Abstract
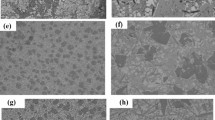
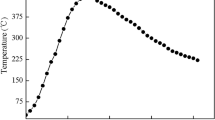
As an alternative to the time-consuming solder pre-forms and pastes currently used, a co-electroplating method of eutectic Au–Sn alloy was used in this study. Using a co-electroplating process, it was possible to plate the Au–Sn solder directly onto a wafer at or near the eutectic composition from a single solution. Two distinct phases, Au5Sn (ζ-phase) and AuSn (δ-phase), were deposited at a composition of 30 at.%Sn. The Au–Sn flip-chip joints were formed at 300 and 400°C without using any flux. In the case where the samples were reflowed at 300°C, only an (Au,Ni)3Sn2 IMC layer formed at the interface between the Au–Sn solder and Ni UBM. On the other hand, two IMC layers, (Au,Ni)3Sn2 and (Au,Ni)3Sn, were found at the interfaces of the samples reflowed at 400°C. As the reflow time increased, the thickness of the (Au,Ni)3Sn2 and (Au,Ni)3Sn IMC layers formed at the interface increased and the eutectic lamellae in the bulk solder coarsened.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Djurfors B, Ivey DG (2001) Pulsed electrodeposition of the eutectic Au/Sn solder for optoelectronic packaging. J Electron Mater 30:1249–1254
Djurfors B, Ivey DG (2002) Microstructural characterization of pulsed electrodeposited Au/Sn alloy thin films. Mater Sci Eng B 90:309–320
Doesburg J, Ivey DG (2000) Microstructure and preferred orientation of Au–Sn alloy plated deposits. Mater Sci Eng B 78:44–52
Elger G, Hutter M, Oppermann H, Aschenbrenner R, Reichl H, Jager E (2002) Development of an assembly process and reliability investigations for flip-chip LEDs using AuSn soldering. Microsyst Technol 7:239–243
Kim DW, Lee CC (2006) Fluxless flip-chip Sn-Au solder interconnect on thin Si wafers and Cu laminated polyimide films. Mater Sci Eng A 416:74–79
Lee KY, Li M, Tu KN (2003) Growth and ripening of (Au,Ni)Sn4 phase in Pb-free and Pb-containing solders on Ni/Au metallization. J Mater Res 18:2562–2570
Tew JWR, Shi XQ, Yuan S (2004) Au/Sn solder for face-down bonding of AlGaAs/GaAs ridge waveguide laser diodes. Mater Lett 58:2695–2699
Tsai JY, Chang CW, Shieh YC, Hu YC, Kao CR (2005) Controlling the microstructures from the gold-tin reaction. J Electron Mater 34:182–187
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant No. RTI04-03-04 from the Regional Technology Innovation Program of the Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy (MOCIE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, JW., Chun, HS., Koo, JM. et al. Au–Sn flip-chip solder bump for microelectronic and optoelectronic applications. Microsyst Technol 13, 1463–1469 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0330-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0330-9