanabe Y, Tokui K, Kawachi K, Sugata S, Ikezoe: CT-guided treatment of ultrasonically invisible hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol 95:2102–2106, 2000
Morikawa S, Inubushi T, Kurumi Y, Naka S, Sato K, Tani T, Yamamoto I, Fujimura M: MR-guided microwave thermocoagulation therapy of liver tumors: initial clinical experiences using a 0.5T open MR system. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:576–583, 2002
Morikawa S, Inubushi T, Kurumi Y, Naka S, Sato K, Tani T, Haque HA, Tokuda J, Hata N: New assistive devices for MR-guided microwave thermocoagulation of liver tumors. Acad Radiol 10:180–188, 2003
Tabuse K: A new operative procedure of hepatic surgery using a microwave tissue coagulator. Arch Jap Chir 48:160–172, 1979
Mukaisho K, Sugihara H, Tani T, Kurumi Y, Kamitani S, Tokugawa T, Hattori T: Effects of microwave irradiation on rat hepatic tissue evaluated by enzyme histochemistry for acid phosphatase. Dig Dis Sci 47:376–379, 2002
Mukaisho K, Kurumi Y, Sugihara H, Tani T, Naka S, Kamitani S, Tsubosa Y, Moritani S, Endo Y, Hanasawa K, Morikawa S, Inubushi T, Hattori T, Tani T: Enzyme histochemistry is useful to assess viability of tumor tissue after microwave coagulation therapy (MCT)-metastatic adenocarcinoma treated by lateral segmentectomy after MCT. Dig Dis Sci 47:2441–2445, 2002
Ozaki T, Mori I, Nakamura M, Utsunomiya H, Tabuse K, Kakudo K: Microwave cell death: Immunohistochemical and enzyme histochemical evaluation. Pathol Int 53:686–692, 2003
Ozaki T, Tabuse K, Tsuji T, Nakamura Y, Kakudo K, Mori I: Microwave cell death: Enzyme histochemical evaluation for metastatic carcinoma of the liver. Pathol Int 53:837–845, 2003
Hirsch J, Menzebach A, Welters ID, Dietrich GV, Katz N, Hempelmann G: Indicators of erythrocyte damage after microwave warming of packed red blood cells. Clin Chem 49:792–799, 2003
Dwivedi RS, Dwivedi U, Chiang B: Low intensity microwave radiation effects on the ultrastructure of Chang liver cells. Exp Cell Res 180:253–265, 1989
Liburdy RP, Vanek PF Jr: Microwaves and the cell membrane. II. Temperature, plasma, and oxygen mediate microwave-induced membrane permeability in the erythrocyte. Radiat Res 102:190–205, 1985
Liburdy RP, Vanek PF Jr: Microwaves and the cell membrane. III. Protein shedding is oxygen and temperature dependent: evidence for cation bridge involvement. Radiat Res 109:382–395, 1987
Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T: Cellular pathology I: cell injury and cell death. In Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6th ed. Philadelphia, W. B. Saunders, 1999, pp 1–29
Yamashiki N, Kato T, Bejarano PA, Berho M, Montalvo B, Shebert RT, Goodman ZD, Seki T, Schiff ER, Tzakis AG: Histopathological changes after microwave coagulation therapy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: review of 15 explanted livers. Am J Gastroenterol 98:2052–2059, 2003
Leong AS, Daymon ME, Milios J: Microwave irradiation as a form of fixation for light and electron microscopy. J Pathol 146:313–321, 1985
Hopwood D, Coghill G, Ramsay J, Milne G, Kerr M: Microwave fixation: its potential for routine techniques, histochemistry, immunocytochemistry and electron microscopy. Histochem J 16:1171–1191, 1984
Hopwood D: Cell and tissue fixation, 1972–1982. Histochem J 17:389–442, 1985
Ohno T, Kawano K, Sasaki A, Aramaki M, Yoshida T, Kitano S: Expansion of an ablated site and induction of apoptosis after microwave coagulation therapy in rat liver. J Hepatobil Pancr Surg 8:360–366, 2001
Login GR: Microwave fixation versus formalin fixation of surgical and autopsy tissue.Am J Med Technol 44:435–437, 1978
Mayers CP: Histological fixation by microwave heating. J Clin Pathol 23:273–275, 1970
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, T., Mukaisho, Ki., Yamamoto, H. et al. Disruption of Erythrocytes Distinguishes Fixed Cells/Tissues from Viable Cells/Tissues Following Microwave Coagulation Therapy. Dig Dis Sci 50, 1347–1355 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2786-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2786-3