Abstract
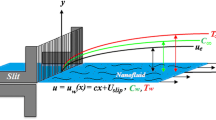
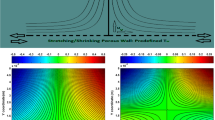
A steady stagnation point flow of an incompressible Williamson nanofluid towards a horizontal linearly stretching/shrinking sheet with active and passive controls on the wall mass flux is numerically studied. The governing partial differential equations are reduced into a system of ordinary differential equations using a similarity transformation and are solved using the bvp4c package in MATLAB. The velocity, temperature and nanoparticle volume fraction profiles together with the reduced skin friction coefficient, reduced Nusselt number and reduced Sherwood number are graphically presented to visualize the effects of parameters involved in the study. Results show that temperature and nanoparticle volume fraction are decreasing functions of the stagnation parameter, r. It is also found that the diffusivity ratio \(N_{\mathrm{bt}}\) and Lewis number Le have almost negligible effects on heat transfer rate in passive control. Increasing value of Williamson parameter \(\lambda\) will increase the skin friction in both stretching and shrinking surfaces.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbar NS, Nadeem S, Lee C, Khan ZH, Haq RU (2013) Numerical study of Williamson nano fluid flow in an asymmetric channel. Results Phys 3:161–166
Nandy SK, Pop I (2014) Effects of magnetic field and thermal radiation on stagnation flow and heat transfer of nanofluid over a shrinking surface. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 53:50–55
Khan WA, Makinde OD, Khan ZH (2014) MHD boundary layer flow of a nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms past a vertical plate with Navier slip. Int J Heat Mass Transf 74:285–291
Ul Haq R, Nadeem S, Khan ZH, Akbar NS (2015) Thermal radiation and slip effects on MHD stagnation point flow of nanofluid over a stretching sheet. Phys E 65:17–23
Mustafa M, Khan JA, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2015) Analytical and numerical solutions for axisymmetric flow of nanofluid due to non-linearly stretching sheet. Int J Nonlinear Mech 71:22–29
Mohyud-din ST, Zaidi ZA, Khan U, Ahmed N (2015) On heat and mass transfer analysis for the flow of a nanofluid between rotating parallel plates. Aerosp Sci Technol 46:514–522
Sheikholeslami M, Rashidi MM (2015) Effect of space dependent magnetic field on free convection of Fe3O4-water nanofluid. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 56:6–15
Sheikholeslami M, Rashidi MM, Ganji DD (2015) Effect of non-uniform magnetic field on forced convection heat transfer of Fe3O4-water nanofluid. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 294:299–312
Freidoonimehr N, Rashidi MM, Mahmud S (2015) Unsteady MHD free convective flow past a permeable stretching vertical surface in a nano-fluid. Int J Therm Sci 87:136–145
Garoosi F, Jahanshaloo L, Rashidi MM, Ali ME-S (2015) Numerical simulation of natural convection of the nanofluid in heat exchangers using a Buongiorno model. Appl Math Comput 254:183–203
Khan U, Ahmed N, Mohyud-Din ST (2015) Heat transfer effects on carbon nanotubes suspended nanofluid flow in a channel with non-parallel walls under the effect of velocity slip boundary condition: a numerical study. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-2035-4
Khan U, Mohyud-Din ST, Mohsin B (2016) Convective heat transfer and thermo-diffusion effects on flow of nanofluid towards a permeable stretching sheet saturated by a porous medium. Aerosp Sci Technol 50:196–203
Buongiorno J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J Heat Transf 128:240–250
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2013) The Cheng–Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary-layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid: a revised model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 65:682–685
Nield DA, Kuznetsov AV (2014) The onset of convection in a horizontal nanofluid layer of finite depth: a revised model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 77:915–918
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA (2014) Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate: a revised model. Int J Therm Sci 77:126–129
Nield DA, Kuznetsov AV (2014) Thermal instability in a porous medium layer saturated by a nanofluid: a revised model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 68:211–214
Rahman MM, Rosca AV, Pop I (2014) Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid apst a permeable exponentially shrinking/stretching surface with second order slip using Buongiornos model. Int J Therm Sci 77:1133–1143
Mustafa M, Khan JA, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2015) Boundary layer flow of nanofluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet with convective boundary condition. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 14(1):159–168
Dhanai R, Rana P, Kumar L (2015) Multiple solutions of MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer behavior of nanofluids induced by a power-law stretching/shrinking permeable sheet with viscous dissipation. Powder Technol 273:62–70
Hiemenz K (1911) Dei Grenzschicht an einem in den gleichformigen Flussigkeitsstrom eingetauchten geraden Kreiszylinder. Dingl Polytech J 32:321–410
Ishak A, Nazar R, Arifin NM, Pop I (2007) Mixed convection of the stagnation-point flow towards a stretching vertical permeable sheet. Malays J Math Sci 1(2):217–226
Mustafa M, Hayat T, Pop I, Asghar S, Obaidat S (2011) Stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid towards a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Tranf 54:5588–5594
Alsaedi A, Awais M, Hayat T (2012) Effects of heat generation/absorption on stagnation point flow of nanofluid over a surface with convective boundary conditions. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17:4210–4223
Bachok N, Ishak A, Pop I (2013) Stagnation point flow toward a stretching/shrinking sheet with a convective surface boundary condition. J Frankl Inst 350:2736–2744
Akbar NS, Khan ZH, Nadeem S (2014) The combined effects of slip and convective boundary conditions on stagnation-point flow of CNT suspended nanofluid over a stretching sheet. J Mol Liq 196:21–25
Khan U, Ahmed N, Khan SIU, Mohyud-din ST (2014) Thermo-diffusion effects on MHD stagnation point flow towards a stretching sheet in a nanofluid. Propuls Power Res 3:151–158
Hayat T, Asad S, Mustafa M, Alsaedi A (2015) MHD stagnation-point flow of Jeffrey fluid over a convectively heated stretching sheet. Comput Fluids 108:179–185
Sajid M, Ahmed B, Abbas Z (2015) Steady mixed convection stagnation point flow of MHD Oldroyd-B fluid over a stretching sheet. J Egypt Math Soc 23:440–444
Noor NFM, Ul Haq R, Nadeem S, Hashim I (2015) Mixed convection stagnation flow of a micropolar nanofluid along a vertically stretching surface with slip effects. Meccanica 50(8):2007–2022
Williamson RV (1929) The flow of pseudoplastic materials. Ind Eng Chem Res 21(11):1108
Nadeem S, Akram S (2010) Peristaltic flow of a Williamson fluid in an asymmetric channel. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 15:1705–1716
Akbar NS, Hayat T, Nadeem S, Obaidat S (2012) Peristaltic flow of a Williamson fluid in an inclined asymmetric channel with partial slip and heat transfer. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:1855–1862
Ellahi R, Riaz A, Nadeem S (2013) Three dimensional peristaltic flow of Williamson fluid in a rectangular duct. Indian J Phys 87(12):1275–1281
Khan NA, Khan S, Riaz F (2014) Boundary layer flow of Williamson fluid with chemically reactive species using scaling transformation and homotopy analysis method. Math Sci Lett 3(3):199–205
Zehra I, Yousaf MM, Nadeem S (2015) Numerical solutions of Williamson fluid with pressure dependent viscosity. Results Phys 5:20–25
Eldabe NT, Elogail MA, Elshaboury SM, Hasan AA (2015) Hall effects on the peristaltic transport of Williamson fluid through a porous medium with heat and mass transfer. Math Model Appl. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2015.04.043
Nadeem S, Hussain ST, Lee C (2013) Flow of a Williamson fluid over a stretching sheet. Braz J Chem Eng 30(3):619–625
Nadeem S, Hussain ST (2014) Heat transfer analysis of Williamson fluid over exponentially stretching surface. Appl Math Mech 35(4):489–502
Nadeem S, Hussain ST (2014) Flow and heat transfer analysis of Williamson nanofluid. Appl Nanosci 4:1005–1012
Acknowledgments
This research is financially supported by Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia under research grant FRGS/1/2015/SG04/UM/02/1 (FP016-2015A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halim, N.A., Sivasankaran, S. & Noor, N.F.M. Active and passive controls of the Williamson stagnation nanofluid flow over a stretching/shrinking surface. Neural Comput & Applic 28 (Suppl 1), 1023–1033 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2380-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2380-y