Abstract
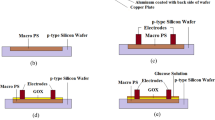
We describe a micro glucose sensor based on glucose oxidase modified mesoporous carbon electrode that is direct prototyped on silicon wafer. Advantages are shown using mesoporous carbon film as working electrode for an amperometric glucose sensor in two aspects. One is that the mesoporous carbon has appropriate pore size, which leads to a high glucose oxidase (GOx) loading and thus improves the sensitivity of the glucose sensor; The other is that direct prototyping of the mesoporous carbon film on silicon wafer allows for scalable design, batch fabrication and compatible integration with micro-fluid chips and micro systems. The mesoporous carbon film sensor shows a linear detecting range from 0.5 to 5 mM and a response time of <20 s. Sensing performance of the glucose sensor with different mesoporous cabon film thicknesses were tested and compared to achieve a high sensitivity of 0.194 mA/(mM cm2) with a 4-μm-thick mesoporous carbon film sample.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisenberger M, Br Buchle C, Hampp N (1995) A triple-step potential waveform at enzyme multisensors with thick-film gold electrodes for detection of glucose and sucrose. Sens Actuators B 28:181–189
Cao H et al (2008) Glucose biosensor based on immobilization of glucose oxidase into 3D macroporous TiO2. Electroanalysis 20:2223–2228
Hecht HJ et al (1993) Crystal-structure of glucose-oxidase from aspergillus-niger refined at 2.3 angstrom resolution. J Mol Biol 229:153–172
Heller A, Feldman B (2008) Electrochemical glucose sensors and their applications in diabetes management. Chem Rev 108:2482–2505
Koschinsky T, Heinemann L (2001) Sensors for glucose monitoring: technical and clinical aspects. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 17:113–123
Lee D et al (2005) Simple fabrication of a highly sensitive and fast glucose biosensor using enzymes immobilized in mesocellular carbon foam. Adv Mater 17:2828–2833
Lee YJ et al (2008) Fabrication and optimization of a nanoporous platinum electrode and a non-enzymatic glucose micro-sensor on silicon. Sensors 8:6154–6164
Olea D, Viratelle O, Faure C (2008) Polypyrrole-glucose oxidase biosensor effect of enzyme encapsulation in multilamellar vesicles on analytical properties. Biosens Bioelectron 23:788–794
Os PJHJ et al (1996) Glucose detection at bare and sputtered platinum electrodes coated with polypyrrole and glucose oxidase. Anal Chim Acta 335:209–216
Salimia A et al (2004) Glucose biosensor prepared by glucose oxidase encapsulated sol–gel and carbon-nanotube-modified basal plane pyrolytic. Anal Biochem 333:49–56
Shen C, Wang X, Zhang W, Kang F (2013) Direct prototyping of patterned nanoporous carbon: a route from materials to on-chip devices. Sci Rep 3:2294
Wang J (2001) Glucose biosensors: 40 years of advances and challenges. Electroanalysis 13:983–988
Wang J (2008) Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem Rev 108:814–825
Wilkins E, Atanasov P (1996) Glucose monitoring: state of the art and future possibilities. Med Eng Phys 18:273–288
Xu H et al (2008) Carbon post-microarrays for glucose sensors. Biosens Bioelectron 23:1637–1644
You C et al (2009) Electrochemistry and biosensing of glucose oxidase immobilized on Pt-dispersed mesoporous carbon. Microchim Acta 167:109–116
You X et al (2010) Enzymatic glucose biosensor based on porous ZnO/Au electrodes. Proceedings 2010 IEEE 4th International Conference on Nano/Molecular Medicine and Engineering (NANOMED 2010). doi:10.1109/NANOMED.2010.5749805
Yu J, Liu S, Ju H (2003) Glucose sensor for flow injection analysis of serum glucose based on immobilization of glucose oxidase in titania sol–gel membrane. Biosens Bioelectron 19:401–409
Zhang S et al (2005) Covalent attachment of glucose oxidase to an Au electrode modified with gold nanoparticles for use as glucose biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry 67:15–22
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science foundation of China (No. 60936003), 973 program (No. 2009CB320304) and 863 program (No. 2009AA04Z319) of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, F., Wang, X., Shen, C. et al. A micro glucose sensor based on direct prototyping mesoporous carbon electrode. Microsyst Technol 21, 1337–1343 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2159-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2159-y