Abstract
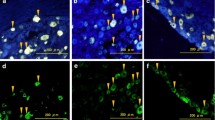
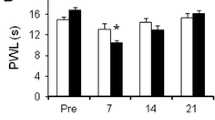
Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) is a gene transcriptional regulator of inflammatory cytokines. We investigated the transduction efficiency of NF-κB decoy to dorsal root ganglion (DRG), as well as the decrease in nerve injury, mechanical allodynia, and thermal hyperalgesia in a rat lumbar disc herniation model. Forty rats were used in this study. NF-κB decoy–fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) was injected intrathecally at the L5 level in five rats, and its transduction efficiency into DRG measured. In another 30 rats, mechanical pressure was placed on the DRG at the L5 level and nucleus pulposus harvested from the rat coccygeal disc was transplanted on the DRG. Rats were classified into three groups of ten animals each: a herniation + decoy group, a herniation + oligo group, and a herniation only group. For behavioral testing, mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia were evaluated. In 15 of the herniation rats, their left L5 DRGs were resected, and the expression of activating transcription factor 3 (ATF-3) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) was evaluated immunohistochemically compared to five controls. The total transduction efficiency of NF-κB decoy–FITC in DRG neurons was 10.8% in vivo. The expression of CGRP and ATF-3 was significantly lower in the herniation + decoy group than in the other herniation groups. Mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia were significantly suppressed in the herniation + decoy group. NF-κB decoy was transduced into DRGs in vivo. NF-κB decoy may be useful as a target for clarifying the mechanism of sciatica caused by lumbar disc herniation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aupperle K, Bennett B, Han Z, Boyle D, Manning A, Firestein GS (2001) NF-kappa B regulation by I kappa B kinase-2 in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J Immunol 166:2705–2711
Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D (1996) NF-kappa B: ten years after. Cell 87:13–20. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81318-5
Barnes PJ, Karin M (1997) Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 336:1066–1071. doi:10.1056/NEJM199704103361506
Chan CF, Sun WZ, Lin JK, Lin-Shiau SY (2000) Activation of transcription factors of nuclear factor kappa B, activator protein-1 and octamer factors in hyperalgesia. Eur J Pharmacol 402:61–68. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(00)00431-3
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL et al (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63. doi:10.1016/0165-0270(94)90144-9
Dixson WJ (1980) Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:441–462. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.002301
Donaldson LF, Harmar AJ, McQueen DS, Seckl JR (1992) Increased expression of preprotachykinin, calcitonin gene-related peptide, but not vasoactive intestinal peptide messenger RNA in dorsal root ganglia during the development of adjuvant monoarthritis in the rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 16:143–149. doi:10.1016/0169-328X(92)90204-O
Han Z, Boyle DL, Manning AM, Firestein GS (1998) AP-1 and NF-kappaB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity 28:197–208. doi:10.3109/08916939808995367
Hölschermann H, Dürfeld F, Maus U, Bierhaus A, Heidinger K, Lohmeyer J, Nawroth PP, Tillmanns H, Haberbosch W (1996) Cyclosporine a inhibits tissue factor expression in monocytes/macrophages. Blood 88:3837–3845
Igarashi T, Kikuchi S, Shubayev V, Myers RR (2000) 2000 Volvo Award winner in basic science studies: exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha mimics nucleus pulposus-induced neuropathology. Molecular, histologic, and behavioral comparisons in rats. Spine 25:2975–2980. doi:10.1097/00007632-200012010-00003
Inoue G, Ochiai N, Ohtori S, Nakagawa K, Gemba T, Doya H, Ito T, Koshi T, Moriya H, Takahashi K (2006) Injection of nuclear factor-kappa B decoy into the sciatic nerve suppresses mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in a rat inflammatory pain model. Spine 31:2904–2908. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000248424.46652.67
Kawakami M, Matsumoto T, Kuribayashi K, Tamaki T (1999) mRNA expression of interleukins, phospholipase A2, and nitric oxide synthase in the nerve root and dorsal root ganglion induced by autologous nucleus pulposus in the rat. J Orthop Res 17:941–946. doi:10.1002/jor.1100170620
Kawakami M, Tamaki T, Hayashi N, Hashizume H, Matsumoto T, Minamide A, Kihira T (2000) Mechanical compression of the lumbar nerve root alters pain-related behaviors induced by the nucleus pulposus in the rat. J Orthop Res 18:257–264. doi:10.1002/jor.1100180214
Kawakami M, Tamaki T, Weinstein JN, Hashizume H, Nishi H, Meller ST (1996) Pathomechanism of pain-related behavior produced by allografts of intervertebral disc in the rat. Spine 21:2101–2107. doi:10.1097/00007632-199609150-00009
Kopp E, Ghosh S (1994) Inhibition of NF-kappa B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science 265:956–959. doi:10.1126/science.8052854
Korhonen T, Karppinen J, Malmivaara A, Autio R, Niinimäki J, Paimela L, Kyllönen E, Lindgren KA, Tervonen O, Seitsalo S, Hurri H (2004) Efficacy of infliximab for disc herniation-induced sciatica: one-year follow-up. Spine 29:2115–2119. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000141179.58778.6c
Korhonen T, Karppinen J, Paimela L, Malmivaara A, Lindgren KA, Bowman C, Hammond A, Kirkham B, Järvinen S, Niinimäki J, Veeger N, Haapea M, Torkki M, Tervonen O, Seitsalo S, Hurri H (2005) The treatment of disc herniation-induced sciatica with infliximab: results of a randomized, controlled, 3-month follow-up study. Spine 30:2724–2728. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000190815.13764.64
Kunz D, Walker G, Eberhardt W, Nitsch D, Pfeilschifter J (1995) Interleukin 1 beta-induced expression of nitric oxide synthase in rat renal mesangial cells is suppressed by cyclosporin A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 216:438–446. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.2642
Lee KM, Kang BS, Lee HL, Son SJ, Hwang SH, Kim DS, Park JS, Cho HJ (2004) Spinal NF-κB activation induces COX-2 upregulation and contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Eur J Neurosci 19:3375–3381. doi:10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03441.x
Ma W, Bisby MA (1998) Increased activation of nuclear factor kappa B in rat lumbar dorsal root ganglion neurons following partial sciatic nerve injuries. Brain Res 797:243–254. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(98)00380-1
Miki K, Fukuoka T, Tokunaga A, Noguchi K (1998) Calcitonin gene-related peptide increase in the rat spinal dorsal horn and dorsal column nucleus following peripheral nerve injury: upregulation in a subpopulation of primary afferent sensory neurons. Neuroscience 82:1243–1252. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(97)00258-3
Morishita R, Sugimoto T, Aoki M, Kida I, Tomita N, Moriguchi A, Maeda K, Sawa Y, Kaneda Y, Higaki J, Ogihara T (1997) In vivo transfection of cis element “decoy” against nuclear factor-kappaB binding site prevents myocardial infarction. Nat Med 8:894–899. doi:10.1038/nm0897-894
Murata Y, Nannmark U, Rydevik B, Takahashi K, Olmarker K (2006) Nucleus pulposus-induced apoptosis in dorsal root ganglion following experimental disc herniation in rats. Spine 31:382–390. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000199618.85326.17
Murata Y, Onda A, Rydevik B, Takahashi I, Takahashi K, Olmarker K (2006) Changes in pain behavior and histologic changes caused by application of tumor necrosis factor-alpha to the dorsal root ganglion in rats. Spine 31:530–535. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000201260.10082.23
Murata Y, Onda A, Rydevik B, Takahashi K, Olmarker K (2004) Selective inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha prevents nucleus pulposus-induced histologic changes in the dorsal root ganglion. Spine 29:2477–2484. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000144406.17512.ea
Myers RR, Wagner R, Sorkin LS (1999) Hyperalgesic actions of cytokines on peripheral nerves. In: Watkins LR, Maier SF (eds) Cytokines and pain. Birkhauser, Basel, pp 133–157
Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Aoki Y, Doya H, Ozawa T, Saito T, Moriya H (2004) Spinal neural cyclooxygenase-2 mediates pain caused in a rat model of lumbar disk herniation. J Pain 5:385–391. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2004.06.004
Olmarker K, Larsson K (1998) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and nucleus-pulposus-induced nerve root injury. Spine 23:2538–2544. doi:10.1097/00007632-199812010-00008
Olmarker K, Rydevik B, Nordborg C (1993) Autologous nucleus pulposus induces neurophysiologic and histologic changes in porcine cauda equina nerve roots. Spine 18:1425–1432. doi:10.1097/00007632-199318110-00005
Rand N, Reichert F, Floman Y, Rotshenker S (1997) Murine NP-derived cells secrete interleukins-1-b, -6, and -10, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in cell culture. Spine 22:2598–2602. doi:10.1097/00007632-199711150-00002
Sakaue G, Shimaoka M, Fukuoka T, Hiroi T, Inoue T, Hashimoto N, Sakaguchi T, Sawa Y, Morishita R, Kiyono H, Noguchi K, Mashimo T (2001) NF-kappa B decoy suppresses cytokine expression and thermal hyperalgesia in a rat neuropathic pain model. Neuroreport 12:2079–2084. doi:10.1097/00001756-200107200-00008
Sakurai H, Shigemori N, Hisada Y, Ishizuka T, Kawashima K, Sugita T (1997) Suppression of NF-kappa B and AP-1 activation by glucocorticoids in experimental glomerulonephritis in rats: molecular mechanisms of anti-nephritic action. Biochim Biophys Acta 1362:252–262
Schreiber S, Nikolaus S, Hampe J (1998) Activation of nuclear factor kappa B inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 42:477–484
Shamash S, Reichert F, Rotshenker S (2002) The cytokine network of Wallerian degeneration: tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1alpha, and interleukin-1beta. J Neurosci 22:3052–3060
Stacey MA, Sun G, Vassalli G, Marini M, Bellini A, Mattoli S (1997) The allergen Der p1 induces NF-kappaB activation through interference with IkappaB alpha function in asthmatic bronchial epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 236:522–526. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6997
Takahashi H, Suguro T, Okazima Y, Motegi M, Okada Y, Kakiuchi T (1996) Inflammatory cytokines in the herniated disc of the lumbar spine. Spine 21:218–224. doi:10.1097/00007632-199601150-00011
Takebayashi T, Cavanaugh JM, Cuneyt Ozaktay A, Kallakuri S, Chen C (2001) Effect of nucleus pulposus on the neural activity of dorsal root ganglion. Spine 26:940–945. doi:10.1097/00007632-200104150-00018
Takahashi Y, Chiba T, Kurokawa M, Aoki Y (2003) Dermatomes and the central organization of dermatomes and body surface regions in the spinal cord dorsal horn in rats. J Comp Neurol 462:29–41. doi:10.1002/cne.10669
Takeuchi H, Kawaguchi S, Ohwada O, Kobayashi H, Hayakawa M, Takebayashi T, Torigoe T, Sato N, Yamashita T (2007) Plasma neuropeptides in patients undergoing lumbar discectomy. Spine 32:79–84. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000252204.88750.cf
Tak PP, Firestein GS (2001) NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest 107:7–11. doi:10.1172/JCI11830
Yabuki S, Onda A, Kikuchi S, Myers RR (2001) Prevention of compartment syndrome in dorsal root ganglia caused by exposure to nucleus pulposus. Spine 26:870–875. doi:10.1097/00007632-200104150-00008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, M., Inoue, G., Gemba, T. et al. Nuclear factor-kappa B decoy suppresses nerve injury and improves mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in a rat lumbar disc herniation model. Eur Spine J 18, 1001–1007 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-009-0940-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-009-0940-x