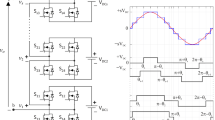
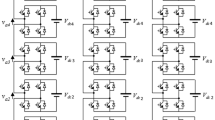
Abstract
Renewable energy sources are installed into both distribution and transmission grids more and more with the introduction of smart grid concept. Hence, efficient usage of cascaded H-bridge multilevel inverters (MLIs) for power control applications becomes vital for sustainable electricity. Conventionally, selective harmonic elimination equations need to be solved for obtaining optimum switching angles of MLIs. The objective of this study is to obtain switching angles for MLIs to minimize total harmonic distortion. This study contributes to the solution of this problem by utilizing two recently developed intelligent optimization algorithms: multi-verse optimization algorithm and salp swarm algorithm. Moreover, well-known particle swarm optimization is utilized for MLI optimization problem. Seven-level, 11-level and 15-level MLIs are used to minimize total harmonic distortions. Simulation results with different modulation indexes for seven-, 11- and 15-level MLIs are calculated and compared in terms of the accuracy and solution quality. Numerical calculations are verified by using MATLAB/Simulink-based models.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(\omega\) :
-
The angular velocity
- \(\theta _i\) :
-
The conducting angle of step i
- a :
-
A predefined minimum number
- \(a_i, \ldots , y_i\) :
-
The objects in the universes
- b :
-
A predefined maximum number
- \(c_1\) :
-
Exploration and exploitation parameter in SSA
- \(c_2\) :
-
Random number in the interval [0,1]
- \(c_3\) :
-
Random number in the interval [0,1]
- d :
-
The number of objects
- \(F_j\) :
-
The position of the food source
- k :
-
The number of separate DC sources
- L :
-
Maximum iteration number
- l :
-
Current iteration number
- \(l_i\) :
-
Learning factors
- \({\text {lb}}_j\) :
-
The lower bound for the variables
- \({\text {loc}}\) :
-
Location of the particle
- \(m_1\) :
-
Modulation index
- \(N_s\) :
-
Number of salps
- \({\text {NI}}(U_i)\) :
-
The normalized inflation rate of universe i
- p :
-
Exploitation factor
- \(r_i\) :
-
Random number between 0 and 1
- s :
-
Number of unknowns in SSA
- Spd:
-
Velocity of the particle
- T :
-
Maximum number of iterations
- t :
-
The current iteration
- \(u_i\) :
-
The ith universe
- \({\text {ub}}_j\) :
-
The upper bound for the variables
- \(v_0\) :
-
The initial speed
- \(V_i\) :
-
The voltage component i
- \(V_{\mathrm{dc}}\) :
-
The voltage magnitude of the DC source
- \(V_{\mathrm{Lmax}}\) :
-
The maximum attainable amplitude of the inverter
- \(V_{L}^*\) :
-
The amplitude command of the inverter for a sine wave output phase voltage
- \(V_{\mathrm{par}}\) :
-
A parameter showing the ratio of final speed to initial speed
- w :
-
Inertia weight
- \(x_j^1\) :
-
The leader salp
- \(x_{i}^{j}\) :
-
The jth object in the universe i
- \(x_{k}^{j}\) :
-
The jth object in the universe k selected by roulette wheel mechanism
- \(z_i\) :
-
The object values obtained by transfer operation using wormholes
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- CPB:
-
Cement paste backfill
- DC:
-
Direct current
- DE:
-
Differential evolution
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
- GWO:
-
Grey wolf optimization
- HB:
-
H-bridge
- MLI:
-
Multilevel inverter
- MVO:
-
Multi-verse optimization
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- SSA:
-
Salp swarm algorithm
- TDR:
-
Travelling distance rate
- THD:
-
Total harmonic distortion
- WEP:
-
Wormhole existence probability
- WOA:
-
Whale optimization algorithm
References
Mohd. Ali JS, Krishnaswamy V (2018) An assessment of recent multilevel inverter topologies with reduced power electronics components for renewable applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82:3379–3399
IEEE Application Guide for IEEE Std (2018) 1547 IEEE standard for inter-connecting distributed resources with electric power systems. IEEE Std. 1547.2-2008
California public utilities commission: Rule 21. http://www.cpuc.ca.gov/Rule21/. Accessed 19 Jan 2019
Ozpineci B, Tolbert LM, Chiasson JN (2005) Harmonic optimization of multilevel converters using genetic algorithms. IEEE Power Electron Lett 3(3):92–95
Patel Hasmukh S, Hoft Richard G (1973) Generalized techniques of harmonic elimination and voltage control in thyristor inverters: part I-harmonic elimination. IEEE Trans Ind Appl IA–9(3):310–317
Chiasson J, Tolbert L, McKenzie K, Du Z (2002) Eliminating harmonics in a multilevel converter using resultant theory. In: 2002 IEEE 33rd annual power electronics specialists conference, 2002. pesc 02, vol 2, pp 503–508
Yang K, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Yuan R, Guan Q, Yu W, Wang J (2017) Unified selective harmonic elimination for multilevel converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(2):1579–1590
Yang K, Lan X, Zhang Q, Tang X (2018) Unified selective harmonic elimination for cascaded h-bridge asymmetric multilevel inverter. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Power Electron 6(4):2138–2146
Hossam RM, Hashem GM, Marei MI (2013) Optimized harmonic elimination for cascaded multilevel inverter. In: 2013 48th international universities power engineering conference (UPEC), Sept, pp 1–6
Kumar J, Das B, Agarwal P (2010) Optimized switching scheme of a cascade multi-level inverter. Electr Power Compon Syst 38(4):445–464
Tang T, Han J, Tan X (2006) Selective harmonic elimination for a cascade multilevel inverter. In: 2006 IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics, vol 2, July, pp 977–981
Ramkumar S, Kamaraj V, Thamizharasan S (2011) Ga based optimization and critical evaluation she methods for three-level inverter. In: 2011 1st international conference on electrical energy systems (ICEES), Jan, pp 115–121
Kavousi A, Vahidi B, Salehi R, Bakhshizadeh MK, Farokhnia N, Fathi SH (2012) Application of the bee algorithm for selective harmonic elimination strategy in multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(4):1689–1696
Majidi B, Baghaee HR, Gharehpetian GB, Milimonfared J, Mirsalim M (2008) Harmonic optimization in multi-level inverters using harmony search algorithm. In: IEEE 2nd international power and energy conference, 2008. PECon 2008, Dec, pp 646–650
Hosseini SH, Shahmohammadi S (2012) A generalized optimization in cascade and modular multi-level inverters by harmony search method. In: 2012 12th international conference on control, automation and systems (ICCAS), Oct, pp 1506–1511
Al-Othman AK, Abdelhamid TH (2008) Elimination of harmonics in multilevel inverters with non-equal dc sources using PSO. In: Power electronics and motion control conference, 2008. EPE-PEMC 2008. 13th, Sept, pp 606–613
Memon MA, Mekhilef S, Mubin M (2018) Selective harmonic elimination in multilevel inverter using hybrid APSO algorithm. IET Power Electron 11(10):1673–1680
Gupta VK, Mahanty R (2015) Optimized switching scheme of cascaded h-bridge multilevel inverter using PSO. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 64:699–707
Haghdar K, Shayanfar HA (2018) Selective harmonic elimination with optimal dc sources in multilevel inverters using generalized pattern search. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 14(7):3124–3131
Dahidah MSA, Konstantinou G, Agelidis VG (2015) A review of multilevel selective harmonic elimination PWM: formulations, solving algorithms, implementation and applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(8):4091–4106
De León-Aldaco SE, Calleja H, Alquicira JA (2015) Metaheuristic optimization methods applied to power converters: a review. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(12):6791–6803
Ahmed MM, Saad M, Marizan M, Muhammad A (2018) Selective harmonic elimination in inverters using bio-inspired intelligent algorithms for renewable energy conversion applications: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82:2235–2253
Routray A, Singh RK, Mahanty R (2020) Harmonic reduction in hybrid cascaded multilevel inverter using modified grey wolf optimization. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 56(2):1827–1838
Kumar Kar P, Priyadarshi A, Bhaskar Karanki S (2019) Selective harmonics elimination using whale optimisation algorithm for a single-phase-modified source switched multilevel inverter. IET Power Electron 12(8):1952–1963
Routray A, Singh RK, Mahanty R, Selective harmonic elimination in hybrid cascaded multilevel inverter using modified whale optimization. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst n/a(n/a):e12298
Haghdar K (2020) Optimal dc source influence on selective harmonic elimination in multilevel inverters using teaching-learning-based optimization. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(2):942–949
Siddique MD, Mekhilef S, Shah NM, Memon MA (2019) Optimal design of a new cascaded multilevel inverter topology with reduced switch count. IEEE Access 7:24498–24510
Nayyar A, Garg S, Gupta D, Khanna A (2018) Evolutionary computation theory and algorithms. In: Nayyar A, Le D-N, Nguyen NG (eds) Advances in swarm intelligence for optimizing problems in computer science, chapter 1. Chapman and Hall/CRC, New York, pp 1–26
Anand N, Dac-Nhuong L, Gia NN (2018) Advances in swarm intelligence for optimizing problems in computer science, 1st edn. Chapman and Hall/CRC, New York
Nayyar A, Nguyen NG (2018) Introduction to swarm intelligence. In: Nayyar A, Le D-N, Nguyen NG (eds) Advances in swarm intelligence for optimizing problems in computer science, chapter 3. Chapman and Hall/CRC, New York, pp 53–78
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95-international conference on neural networks, vol 4, pp 1942–1948
Mirjalili S (2015) Moth-flame optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl Based Syst 89:228–249
Ceylan O (2016) Harmonic elimination of multilevel inverters by moth-flame optimization algorithm. In: 2016 international symposium on industrial electronics (INDEL), Nov, pp 1–5
Seyedali M, Mohammad MS, Abdolreza H (2016) Multi-verse optimizer: a nature-inspired algorithm for global optimization. Neural Comput Appl 27(2):495–513
Kumar A, Suhag S (2017) Multiverse optimized fuzzy-PID controller with a derivative filter for load frequency control of multisource hydrothermal power system. Turk J Electr Eng Comput Sci 25:4187–4199
Sulaiman M, Ahmad S, Iqbal J, Khan A, Khan R (2019) Optimal operation of the hybrid electricity generation system using multiverse optimization algorithm. Comput Intell Neurosci 2019:6192980
Ilyas B, Kun X, Mouna C (2017) A new evolutionary neural networks based on intrusion detection systems using multiverse optimization. Appl Intell 48:2315–2327
Hossam F, Hassonah MA, Al-Zoubi MA, Mirjalili S, Aljarah I (2017) A multi-verse optimizer approach for feature selection and optimizing SVM parameters based on a robust system architecture. Neural Comput Appl 30:2355–2369
Seyedali M, Gandomi Amir H, Zahra MS, Shahrzad S, Hossam F, Mohammad MS (2017) Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv Eng Softw 114:163–191
Xing Z, Jia H (2019) Multilevel color image segmentation based on GLCM and improved salp swarm algorithm. IEEE Access 7:37672–37690
Gurav SB, Kulhalli KV, Desai VV (2020) Fuzzy integrated salp swarm algorithm-based RideNN for prostate cancer detection using histopathology images. Evol Intel. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00402-y
Zhang J, Wang Z, Luo X (2018) Parameter estimation for soil water retention curve using the salp swarm algorithm. Water 10(6):815
Li E, Zhou J, Shi X, Jahed Armaghani D, Yu Z, Chen X, Huang P (2020) Developing a hybrid model of salp swarm algorithm-based support vector machine to predict the strength of fiber-reinforced cemented paste backfill. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01014-x
Figlu M, Suvendu R, Bodhisattva D, Banshidhar M, Swamy MNS (2020) An improved scheme for digital mammogram classification using weighted chaotic salp swarm algorithm-based kernel extreme learning machine. Appl Soft Comput 91:106266
Kandiri A, Golafshani EM, Behnood A (2020) Estimation of the compressive strength of concretes containing ground granulated blast furnace slag using hybridized multi-objective ANN and salp swarm algorithm. Construct Build Mater 248:118676
Saleh AS, Songfeng L, Mohamed AE, Ewees Ahmed A (2019) Improved multiobjective salp swarm optimization for virtual machine placement in cloud computing. Human Centric Comput Inf Sci 9(1):15
Rabeh A, Abdelkader A, Asghar HA, Seyedali M (2019) An efficient salp swarm-inspired algorithm for parameters identification of photovoltaic cell models. Energy Convers Manag 179:362–372
Qais MH, Hasanien HM, Alghuwainem S (2019) Enhanced salp swarm algorithm: application to variable speed wind generators. Eng Appl Artif Intell 80:82–96
Mohamed T, Hegazy R, Diab AA, Zaki A-DM (2018) A novel robust methodology based salp swarm algorithm for allocation and capacity of renewable distributed generators on distribution grids. Energies 11:2556
Hasanien HM, El-Fergany AA (2019) Salp swarm algorithm-based optimal load frequency control of hybrid renewable power systems with communication delay and excitation cross-coupling effect. Electr Power Syst Res 176:105938
Fathy A, Rezk H, Nassef AM (2019) Robust hydrogen-consumption-minimization strategy based salp swarm algorithm for energy management of fuel cell/supercapacitor/batteries in highly fluctuated load condition. Renew Energy 139(C):147–160
Abualigah L, Shehab M, Alshinwan M, Alabool H (2019) Salp swarm algorithm: a comprehensive survey. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04629-4
Holland JH (1992) Professor of psychology and of electrical engineering and computer science John H. Holland, and Senior lecturer in human Resource Management Holland. In: Adaptation in natural and artificial systems: an introductory analysis with applications to biology, control, and artificial intelligence, Google-Books-ID: 5EgGaBkwvWcC. MIT Press
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Global Optim 11(4):341–359
Hossein GA, Xin-She Y, Hossein AA (2013) Cuckoo search algorithm: a metaheuristic approach to solve structural optimization problems. Eng Comput 29(1):17–35
Khomfoi S, Tolbert L (2011) Multilevel power converters. In: Rashid MH (ed) Power electronics handbook; devices, circuits and applications, chapter 17, 3rd edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, pp 455–487
Awais M, Raza MA, Ilyas H, Younus HB, Abbas T (2016) A novel problem formulation for selection of switching angles for minimization of total harmonic distortion in cascaded multilevel inverters. In: 2016 international conference on emerging technologies (ICET), Oct 2016, pp 1–6
Awais M, Ilyas H, Younus HB, Raza MA, Abbas T (2016) Optimal switching angles for minimization of total harmonic distortion in single phase cascaded multilevel inverters. In: 2016 19th international multi-topic conference (INMIC), Dec, pp 1–6
Seyedali M, Mohammad MS, Andrew L (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61
Ssa source codes. http://www.alimirjalili.com/SourceCodes/SSA.zip. Accessed 10 Apr 2019
Mvo source codes. http://www.alimirjalili.com/SourceCodes/MVO.zip. Accessed 10 Apr 2019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceylan, O. Multi-verse optimization algorithm- and salp swarm optimization algorithm-based optimization of multilevel inverters. Neural Comput & Applic 33, 1935–1950 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05062-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05062-8