Abstract
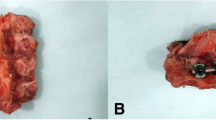
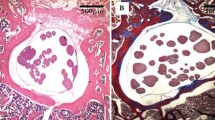
An animal model of vertebral instability was used to analyze the effect of chronic lumbar instability on the peridural vasculature and fibrosis formation. Fifty mature male domestic rabbits were divided into five equal groups. The vertebral instability was performed by excision of supra and interspinous ligaments between L2-L3 and L3-L4, excision of transverse and spinous processes and making bilateral laminectomies and facetectomies in groups I, II, III and IV. In group V only para vertebral muscle dissection was performed without vertebral instability. The simulation of the long term effects of overuse model on unstable spines (chronic instability) were performed with the use of Electrical Neuromuscular Stimulator to simulate cyclic flexion–extension movement in groups I, II. The rabbits in group I and III were sacrified for the histological evaluation at postoperative fifth day. The rabbits in groups I II, IV and V were sacrified at postoperative 21st day. There was no peridural venous endothelial injury or stasis but there was an increased amount of polymorph nuclear leukocytes in both group I (unstable-overuse) and group III (unstable-no overuse) after sacrification at postoperative fifth day. Peridural fibrosis and also vascular changes with different grades were seen in group II, VI and V after sacrification at postoperative 21th day. The grade of the venous changes and the mean amount of peridural scar formation were prominently higher in group II (unstable-overuse) than in group IV (unstable-no overuse) and V (control group). There was no difference between group IV and V for peridural scar formation and vascular changes. In conclusion, the instability of the lumbar spine with overuse could be a cause of peridural venous circulatory impairment, resulting in fibrosis formation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abitbol JJ, Lincoln TL, Lind BI et al (1994) Preventing postlaminectomy adhesion: a new experimental model. Spine 19:1809–1814
Barbera J, Gonzalez J, Esquerdo J et al (1978) Prophylaxis of the laminectomy membrane: an experimental study in dogs. J Neurosurg 49:419–424
Barr JS (1951) Low-back and sciatic pain. J Bone Joint Surg 33(A):633–649
Benoist M, Ficat C, Baraf P et al (1980) Post-operative lumbar epiduro-arachnoiditis: diagnosis and therapeutic aspects. Spine 5:432–436
DiFazio FA, Nichols JB, Pope MH et al (1995) The use of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene as an interpositional membrane after lumbar laminectomy. Spine 20:986–991
Einhaus S, Robertson J, Dohan C, Wujek J, Ahmad S (1997) Reduction of peridural fibrosis after lumbar laminectomy and diskectomy in dogs by areabsorbabl gel (ADCON-L). Spine 22(13):1440–1447
Fritsch EW, Heisel J, Rupp S (1996) The failed back surgery syndrome. Reasons, intraoperative findings, and long-term results: a report of 182 operative treatments. Spine 21:626–633
Gerszten P, Moossy J, Bahri S, Kalend A, Martinez J (1999) Inhibition of peridural fibrosis after laminectomy using low-dose external beam radiation in a rat model. Neurosurgery 44(3):597–603
Greenwood J Jr, McGuire TH, Kimbell F (1952) Study of causes of failure in herniated intervertebral disc operation: analysis of 67 reoperated cases. J Neurosurg 9:15–20
Guven O, Bezer M, Gokkus K, et al (2001) Transpedicular decancellation osteotomy in the treatment of peridural fibrosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 121:517–520
He Y, Revel M, Loty B (1995) A quantitive model of post laminectomy scar formation, effects of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Spine 20(5):557–563
Hoyland JA, Freemont AJ, Jayson MIV (1989) Intervertebral foramen venous obstruction. A cause of periradicular fibrosis? Spine 14:558–568
Jacobs RR, McClain O, Neff J (1980) Control of postlaminectomy scar formation. An experimental and clinical study. Spine 5:223–229
Kaigle AM, Holm SH, Hansson TH (1995) Experimental instability in the lumbar spine. Spine 20(4):421–430
Keller JT, Dunsker SB, McWhorter JM et al (1978) The fate of autogenous grafts to the spinal dura. J Neurosurg 49:412–418
Langenskiold A, Kiviluoto O (1976) Prevention of epidural scar formation after operations on the lumbar spine by means of free fat transplants; a preliminary report. Clin Orthop 115:92–95
Quist J, Dhert W, Meij B, Visser W, Oner C et al (1998) The prevention of peridural adhesions: a comparative long term histomorphometric study using biodegradable barrier and a fat graft. J Bone Joint Surg 80(3):520–526
Richter HP, Kast E, Tomczak R, Besenfelder W, Gaus W (1995) Results of applying ADCON-L gel after lumbar discectomy: the German ADCON-L study. J Neurosurg Spine 95(2):179–189
Sakurai M, Miyasaka Y (1986) Neural fibrosis and the effect of neurolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 68(3):483–488
Wada E, Ebara S, Sahito S, Ono K (1992) Experimental spondilosis in rabbit spine, overuse could accelerate spondylosis? Spine 17:421–430
Warejcka DJ, Mei Y et al (1995) Inhibition of epidural scar formation after lumbar laminectomy in the rat. Spine 20:564–570; discussion 79–80
Yong-Hing K, Reilly J, Korompany V et al (1980) Prevention of nerve root adhesions after laminectomy. Spine 5:59–64
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bezer, M., Gokkus, K., Kocaoglu, B. et al. The influence of vertebral instability on peridural circulation and concomitant peridural fibrosis formation. Eur Spine J 15, 959–964 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-005-0959-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-005-0959-6