Abstract
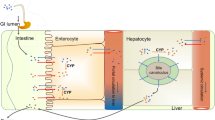
The enzymes in the cytochrome p450 monooxygenase system (CYP) are the major enzymes responsible for metabolizing medications. The CYP2D6 isomer is responsible for metabolizing certain opioids, neuroleptics, antidepressants and cardiac medications. Owing to CYP2D6's low capacity and high affinity it is easily saturated by substrate and/or inhibited, resulting in pharmacokinetic interactions. Polymorphisms of the structural gene are common, leading to wide inter-individual and ethnic differences in drug metabolism. Clinically important drug interactions, which may be anticipated in the palliative medicine population, are reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, M.P., Homsi, J. The importance of cytochrome P450 monooxygenase CYP2D6 in palliative medicine. Support Care Cancer 9, 442–451 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005200000222
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005200000222