Abstract
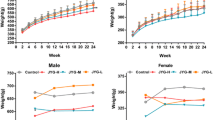
The study was aimed at evaluating the 28-day repeated dose oral toxicity of onion skin quercetin (OSQ) in mice. Twenty-five mice were divided into five groups of 5 mice each. Group 1 served as the control, and groups 2 and 3 received OSQ at 95 mg/kg and 190 mg/kg, respectively, while groups 4 and 5 received OSQ at 380 mg/kg for 28 consecutive days. Mice in groups 1–4 were euthanized on day 29, while the mice in group 5 were left for 14 days without treatment before euthanasia. The kidneys and liver were processed for light microscopy, while the levels of AST, ALT, albumin, total protein concentration, cholesterol, creatinine, urea, and electrolyte were determined from the serum. A significant increase in serum albumin and total protein concentration was observed in mice that received 95 mg/kg OSQ (5.34 and 20.76) when compared with the control (2.01 and 5.61) at P < 0.05. Serum cholesterol and creatinine levels of mice that received 95 mg/kg OSQ (380.37 and 1.38) significantly increased when compared with the control (219.35 and 0.83) at P < 0.05. A significant increase in right kidney index was observed in mice that received OSQ at 190 mg/kg (0.61) when compared with the control mice (0.45) at P < 0.05. There was no significant change in the levels of catalase, glutathione reductase, superoxide dismutase, and malondialdehyde of mice that received OSQ at 95 mg/kg, 190 mg/kg, and 380 mg/kg when compared with the control mice. The kidney of mice that receive 190 mg/kg and 380 mg/kg OSQ for 28 days showed distorted glomeruli and degenerating convoluted tubules. In conclusion, long-term (28 days) administration of OSQ at a dose of 190 mg/kg and above could lead to renal and liver injury.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adefegha SA, Ogunsuyi OB, Oboh G (2020). Purple onion in combination with garlic exerts better ameliorative effects on selected biomarkers in high-sucrose diet-fed fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). Comp Clin Pathol 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-020-03117-9
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Verlag Chemie/Academic Press Inc., Weinheim/NewYork, pp 673–680
Akanji MA, Adeyemi OS, Oguntoye SO, Sulyman F (2009) Psidium guajava extract reduces trypanosomosis associated lipid peroxidation and raises glutathione concentrations in infected animals. EXCLI J 8:148–154
Alamri ZZ (2019) Effect of luteolin and quercetin on thioacetamide induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Int J Pharmacol 15:863–871. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijo.2019.863.871
Alidadi H, Khorsandi L, Shirani M (2018) Effects of quercetin on tubular cell apoptosis and kidney damage in rats induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Malaysian J Med Sci 25:72–81. https://doi.org/10.21315/mjms2018.25.2.8
Amin ZA, Bilgen M, Alshawsh MA, Ali HM, Hadi AHA, Abdulla MA (2012) Protective role of Phyllanthus niruri extract against thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis in rat model. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2012:241583–241589. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/241583
Arome D, Chinedu E (2013) The importance of toxicity testing. J Pharmaceut Biosci 4:146–148
Auti ST, Kulkarni YA (2019) Acute and 28-day repeated dose oral toxicity study of caraway oil in rats. Drug Metab Personalized Ther 2019:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1515/dmpt-2019-0011
Brima EI (2017) Toxic elements in different medicinal plants and the impact on human health. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:1209. https://doi.org/10.3390ijerph14101209
Bulus T, Atawodi SE, Mamman M (2011) Acute toxicity effect of the aqueous extract of Terminalia avicennioides on white albino rats. Sci World J 6:1–4
Carvalho JR, Machado MV (2018) New insights about albumin and liver disease. Ann Hepatol 17:547–560. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0012.0916
Chang JH, Song KJ, Kim HJ, Kim JH, Kim NH, Kim KS (2010) Dietary polyphenols affect MUC5AC expression and ciliary movement in respiratory cells and nasal mucosa. Am J Rhinol Allergy 24:59–62. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2010.24.3447
Craig EA, Yan Z, Zhao QJ (2014) The relationship between chemical-induced kidney weight increases and kidney histopathology in rats. J Appl Toxicol 34:7–736. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3036
Duarte J, Jimenez R, O’Valle F, Galisteo M, Perez-Palencia R, Vargas F, Perez-Vizcaıno F, Zarzuelo A, Tamargo J (2002) Protective effects of the flavonoid quercetin in chronic nitric oxide deficient rats. J Hypertens 20:1843–1854
Fredotovic Ž, Šprung M, Soldo B, Ljubenkov I, Budic-Leto I, Bilušic T (2017) Chemical composition and biological activity of Allium cepa L. and Allium cornutum (Clementi ex Visiani 1842) methanolic extracts. Molecules 22:448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030448
Fridovich I (1989) Superoxide dismutases. An adaptation to a paramagnetic gas. J Biol Chem 264:7761–7764
Garcia-Martinez R, Caraceni P, Bernardi M, Gines P, Arroyo V, Jalan R (2013) Albumin: pathophysiologic basis of its role in the treatment of cirrhosis and its complications. Hepatol 58:1836–1846. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26338
George B, You D, Joy MS, Aleksunes LM (2017) Xenobiotic transporters and kidney injury. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 116:73–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2017.01.005
Goliomytis M, Tsoureki D, Simitzis PE, Charismiadou MA, Hager-Theodorides AL, Deligeorgis SG (2014) The effects of quercetin dietary supplementation on broiler growth performance, meat quality, and oxidative stability. Poultry Sci 93:1957–1962. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2013-03585
Harwood M, Danielewska-Nikiel B, Borzelleca JF, Flamm GW, Williams GM, Lines TC (2007) (2007). A critical review of the data related to the safety of quercetin and lack of evidence of in vivo toxicity, including lack of genotoxic/carcinogenic properties. Food Chem Toxicol 45:2179–2205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.05.015
Heijnen CG, Haenen GR, Oostveen RM, Stalpers EM, Bast A (2002) Protection of flavonoids against lipid peroxidation: the structure activity relationship revisited. Free Radic Res 36:575–581
Heim KE, Tagliaferro AR, Bobilya DJ (2002) Flavonoid antioxidants: chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. J Nutr Biochem 13:572–584
Horbowicz M (2002) Method of quercetin extraction from dry scales of onion. Veget Crops Res Bulletin 57:119–124
Hosseinzadeh S, Jafarikukhdan A, Hosseini A, Armand R (2015) The application of medicinal plants in traditional and modern medicine: a review of Thymus vulgaris. Int J Clinic Med 6:635–642. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijcm.2015.69084
Jafarinia M, Hosseini MS, Kasiri N, Fazel N, Fathi F, Hakemi MG, Eskandari N (2020) Quercetin with the potential effect on allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 16:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-020-00434-0
Jerine PS, Kadar BS, Giridharan R, Udhaya LB, Evan PS (2017) Suppressive effect of Spirulina fusiformis on diclofenac-induced hepato-renal injury and gastrointestinal ulcer in Wistar albino rats: a biochemical and histological approach. Biomed Pharmacother 88:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.032
Jiang X, Yu J, Wang X, Ge J, Li N (2019) Quercetin improves lipid metabolism via SCAP-SREBP2-LDLr signaling pathway in early stage diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity Targets Ther 12:827–839
Jothy SL, Zakaria Z, Chen Y, Lau YL, Latha LY, Sasidharan S (2011) Acute oral toxicity of methanolic seed extract of Cassia fistula in mice. Molecules 16:5268–5282. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16065268
Karanicolas PJ (2017). Assessment of hepatic function: implications for the surgical patient: in Blumgart’s surgery of the liver, biliary tract and pancreas. 6th edition. 60-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-34062-5.00003-0
Kawai Y, Masutani K, Torisu K, Katafuchi R, Tanaka S, Tsuchimoto A, Mitsuiki K, Tsuruya K, Kitazono T (2018) Association between serum albumin level and incidence of end-stage renal disease in patients with immunoglobulin a nephropathy: a possible role of albumin as an antioxidant agent. PLoS One 13:e0196655. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196655
Kitamura Y, Nishikawa A, Nakamura H, Furukawa F, Imazawa T, Umemura T (2005) Effects of N-acetylcysteine, quercetin, and phytic acid on spontaneous hepatic and renal lesions in LEC rats. Toxicol and Pathol 33:584–592
Kork F, Balzer F, Spies CD, Wernecke K, Ginde AA, Jankowski J, Eltzschig HK (2015) Minor postoperative increases of creatinine are associated with higher mortality and longer hospital length of stay in surgical patients. Anesthesiology 123:1301–1311
Li Y, Guo H, Zhao YQ, Li A, Ren YQ, Zhang JW (2017) Quercetin protects neuronal cells from oxidative stress and cognitive degradation induced by amyloid β-peptide treatment. Mole Med Rep 16:1573–1577
Liguori L, Califano R, Albanese D, Raimo F, Crescitelli A, Di Matteo M (2017) Chemical composition and antioxidant properties of five white onion (Allium cepa L.) landraces. J. Food Quality 2017:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6873651
Lorke D (1983) A new approach to practical acute toxicity. Arch Toxicol 54:275–287
Lucida H, Primadini Y, Suhatri A (2019) A study on the acute toxicity of quercetin solid dispersion as a potential nephron-protector. Rasayan J Chem 12:727–732. https://doi.org/10.31788/RJC.2019.1224068
Mahdavinia M, Alizadeh S, Vanani AR, Dehghani MA, Shirani M, Alipour M, Shahmohammadi HA, Asl SR (2019) Effects of quercetin on bisphenol A-induced mitochondrial toxicity in rat liver. Iran J Basic Med Sci 22:499–505. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2019.32486.7952
Mao C, Yuan J, Lv Y, Gao X, Yin Z, Kraus VB, Luo J, Chei C, Matchar DB, Zeng Y, Shi X (2019) Associations between superoxide dismutase, malondialdehyde and all-cause mortality in older adults: a communitybased cohort study. BMC Geriatr 19:104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-019-1109-z
Maronpot RR, Yoshizawa K, Nyska A, Harada T, Flake G, Mueller G, Singh B, Ward JM (2010) Hepatic enzyme induction: histopathology. Toxicol Pathol 38:776–795. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623310373778
Mehta A, Kaur G, Chintamaneni M (2012) Piperine and quercetin enhances antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of curcumin in paracetamol induced oxidative stress. Int J Pharmacol 8:101–107. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijp.2012.101.107
Mookerjee RP, Stadlbauer V, Lidder S, Wright GA, Hodges SJ, Davies NA, Jalan R (2007) Neutrophil dysfunction in alcoholic hepatitis superimposed on cirrhosis is reversible and predicts the outcome. Hepatol 46:831–840. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21737
NTP Technical Report Series No.409 (1992). Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of quercetin (CAS No., 117–39-5) in F344/N Rats (Feed Study). http://www.ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/ (accessed on 20 December 2019)
OECD (2008). OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals 407: repeated dose 28-day oral toxicity study in rodents. 1-13
Orsolic N, Jembrek J, Terzic S (2017) Honey and quercetin reduce ochratoxin A-induced DNA damage in the liver and kidney through the modulation of intestinal microflora. Food Agric Immunolol 28:812–833. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2017.1313819
Panche AN, Diwan AD, Chandra SR (2016) Flavonoids: an overview. J Nutr Sci 5:e47. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2016.41
Pareek S, Sagar NA, Sharma S, Kumar V (2018). Onion (Allium cepa L.). fruit and vegetable phytochemicals: chemistry and human health, volume II, 2nd Edn.John Wiley & Sons ltd.
Quecan BXV, Santos JTC, Rivera MLC, Hassimotto NMA, Almeida FA, Pinto UM (2019) Effect of quercetin rich onion extracts on bacterial quorum sensing. Front Microbiol 10:867. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00867
Rajagopalan R, Kode A, Penumatha SV, Kallikat NR, Venugopal PM (2004) Comparative effects of curcumin and an analog of curcumin on alcohol and PUFA induced oxidative stress. J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci 83:2747–2752
Rangan GK, Wang Y, Harris DCH (2002) Dietary quercetin augments activator protein-1 and does not reduce nuclear facto-jB in the renal cortex of rats with established chronic glomerular disease. Nephron 90:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1159/000049067
Russ M, Ott S, Bedarf JR, Kirschfink M, Hiebl B, Unger JK (2019) Increased compensatory kidney workload results in cellular damage in a short time porcine model of mixed academia - is acidemia a ‘first hit’ in acute kidney injury? PLoS One 14:e0218308. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0218308
Salazar JH (2014) Overview of urea and creatinine. Lab Med 45:19–20. https://doi.org/10.1309/LM92OSBNZPJRJGUT
Sidhu JS, Ali M, Al-Rashdan A, Ahmed N (2019) Onion (Allium cepa L.) is potentially a good source of important antioxidants. J Food Sci Technol 56:1811–1819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03625-9
Singh D, Cho WC, Upadhyay G (2016) Drug-induced liver toxicity and prevention by herbal antioxidants: an overview. Front Physiol 6:363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00363
Somade OT, Akinloye OA, Adeyeye MO, Fabunmi GD, Idowu OO, Badmus FO, Salaudeen BO (2015) Quercetin, a natural phytochemical and antioxidant protects against sodium azide-induced hepatic and splenic oxidative stress in rats. J Investig Biochem 4:69–74. https://doi.org/10.5455/jib.20151220014400
Spinella R, Sawhney R, Jalan R (2016) Albumin in chronic liver disease: structure, functions and therapeutic implications. Hepatol Int 10:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-015-9665-6
Stadlbauer V, Mookerjee RP, Wright GA, Davies NA, Jurgens G, Hallstrom S, Jalan R (2009) Role of toll-like receptors 2, 4, and 9 in mediating neutrophil dysfunction in alcoholic hepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.90512.2008
Tufoni M, Zaccherini G, Caraceni P, Bernardi M (2020) Albumin: indications in chronic liver disease. United European Gastroenterol J 8:528–535. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050640620910339
Walum A (1998) Acute oral toxicity. Environ Health Perspect 106:497–503
WHO (2000). General guidelines for methodologies on research and evaluation of traditional medicine. 1:1–74. http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/pdf/whozip42e/whozip42e.pdf. (accessed on 16 September, 2020)
Zelber-Sagi S, Ivancovsky-Wajcman D, Fliss-Isakov N, Hahn M, Webb M, Shibolet O, Kariv R, Tirosh O (2020) Serum malondialdehyde is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver and related liver damage Di_erentially in men and women. Antioxidants 9:578. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9070578
Zhang YN, Zhang YJ, Deng CY, Gong DY, Kang Y, Liu J, Zhang WS (2020) Non-clinical single and repeated-dose toxicity studies of ET-26 hydrochloride in rats. J Appl Toxicol 2020:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3970
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: Nathan Isaac Dibal, Sani Hyedima Garba, and Tamunotonye Watson Jacks
Methodology: Nathan Isaac Dibal, Sani Hyedima Garba, and Tamunotonye Watson Jacks Resources: Nathan Isaac Dibal
Data collection and processing: Nathan Isaac Dibal
Analysis and interpretation: Nathan Isaac Dibal, Sani Hyedima Garba, and Tamunotonye Watson Jacks
Writing-original draft: Nathan Isaac Dibal
Critical review and editing: Sani Hyedima Garba and Tamunotonye Watson Jacks
Supervision: Sani Hyedima Garba, Tamunotonye Watson Jacks
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The research was approved by the Department of Human Anatomy Ethical Committee (Code No. UM/HA/PGR18.19–09900) and was conducted according to the ARRIVE Guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dibal, N.I., Garba, S.H. & Jacks, T.W. Repeated 28-day oral dose toxicity of onion skin quercetin in mice. Comp Clin Pathol 29, 1219–1227 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-020-03174-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-020-03174-0