Abstract
Background
Liver histology is the gold standard for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Noninvasive, simple, reproducible, and reliable biomarkers are greatly needed to differentiate NASH from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Methods
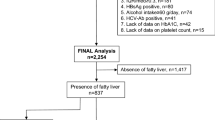
To construct a scoring system for predicting NASH, 177 Japanese patients with biopsy-proven NAFLD were enrolled. To validate the scoring system, 442 biopsy-proven NAFLD patients from eight hepatology centers in Japan were also enrolled.
Results
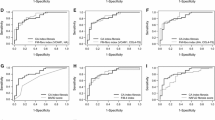
In the estimation group, 98 (55%) patients had NASH. Serum ferritin [≥200 ng/ml (female) or ≥300 ng/ml (male)], fasting insulin (≥10 μU/ml), and type IV collagen 7S (≥5.0 ng/ml) were selected as independent variables associated with NASH, by multilogistic regression analysis. These three variables were combined in a weighted sum [serum ferritin ≥200 ng/ml (female) or ≥300 ng/ml (male) = 1 point, fasting insulin ≥10 μU/ml = 1 point, and type IV collagen 7S ≥5.0 ng/ml = 2 points] to form an easily calculated composite score for predicting NASH, called the NAFIC score. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve for predicting NASH was 0.851 in the estimation group and 0.782 in the validation group. The NAFIC AUROC was the greatest among several previously established scoring systems for detecting NASH, but also for predicting severe fibrosis.
Conclusions
NAFIC score can predict NASH in Japanese NAFLD patients with sufficient accuracy and simplicity to be considered for clinical use.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ludwig J, Viggiano TR, McGill DB, Ott BJ. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980;55:434–8.
Matteoni CA, Younossi ZM, Gramlich T, Boparai N, Liu YC, McCullough AJ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases: a spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology. 1999;116:1413–9.
Rafiq N, Bai C, Fang Y, Srishord M, McCullough A, Gramlich T, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:234–8.
Saibara T. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in Asia-Oceania. Hepatol Res. 2005;33:64–7.
Hamaguchi M, Kojima T, Takeda N, Nakagawa T, Taniguchi H, Fujii K, et al. The metabolic syndrome as a predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143:722–8.
Vuppalanchi R, Chalasani N. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: selected practical issues in their evaluation and management. Hepatology. 2009;49:306–17.
Wieckowska A, McCullough AJ, Feldstein AE. Noninvasive diagnosis and monitoring of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: present and future. Hepatology. 2007;46:582–9.
Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Heurtier A, Gombert S, Giral P, Bruckert E, et al. Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1898–906.
Merriman RB, Ferrell LD, Patti MG, Weston SR, Pabst MS, Aouizerat BE, et al. Correlation of paired liver biopsies in morbidly obese patients with suspected nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2006;44:874–80.
Pagadala M, Zein CO, McCullough AJ. Predictors and advanced fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2009;13:591–606.
Sumida Y, Nakashima T, Yoh T, Furutani M, Hirohama A, Kakisaka Y, et al. Serum thioredoxin levels as a predictor of steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2003;38:32–8.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–21.
Japanese Society for the Study of Obesity. New criteria of obesity (in Japanese). J Jpn Soc Study Obes. 2000;6:18–28.
American Diabetes Association. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:1183–97.
Dixon JB, Bhathal PS, O’Brien PE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: predictors of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in the severely obese. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:91–100.
Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD, Follmann DA, Sullivan G, et al. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:2402–10.
Palekar NA, Naus R, Larson SP, Ward J, Harrison SA. Clinical model for distinguishing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis from simple steatosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2006;26:151–6.
Gholam PM, Flancbaum L, Machan JT, Charney DA, Kotler DP. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in severely obese subjects. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:399–408.
Ratziu V, Giral P, Charlotte F, Bruckert E, Thibault V, Theodorou I, et al. Liver fibrosis in overweight patients. Gastroenterology. 1999;118:1117–23.
Harrison SM, Oliver D, Arnold HLM, Gogia SM, Neuschwander-Tetri BAM. Development and validation of a simple NAFLD clinical scoring system for identifying patients without advanced disease. Gut. 2008;57:1441–7.
Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, George J, Farrell GC, et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007;45:846–54.
Miyaaki H, Ichikawa T, Nakao K, Yatsuhashi H, Furukawa R, Ohba K, et al. Clinicopathological study of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Japan: the risk factors for fibrosis. Liver Int. 2008;28:519–24.
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:2467–74.
Bonkovsky HL, Jawaid Q, Tortorelli K, LeClair P, Cobb J, Lambrecht RW, et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and iron: increased prevalence of mutations of the HFE gene in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 1999;31:421–9.
Bugianesi E, Manzini P, D’Antico S, Vanni E, Longo F, Leone N, et al. Relative contribution of iron burden, HFE mutations, and insulin resistance to fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver. Hepatology. 2004;39:179–87.
Yoneda M, Nozaki Y, Endo H, Mawatari H, Iida H, Fujita K, et al. Serum ferritin is a clinical biomarker in Japanese patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) independent of HFE gene mutation. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:808–14.
Chitturi S, Weltman M, Farrell GC, McDonald D, Kench J, Liddle C, et al. HFE mutations, hepatic iron, and fibrosis: ethnic-specific association of NASH and C282Y but not with fibrotic severity. Hepatology. 2002;36:142–9.
Sumida Y, Yoshikawa T, Okanoue T. Role of hepatic iron in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol Res. 2009;39:213–22.
Jehn M, Clark JM, Guallar E. Serum ferritin level and risk of the metabolic syndrome in U.S. adults. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2422–8.
Chitturi S, Abeygunasekera S, Farrell GC, Holmes-Walker J, Hui JM, Fung C, et al. NASH and insulin resistance: insulin hypersecretion and specific association with the insulin resistance syndrome. Hepatology. 2002;35:373–9.
Pagano G, Pacini G, Musso G, Gambino R, Mecca F, Depetris N, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome: further evidence for an etiologic association. Hepatology. 2002;35:367–72.
Marcheisini G, Bugianesi E, Forlani G, Cerrelli F, Lenzi M, Manini R, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic syndrome. Hepatology. 2003;37:917–23.
Ono M, Saibara T. Clinical features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in Japan: evidence from literature. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:725–32.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–9.
Boza C, Riquelme A, Ibañez L, Duarte I, Norero E, Viviani P, et al. Predictors of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in obese patients undergoing gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2005;15:1148–53.
Murawaki Y, Ikuta K, Koda M, Kawasaki H. Serum type III procollagen peptide, type IV collagen 7S domain, central triple-helix of type IV collagen and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in patients with chronic viral liver disease: relationship to liver histology. Hepatology. 1994;20:780–7.
Sakugawa H, Nakayoshi T, Kobashigawa K, Yamashiro T, Maeshiro T, Miyagi S, et al. Clinical usefulness of biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:255–9.
Yoneda M, Mawatari H, Fujita K, Yonemitsu K, Kato S, Takahashi H, et al. Type IV collagen 7s domain is an independent clinical marker of the severity of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis before the cirrhotic stage. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:375–81.
Shimada M, Kawahara H, Ozaki K, Fukura M, Yano H, Tsuchishima M, et al. Usefulness of a combined evaluation of the serum adiponectin level, HOMA-IR, type IV collagen 7S level to predict the early stage of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1931–8.
Kaneda H, Hashimoto E, Yatsuji S, Tokushige K, Shiratori K. Hyaluronic acid levels can predict severe fibrosis and platelet counts can predict cirrhosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21:1459–65.
Suzuki A, Angulo P, Lymp J, Li D, Satomura S, Lindor K. Hyaluronic acid, an accurate serum marker for severe fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2005;25:779–86.
Wong VW, Wong GL, Chim AM, Tse AM, Tsang SW, Hui AY, et al. Validation of the NAFLD fibrosis score in a Chinese population with low prevalence of advanced fibrosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:1682–8.
Fujii H, Enomoto M, Fukushima W, Tamori A, Sakaguchi H, Kawada N. Applicability of BARD score to Japanese patients with NAFLD. Gut. 2009;58:1566–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the following individuals for assistance in preparation of this manuscript: Atsushi Nakajima, M.D., Ph.D., Division of Gastroenterology, Yokohama City University Graduate School of Medicine; Kyoko Sakai, M.D., Yutaka Inada, M.D., Akitoshi Douhara, M.D., Tasuku Hara, M.D., Center for Digestive and Liver Diseases, Nara City Hospital; Tomokazu Ishitobi, M.D., Department of Medicine and Molecular Science, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Hiroshima University; Yoshihiro Kamada, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine; Takaaki Ohtake, M.D., Ph.D., Division of Gastroenterology and Hematology/Oncology, Department of Medicine, Asahikawa; Yoshito Itoh, M.D., Ph.D., Toshikazu Yoshikawa, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
All authors are members of the Japan Study Group of NAFLD (JSG-NAFLD).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sumida, Y., Yoneda, M., Hyogo, H. et al. A simple clinical scoring system using ferritin, fasting insulin, and type IV collagen 7S for predicting steatohepatitis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol 46, 257–268 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0305-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-010-0305-6