Abstract
Purpose
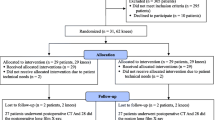
This study evaluated whether patients with particular lower limb morphological factors have femoral and tibial component malpositioning during mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and lower postoperative satisfaction.
Methods
This study included 146 knees in 117 Asian patients undergoing TKA for medial osteoarthritis. Preoperative bony morphological factors such as the angle between the femoral mechanical and anatomical axes (MA-AA angle), angle between the anatomical axes of the proximal and distal femur (lateral bowing femoral angle, LBFA), mechanical lateral distal femoral angle, medial proximal tibial angle, and % anatomical axis of the tibia were evaluated, as well as preoperative and 1-year postoperative 2011 Knee Society scores (KSSs).
Results
MA-AA angle and LBFA were significantly larger in knees with varus femoral component alignment versus neutral alignment. Preoperative MA-AA angle was underestimated in patients with larger MA-AA angle or LBFA, especially by inexperienced surgeons. Tibial morphological factors did not affect tibial component alignment. Changes in 2011 KSSs were similar among groups by lower limb alignment or femoral and tibial component alignment.
Conclusion
Femoral bowing affects varus femoral component alignment by obscuring preoperative planning, but it had little impact on patient satisfaction when mechanical alignment is targeted during TKA.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
29 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03175-x
References
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE (2009) Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty 24:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2009.04.034
Kuriyama S, Ishikawa M, Nakamura S, Furu M, Ito H, Matsuda S (2016) No condylar lift-off occurs because of excessive lateral soft tissue laxity in neutrally aligned total knee arthroplasty: a computer simulation study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24:2517–2524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3687-4
Matsuda S, Kawahara S, Okazaki K, Tashiro Y, Iwamoto Y (2013) Postoperative alignment and ROM affect patient satisfaction after TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2533-y
van Hamersveld KT, Marang-van de Mheen PJ, Nelissen R (2019) The effect of coronal alignment on tibial component migration following total knee arthroplasty: a cohort study with long-term radiostereometric analysis results. J Bone Joint Surg Am 101:1203–1212. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.18.00691
Dossett HG, Estrada NA, Swartz GJ, LeFevre GW, Kwasman BG (2014) A randomised controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee replacements: two-year clinical results. Bone Joint J 96:907–913. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.96B7.32812
Howell SM, Kuznik K, Hull ML, Siston RA (2008) Results of an initial experience with custom-fit positioning total knee arthroplasty in a series of 48 patients. Orthopedics 31:857–863. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20080901-15
Ishikawa M, Kuriyama S, Ito H, Furu M, Nakamura S, Matsuda S (2015) Kinematic alignment produces near-normal knee motion but increases contact stress after total knee arthroplasty: a case study on a single implant design. Knee 22:206–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2015.02.019
Kim CW, Lee CR (2018) Effects of femoral lateral bowing on coronal alignment and component position after total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of conventional and navigation-assisted surgery. Knee Surg Relat Res 30:64–73. https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.056
Lasam MP, Lee KJ, Chang CB, Kang YG, Kim TK (2013) Femoral lateral bowing and varus condylar orientation are prevalent and affect axial alignment of TKA in Koreans. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:1472–1483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2618-7
Mullaji A, Shetty GM (2009) Computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty for arthritis with extra-articular deformity. J Arthroplasty 24:1164–1169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2009.05.005
Tang WM, Zhu YH, Chiu KY (2000) Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:1603–1608. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200011000-00014
Nishida K, Matsumoto T, Takayama K, Ishida K, Nakano N, Matsushita T, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2017) Remaining mild varus limb alignment leads to better clinical outcome in total knee arthroplasty for varus osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:3488–3494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4260-5
Akagi M, Nakamura T, Matsusue Y, Ueo T, Nishijyo K, Ohnishi E (2000) The Bisurface total knee replacement: a unique design for flexion. four-to-nine-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:1626–1633. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200011000-00017
Nakamura S, Ito H, Nakamura K, Kuriyama S, Furu M, Matsuda S (2017) Long-term durability of ceramic tri-condylar knee implants: a minimum 15-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty 32:1874–1879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2017.01.016
Matsuda S, Mizu-uchi H, Miura H, Nagamine R, Urabe K, Iwamoto Y (2003) Tibial shaft axis does not always serve as a correct coronal landmark in total knee arthroplasty for varus knees. J Arthroplasty 18:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1054/arth.2003.50002
Nishikawa K, Mizu-uchi H, Okazaki K, Matsuda S, Tashiro Y, Iwamoto Y (2015) Accuracy of proximal tibial bone cut using anterior border of tibia as bony landmark in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 30:2121–2124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2015.06.055
Akagi M, Oh M, Nonaka T, Tsujimoto H, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2004) An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200403000-00030
Vanlommel L, Vanlommel J, Claes S, Bellemans J (2013) Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2325–2330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2481-4
Hamamoto Y, Ito H, Furu M, Ishikawa M, Azukizawa M, Kuriyama S, Nakamura S, Matsuda S (2015) Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Japanese version of the new Knee Society Scoring System for osteoarthritic knee with total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci 20:849–853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-015-0736-2
Nakahara H, Matsuda S, Moro-oka TA, Okazaki K, Tashiro Y, Iwamoto Y (2012) Cutting error of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty by use of a navigation system. J Arthroplasty 27:1119–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2011.09.018
Catani F, Biasca N, Ensini A, Leardini A, Bianchi L, Digennaro V, Giannini S (2008) Alignment deviation between bone resection and final implant positioning in computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90:765–771. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.G.00293
Haruta Y, Kawahara S, Tsuchimochi K, Hamasaki A, Hara T (2018) Deviation of femoral intramedullary alignment rod influences coronal and sagittal alignment during total knee arthroplasty. Knee 25:644–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2018.04.011
Kim JM, Hong SH, Kim JM, Lee BS, Kim DE, Kim KA, Bin SI (2015) Femoral shaft bowing in the coronal plane has more significant effect on the coronal alignment of TKA than proximal or distal variations of femoral shape. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23:1936–1942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-3006-5
Magnussen RA, Weppe F, Demey G, Servien E, Lustig S (2011) Residual varus alignment does not compromise results of TKAs in patients with preoperative varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:3443–3450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1988-6
Lee BS, Cho HI, Bin SI, Kim JM, Jo BK (2018) Femoral component varus malposition is associated with tibial aseptic loosening after TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 476:400–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999.0000000000000012
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organizations for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N. Umatani acquired and analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. S. Kuriyama designed the study, acquired and analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. K. Nishitani, S. Nakamura, and H Ito acquired the data. S. Matsuda designed the study, acquired the data, and advised on the study. All authors approved the submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no financial interests.
Consent to participate
All patients provided informed consent for participation in this study.
Consent for publication
All participants provided informed consent for publication of this study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed during studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of our institution (registration number R1144) and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Modifications have been made in the section ‘’Bony morphological factors’’. Full information regarding the corrections made can be found in the erratum/correction for this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umatani, N., Kuriyama, S., Nishitani, K. et al. Femoral bowing affects varus femoral alignment but not patient satisfaction in mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasty. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 33, 89–96 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03164-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03164-0