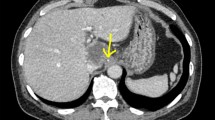
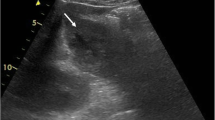
Abstract
Pyogenic liver abscess is an unusual cause of fever and abdominal pain, but it is potentially fatal. It is rarely caused by a local event, but rather by hematogenous dissemination or biliary tract disease. We report an uncommon case of liver abscess caused by the migration of a fish bone through the gastrointestinal wall.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vilgrain V, Menu Y. Imagerie du foie, des voies biliaires et de la rate. Paris: Ed. Flammarion Médecine Sciences; 2002.
Seeto RK, Rockey DC. Pyogenic liver abscess: changes in aetiology, management, and outcome. Medicine 1996;75:99–113.
Georges RN, Deitch EA. Pyogenic hepatic abscess. South Med J 1993;86:1233–1235.
Branum GD, Tyson GS, Branum MA, Meyers WC. Hepatic abscess: changes in aetiology, diagnosis and management. Ann Surg 1990;212:655–662.
Ralls PW. Focal inflammatory disease of the liver. Radiol Clin North Am 1998;36:377–389.
McDonald AP, Howard RJ. Pyogenic liver abscess. World J Surg 1980;4:369–380.
Land MA, Moinuden M, Biano AL. Pyogenic liver abscess: changing epidemiology and prognosis. South Med J 1985;78:1426–1430.
McDonald MI, Corey RG, Gallis HA, Durack DT. Single and multiple pyogenic liver abscesses: natural history, diagnosis and treatment with emphasis on percutaneous drainage. Medicine 1984;63:291–302.
Theodoropoulou A, Roussomoustakaki M, Michalodimitrakis MN, Kanaki C, Kouroumalis EA. Fatal hepatic abscess caused by a fish bone. Lancet 2002;359:977.
Masunaga S, Abe M, Imura T, Asano M, Minami S, Fujisawa I. Hepatic abscess secondary to a fishbone penetrating the gastric wall: CT demonstration. Comput Med Imaging Graph 1991;15:113–116.
De la Vega M, Rivero JC, Ruiz L, Suarez S. A fish bone in the liver. Lancet 2001;358:982.
Kessler AT, Kourtis AP. Images in clinical medicine. Liver abscess due to Eikenella corrodens from a fishbone. N Engl J Med 2001;6:345.
Bouchit G, Lamezc H. Fishbone and sub-hepatic abcess. Bord Chir 1964;42:22–24.
Chintamani, Singhal V, Lubhana P, Durkhere R, Bhandari S. Liver abscess secondary to a broken needle migration—a case report. BMC Surg 2003;3:8.
Drnovsek V, Fontanez-Garcia D, Wakabayashi MN, Plavsic BM. Gastrointestinal case of the day. Pyogenic liver abscess caused by perforation by a swallowed wooden toothpick. Radiographics 1999;19:820–822.
Shaw PJ, Feeman JG. The antemortem diagnosis of pyogenic liver abscess due to perforation of the gut by a foreign body. Postgrad Med J 1983;59:455–456.
Lambert A. Abscess of the liver of unusual origin. NY Med J 1898;177–178.
Ell SR, Sprigg A. The radio-opacity of fishbone-species variation. Clin Radiol 1991;44:104–107.
Kumar M, Joseph G, Kumar S, Clayton M. Fish bone as a foreign body. J Laryngol Otol 2003;117(7):568–569.
Ngan JH, Fok PJ, Lai EC, Branicki FJ, Wong J. A prospective study on fish bone ingestion. Experience of 358 patients. Ann Surg 1990;211:459–462.
Volk M, Geissler A, Herold T, Schaffler A, Gross V, Gmeinwieser J. The computed tomographic demonstration of duodenal perforation caused by a fish bone. Rofo 1997;167:198–200.
Gonzalez JG, Gonzalez RR, Patino JV, Garcia AT, Alvarez CP, Pedrosa CS. CT findings in gastrointestinal perforation by ingested fish bones. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1988;12:88–90.
Strauss JE, Balthazar EJ, Naidich DP. Jejunal perforation by a toothpick: CT demonstration. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1985;9:812–814.
McCanse DE, Kurchin A, Hinshaw JR. Gastrointestinal foreign bodies. Am J Surg 1981;142:335–337.
Maleki M, Evans WE. Foreign-body perforation of the intestinal tract. Report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Arch Surg 1970;101:474–477.
Horii K, Yamazaki O, Matsuyama M, Higaki I, Kawai S, Sakaue Y. Successful treatment of a hepatic abscess that formed secondary to fish bone penetration by percutaneous transhepatic removal of the foreign body: report of a case. Surg Today 1999;29:922–926.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clarençon, F., Scatton, O., Bruguière, E. et al. Recurrent liver abscess secondary to ingested fish bone migration: Report of a case. Surg Today 38, 572–575 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-007-3670-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-007-3670-x