Abstract
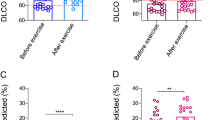
We assessed the presence of lung dysfunction in children with type 1 diabetes, evaluated as reduced diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO), and its components: membrane diffusing capacity (DM) and pulmonary capillary blood volume (Vc). A total of 42 children, aged 15.6 ± 3.8 years, with type 1 diabetes for 8.3 ± 5.5 years, and 30 healthy age and sex-matched peers were recruited for the study. Lung volumes and spirometric dynamic parameters were assessed by plethysmography. Single-breath DLCO was measured according to international recommendation. DM and Vc volume were calculated. Lung volumes were significantly reduced in young patients with type 1 diabetes when compared to controls. Moreover, DLCO was reduced in patients compared to controls (78% ± 16% vs. 120% ± 1%, P = 0.0001). However, when differentiating DM and Vc compartments, we observed a significant impairment only about Vc (34 ± 20 ml vs. 88 ± 18 ml; P = 0.0001), while no difference was observed about DM compartment (23 ± 4 vs. 26 ± 3 ml/min/mmHg, P = 0.798). Whether this might be seen as the “first” sign of microangiopathic involvement in patients with type 1 diabetes has to be confirmed on larger groups but is still fascinating. Meanwhile, we suggest to screen DLCO in all patients with type 1 diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DLCO:
-
Diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide
- DM:
-
Membrane diffusing capacity
- FEV1 :
-
Forced expiratory volume in 1 s
- FVC:
-
Forced vital capacity
- HbA1c:
-
Glycated hemoglobin
- KCO:
-
Carbon monoxide transfer coefficient
- RV:
-
Residual volume
- TLC:
-
Total lung capacity
- VC:
-
Vital capacity
- Vc:
-
Pulmonary capillary blood volume
References
Spiro RG (1976) Search for a biochemical basis of diabetic microangiopathy. Diabetologia 12:1–14
Brownlee M (2005) The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes 54:1615–1625
Sandler M (1990) Is the lung a target organ in diabetes mellitus? Arch Intern Med 150:1385–1388
Primhak RA, Whincup G, Tsanakas JN, Milner RD (1987) Reduced vital capacity in insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes 36:324–326
Buckingham B, Perejda AJ, Sandborg C, Kershnar AK, Uitto J (1986) Skin, joint, and pulmonary changes in type I diabetes mellitus. Am J Dis Child 140:420–423
Verrotti A, Verini M, Chiarelli F, Verdesca V, Misticoni G, Morgese G (1993) Pulmonary function in diabetic children with and without persistent microalbuminuria. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 21:171–176
van Gent R, Brackel HJ, de Vroede M, van der Ent CK (2002) Lung function abnormalities in children with type I diabetes. Respir Med 96:976–978
Villa MP, Montesano M, Barreto M, Pagani J, Stegagno M, Multari G, Ronchetti R (2004) Diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 47:1931–1935
Cazzato S, Bernardi F, Salardi S, Tassinari D, Corsini I, Ragni L, Cicognani A, Cacciari E (2004) Lung function in children with diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Pulmonol 37:17–23
Lucini D, Zuccotti G, Malacarne M, Scaramuzza A, Riboni S, Palombo C, Pagani M (2009) Early progression of the autonomic dysfunction observed in pediatric type 1 diabetes mellitus. Hypertension 54:987–994
Lorini R, d’Annunzio G, Vitali L, Scaramuzza A, Bacchella L, Zonta LA (1998) Normal values of overnight albumin excretion rate in a sample of healthy Italian children and adolescents. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 11:639–643
Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Crapo R, Enright P, van der Grinten CP, Gustafsson P, Jensen R, Johnson DC, MacIntyre N, McKay R, Navajas D, Pedersen OF, Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Wanger J (2005) ATS/ERS Task Force. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J 26:319–338
Wanger J, Clausen JL, Coates A, Pedersen OF, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Crapo R, Enright P, van der Grinten CP, Gustafsson P, Hankinson J, Jensen R, Johnson D, Macintyre N, McKay R, Miller MR, Navajas D, Pellegrino R, Viegi G (2005) Standardisation of the measurements of lung volumes. Eur Respir J 26:511–522
Macintyre N, Crapo RO, Viegi G, Johnson DC, van der Grinten CP, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Enright P, Gustafsson P, Hankinson J, Jensen R, McKay R, Miller MR, Navajas D, Pedersen OF, Pellegrino R, Wanger J (2005) Standardisation of the single-breath determination of carbon monoxide uptake in the lung. Eur Respir J 26:720–735
Rouhton FJW, Foster RE (1957) Relative importance of diffusion and chemical reaction rates in determining rate of exchange of gases in the human lung, with special reference to true diffusing capacity of pulmonary membrane and volume of blood in the capillaries. J Appl Physiol 11:277–289
Rosenthal M, Bain SH, Cramer D, Helms P, Denison D, Bush A, Warner JO (1993) Lung function in white children aged 4 to 19 years: I. Spirometry. Thorax 48:794–802
Rosenthal M, Cramer D, Bain SH, Denison D, Bush A, Warner JO (1993) Lung function in white children aged 4 to 19 years: II. Single breath analysis and plethysmography. Thorax 48:803–808
van den Boost B, Gosker HR, Zeegers MP, Schols AMWJ (2010) Pulmonary function in diabetes: a metaanalysis. Chest 138:393–406
Sandler M, Bunn AE, Stewart RI (1987) Cross-section study of pulmonary function in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:223–229
Pitocco D, Santangeli P, Fuso L, Zaccardi F, Longobardi A, Infusino F, Incalzi RA, Lanza GA, Crea F, Ghirlanda G (2008) Association between reduced pulmonary diffusing capacity and cardiac autonomic dysfunction in Type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med 25:1366–1368
Pan HZ, Zhang L, Guo MY, Sui H, Li H, Wu WH et al (2010) The oxidative stress status in diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy. Acta Diabetol 47(Suppl 1):71–76
Atkins RC, Zimmet P (2010) Diabetic kidney disease: act now or pay later. Acta Diabetol 47:1–4
Greco D, Gambina F, Maggio F (2009) Ophthalmoplegia in diabetes mellitus: a retrospective study. Acta Diabetol 46:23–26
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00592-011-0363-0.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scaramuzza, A.E., Morelli, M., Rizzi, M. et al. Impaired diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide in children with type 1 diabetes: is this the first sign of long-term complications?. Acta Diabetol 49, 159–164 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-011-0353-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-011-0353-2