Abstract
Purpose
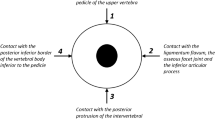
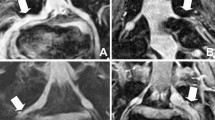
To assess the inter- and intra-reader agreement of commonly used quantitative and qualitative image parameters for the assessment of degenerative lumbar spinal canal stenosis (LSS) by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods
In this ethical board approved cross-sectional multicenter study, MRI of 100 randomly selected patients (median age 72.5 years, 48 % female) of the prospective Lumbar Stenosis Outcome Study (LSOS) were evaluated by two independent readers. A set of five previously published core imaging parameters as well as nine qualitative and five quantitative additional parameters regarding LSS and degenerative changes of the lumbar spine were assessed to calculate κ and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) for the inter-reader agreement. Additional repeated image evaluations were performed by one reader to calculate the intra-reader agreement.
Results
κ values for the core image parameters ranged between 0.42 (compromise of the foraminal zone) and 0.77 (relation between fluid and cauda equina) for inter-reader agreement and between 0.59 (compromise of the foraminal zone) and 0.8 (compromise of the central zone) for intra-reader agreement. The inter-reader agreement for the non-core parameters showed κ values of 0.27–0.69 and ICC values of 0.46–0.85. The intra-reader agreement showed κ values of 0.53–0.69 and ICC values of 0.81–0.88.
Conclusions
The inter- and intra-reader agreement of commonly used quantitative and qualitative image parameters for the assessment of LSS showed quite a variability with previously defined core parameters having good to excellent inter- and intra-reader agreements.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Society NAS (2011) Evidence Based Clinical Guidelines for multidisciplinary spine care: diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. 8
Katz JN, Harris MB (2008) Clinical practice. Lumbar spinal stenosis. N Engl J Med 358:818–825. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp0708097
Deyo RA, Gray DT, Kreuter W, Mirza S, Martin BI (2005) United States trends in lumbar fusion surgery for degenerative conditions. Spine 30:1441–1445 (discussion 1446–1447)
Szpalski M, Gunzburg R (2003) Lumbar spinal stenosis in the elderly: an overview. Eur Spine J 12(Suppl 2):S170–S175. doi:10.1007/s00586-003-0612-1
Malfair D, Beall DP (2007) Imaging the degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 15:221–238. doi:10.1016/j.mric.2007.04.001
Andreisek G, Hodler J, Steurer J (2011) Uncertainties in the diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis. Radiology 261:681–684. doi:10.1148/radiol.11111086
Ross JS (2010) Babel 2.0. Radiology 254:640–641. doi:10.1148/radiol.09092250
Arana E, Royuela A, Kovacs FM, Estremera A, Sarasibar H, Amengual G, Galarraga I, Martinez C, Muriel A, Abraira V, Gil Del Real MT, Zamora J, Campillo C (2010) Lumbar spine: agreement in the interpretation of 1.5-T MR images by using the Nordic Modic Consensus Group classification form. Radiology 254:809–817. doi:10.1148/radiol.09090706
Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N (1998) MR imaging of the lumbar spine: prevalence of intervertebral disk extrusion and sequestration, nerve root compression, end plate abnormalities, and osteoarthritis of the facet joints in asymptomatic volunteers. Radiology 209:661–666. doi:10.1148/radiology.209.3.9844656
Kim YU, Kong YG, Lee J, Cheong Y, Kim SH, Kim HK, Park JY, Suh JH (2015) Clinical symptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis associated with morphological parameters on magnetic resonance images. Eur Spine J 24:2236–2243. doi:10.1007/s00586-015-4197-2
Zhang L, Chen R, Liu B, Zhang W, Zhu Y, Rong L (2016) The nerve root sedimentation sign for differential diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis: a retrospective, consecutive cohort study. Eur Spine J. doi:10.1007/s00586-016-4435-2
Genevay S, Atlas SJ, Katz JN (2010) Variation in eligibility criteria from studies of radiculopathy due to a herniated disc and of neurogenic claudication due to lumbar spinal stenosis: a structured literature review. Spine 35:803–811. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181bc9454
Andreisek G, Deyo RA, Jarvik JG, Porchet F, Winklhofer SF, Steurer J, group Lw (2014) Consensus conference on core radiological parameters to describe lumbar stenosis—an initiative for structured reporting. Eur Radiol 24:3224–3232. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3346-z
Steurer J, Nydegger A, Held U, Brunner F, Hodler J, Porchet F, Min K, Mannion AF, Michel B, LumbSten Research C (2010) LumbSten: the lumbar spinal stenosis outcome study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:254. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-11-254
Andreisek G, Deyo RA, Jarvik JG, Porchet F, Winklhofer SF, Steurer J (2014) Consensus conference on core radiological parameters to describe lumbar stenosis—an initiative for structured reporting. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3346-z
Steurer J, Roner S, Gnannt R, Hodler J, LumbSten Research C (2011) Quantitative radiologic criteria for the diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 12:175. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-12-175
Andreisek G, Imhof M, Wertli M, Winklhofer S, Pfirrmann CW, Hodler J, Steurer J, Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Outcome Study Working Group Z (2013) A systematic review of semiquantitative and qualitative radiologic criteria for the diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201:W735–W746. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.10163
Mamisch N, Brumann M, Hodler J, Held U, Brunner F, Steurer J, Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Outcome Study Working Group Z (2012) Radiologic criteria for the diagnosis of spinal stenosis: results of a Delphi survey. Radiology 264:174–179. doi:10.1148/radiol.12111930
Lurie JD, Tosteson AN, Tosteson TD, Carragee E, Carrino JA, Kaiser J, Sequeiros RT, Lecomte AR, Grove MR, Blood EA, Pearson LH, Weinstein JN, Herzog R (2008) Reliability of readings of magnetic resonance imaging features of lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine 33:1605–1610. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181791af3
Schizas C, Theumann N, Burn A, Tansey R, Wardlaw D, Smith FW, Kulik G (2010) Qualitative grading of severity of lumbar spinal stenosis based on the morphology of the dural sac on magnetic resonance images. Spine 35:1919–1924. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181d359bd
Bartynski WS, Lin L (2003) Lumbar root compression in the lateral recess: MR imaging, conventional myelography, and CT myelography comparison with surgical confirmation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:348–360
Pfirrmann CW, Dora C, Schmid MR, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N (2004) MR image-based grading of lumbar nerve root compromise due to disk herniation: reliability study with surgical correlation. Radiology 230:583–588. doi:10.1148/radiol.2302021289
Jonsson B, Annertz M, Sjoberg C, Stromqvist B (1997) A prospective and consecutive study of surgically treated lumbar spinal stenosis. Part I: clinical features related to radiographic findings. Spine 22:2932–2937
Kalichman L, Cole R, Kim DH, Li L, Suri P, Guermazi A, Hunter DJ (2009) Spinal stenosis prevalence and association with symptoms: the Framingham Study. Spine J 9:545–550. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2009.03.005
Hamanishi C, Matukura N, Fujita M, Tomihara M, Tanaka S (1994) Cross-sectional area of the stenotic lumbar dural tube measured from the transverse views of magnetic resonance imaging. J Spinal Disord 7:388–393
Laurencin CT, Lipson SJ, Senatus P, Botchwey E, Jones TR, Koris M, Hunter J (1999) The stenosis ratio: a new tool for the diagnosis of degenerative spinal stenosis. Int J Surg Investig 1:127–131
Fardon DF (2001) Nomenclature and classification of lumbar disc pathology. Spine 26:461–462
Mikhael MA, Ciric I, Tarkington JA, Vick NA (1981) Neuroradiological evaluation of lateral recess syndrome. Radiology 140:97–107. doi:10.1148/radiology.140.1.7244248
Goutallier D, Postel JM, Bernageau J, Lavau L, Voisin MC (1995) Fatty infiltration of disrupted rotator cuff muscles. Rev Rhum Engl Ed 62:415–422
Chen YY, Pao JL, Liaw CK, Hsu WL, Yang RS (2014) Image changes of paraspinal muscles and clinical correlations in patients with unilateral lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J 23:999–1006. doi:10.1007/s00586-013-3148-z
Aebi M (2005) The adult scoliosis. Eur Spine J 14:925–948. doi:10.1007/s00586-005-1053-9
Modic MT, Steinberg PM, Ross JS, Masaryk TJ, Carter JR (1988) Degenerative disk disease: assessment of changes in vertebral body marrow with MR imaging. Radiology 166:193–199. doi:10.1148/radiology.166.1.3336678
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N (2001) Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine 26:1873–1878
Grenier N, Kressel HY, Schiebler ML, Grossman RI, Dalinka MK (1987) Normal and degenerative posterior spinal structures: MR imaging. Radiology 165:517–525. doi:10.1148/radiology.165.2.3659376
Park JB, Chang H, Lee JK (2001) Quantitative analysis of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in ligamentum flavum of lumbar spinal stenosis and disc herniation. Spine 26:E492–E495
Kalichman L, Hunter DJ (2007) Lumbar facet joint osteoarthritis: a review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 37:69–80. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2007.01.007
Lattig F, Fulop Fekete T, Kleinstuck FS, Porchet F, Jeszenszky D, Mannion AF (2012) Lumbar facet joint effusion on MRI as a sign of unstable degenerative spondylolisthesis: should it influence the treatment decision? J Spinal Disord Tech. doi:10.1097/BSD.0b013e318269c261
Lattig F, Fekete TF, Grob D, Kleinstuck FS, Jeszenszky D, Mannion AF (2012) Lumbar facet joint effusion in MRI: a sign of instability in degenerative spondylolisthesis? Eur Spine J 21:276–281. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1993-1
Borre DG, Borre GE, Aude F, Palmieri GN (2003) Lumbosacral epidural lipomatosis: MRI grading. Eur Radiol 13:1709–1721. doi:10.1007/s00330-002-1716-4
Kauppila LI, Eustace S, Kiel DP, Felson DT, Wright AM (1998) Degenerative displacement of lumbar vertebrae. A 25-year follow-up study in Framingham. Spine 23:1868–1873 (discussion 1873–1864)
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Kirkwood BR, Sterne JAC, Kirkwood BR (2003) Essential medical statistics. Blackwell Science, Malden
Carrino JA, Lurie JD, Tosteson AN, Tosteson TD, Carragee EJ, Kaiser J, Grove MR, Blood E, Pearson LH, Weinstein JN, Herzog R (2009) Lumbar spine: reliability of MR imaging findings. Radiology 250:161–170. doi:10.1148/radiol.2493071999
Fu MC, Buerba RA, Long WD 3rd, Blizzard DJ, Lischuk AW, Haims AH, Grauer JN (2014) Interrater and intrarater agreements of magnetic resonance imaging findings in the lumbar spine: significant variability across degenerative conditions. Spine J 14:2442–2448. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2014.03.010
Splendiani A, Perri M, Grattacaso G, Di Tunno V, Marsecano C, Panebianco L, Gennarelli A, Felli V, Varrassi M, Barile A, Di Cesare E, Masciocchi C, Gallucci M (2016) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine with dedicated G-scan machine in the upright position: a retrospective study and our experience in 10 years with 4305 patients. Radiol Med (Torino) 121:38–44. doi:10.1007/s11547-015-0570-9
Speciale AC, Pietrobon R, Urban CW, Richardson WJ, Helms CA, Major N, Enterline D, Hey L, Haglund M, Turner DA (2002) Observer variability in assessing lumbar spinal stenosis severity on magnetic resonance imaging and its relation to cross-sectional spinal canal area. Spine 27:1082–1086
Laudato PA, Kulik G, Schizas C (2015) Relationship between sedimentation sign and morphological grade in symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J 24:2264–2268. doi:10.1007/s00586-015-4021-z
Lonne G, Odegard B, Johnsen LG, Solberg TK, Kvistad KA, Nygaard OP (2014) MRI evaluation of lumbar spinal stenosis: is a rapid visual assessment as good as area measurement? Eur Spine J 23:1320–1324. doi:10.1007/s00586-014-3248-4
Weber C, Rao V, Gulati S, Kvistad KA, Nygaard OP, Lonne G (2015) Inter- and intraobserver agreement of morphological grading for central lumbar spinal stenosis on magnetic resonance imaging. Global Spine J 5:406–410. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1551651
Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Boos N, Hodler J (1999) MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints. Skeletal Radiol 28:215–219
Jyoti Z (2016) Image interpretations variability and bias. In: U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Poureisa M, Daghighi MH, Eftekhari P, Bookani KR, Fouladi DF (2015) Redundant nerve roots of the cauda equina in lumbar spinal canal stenosis, an MR study on 500 cases. Eur Spine J 24:2315–2320. doi:10.1007/s00586-015-4059-y
Fazal A, Yoo A, Bendo JA (2013) Does the presence of the nerve root sedimentation sign on MRI correlate with the operative level in patients undergoing posterior lumbar decompression for lumbar stenosis? Spine J 13:837–842. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2013.02.067
Moses RA, Zhao W, Staub LP, Melloh M, Barz T, Lurie JD (2015) Is the sedimentation sign associated with spinal stenosis surgical treatment effect in SPORT? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 40:129–136. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000672
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This study was supported by the Helmut Horten Foundation, OPO-Foundations, Symphasis Foundation, Baugarten Foundation and Pfizer-Foundation for geriatrics and research in geriatrics. We disclose any financial support or author involvement with organization(s) with financial interest in the subject matter.
Additional information
On behalf of the LSOS working group.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winklhofer, S., Held, U., Burgstaller, J.M. et al. Degenerative lumbar spinal canal stenosis: intra- and inter-reader agreement for magnetic resonance imaging parameters. Eur Spine J 26, 353–361 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4667-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4667-1