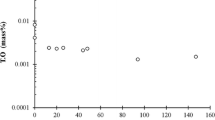
Summary
A rd750 mm ESR-ingot of the steel grade 1.4938 was remelted under protective gas atmosphere in a short collar mould. A CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-standard-ESR-slag was used for remelting. The investigations were done by using three different meltrates during remelting of the entire ingot. After stable conditions were achieved, the liquid metal pool was marked by adding solid tungsten granulate. To investigate the cleanliness of the ingot in the condition as cast, samples from the surface, half radius and centre of the ingot were taken along the marked pool. An automated method of the SEM-EDX-analysis was applied for the characterization of non-metallic inclusions (NMI). The classification of the NMI was carried out for type, size and quantitiy and was related to the meltrate. The main non-metallic inclusion types were determined as Al2O3, calcium-aluminate and Al-rich oxisulfides. The best cleanliness was found in the ingot area where the lowest meltrate was applied. An increasing cleanliness from surface to centre was established in each ingot area. The explanation of the relationship between cleanliness and meltrate is given by a thermodynamic equilibrated approach of the ESR process.
Zusammenfassung
An der ESU-Gleittiegelanlage der Breitenfeld AG wurde bei dreimaliger Variation der Schmelzrate ein ø750 mm Block der Stahlmarke 1.4938 mit einer CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-Standard-ESU-Schlacke unter Schutzgas umgeschmolzen. Nach dem Erreichen der jeweils gewünschten Abschmelzbedingungen diente die Zugabe eines Feststoffgranulats zur Markierung des flüssigen Metallpools. Anschließend erfolgte das Zerteilen des Blockes und die Entnahme repräsentativer Proben (Gussgefüge) entlang des markierten Pools an den Positionen Rand, R/2 und Zentrum. Die Methode der automatisierten REM-EDX-Analyse zur Charakterisierung der detektierten nichtmetallischen Einschlüsse (NME) folgte. Die Klassifizierung der NME wurde für jede Blockzone und Probenposition nach Typ, Größe und Menge vorgenommen und mit der Schmelzrate in Beziehung gesetzt. Al2O3 und Al-reiche Oxisulfide wurden am häufigsten detektiert. Die Blockzone mit der geringsten Schmelzrate ergab die vergleichsweise beste Stahlreinheit, wobei diese vom Rand in Richtung Zentrum zunahm. Eine ansatzweise Erklärung des Zusammenhangs zwischen abnehmender Stahlreinheit mit steigender Schmelzrate wurde mit einer thermodynamischen Gleichgewichtsbetrachtung des ESU-Prozesses gegeben.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literaturverzeichnis
Vacugov, G. A., V. V. Chlynov und G. A. Chasin: Entfernung der nichtmetallischen Einschlüsse beim Elektroschlackenumschmelzen. STAL in Deutsch (1967), S. 969–971
Kljuev, M. M. und V. M. Spicberg: Abscheidung und Bildung nichtmetallischer Einschlüsse im Metall beim Elektroschlacke-Umschmelzverfahren. STAL in Deutsch (1969), S. 590–594
Kay, D. A. R. and R. J. Pomfret: Removal of oxide inclusions during AC electroslag remelting. Journal of The Iron and Steel Institute (1971), pp. 962–965
Mitchell, A.: Oxide inclusion behaviour during consumable electrode remelting. Ironmaking and Steelmaking (1974), pp. 172–179
Zhengbang, Li: Mechanism of oxide inclusions removal in the ESR Process. Special Melting and Processing Technologies (1988), pp. 732–743
Schneider, R. et al.: DESU-Prozessoptimierung zur Herstellung stickstofflegierter Stähle mit höchstem Reinheitsgrad. BHM 147 (2002), S. 1–6
Klujev, M. M. und Ju. M. Mironov: Über die Größe der Reaktionsfläche beim Elektroschlackenumschmelzverfahren. STAL in Deutsch (1967), S. 964–968
Fraser, M. E. and A., Mitchell: Mass transfer in the electroslag process: Part 1 mass-transfer coefficients. Ironmaking and Steelmaking (1976), pp. 279–287
Povolotskii, D. Ya., V. A. Voronov und B. M. Nikitin: Removal of non-metallic inclusions during electroslag remelting. Steel in the USSR (1971), pp. 952–954
Chan, J. C. F., J. W. Guerard and D. Miller: The re-solution of inclusions in remelted stainless steels. Metallurgical Transactions B 7B (1976), pp. 135–141
Roshchin, V. E., et al: Transformation of non-metallic inclusions in metal of consumable electrodes during remelting. Steel in the USSR (1978), pp. 679–681
Ueda, S., et al.: 36Ni-Fe ingot with high cleanliness with ESR prozess. Proceedings of the 15th International Forgemaster Meeting. Kobe (2003), pp. 94–101
Nuspl, M., et al.: Qualitative and quantitative determination of micro-inclusions by automated SEM/EDX analysis. Anal. and Bioanalytical Chemistry 379, (2004), pp. 640–645
Nadif M., C. Gatellier: Influence d'une addition de cacium ou de magnesium sur la solubilité de l'oxygéne et du soufre dans l'acier liquide. Revue de Métallurgie – CIT (1986), 377–394
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korp, J. Einfluss der Schmelzrate auf die Charakteristiken nichtmetallischer Einschlüsse beim Elektroschlacke-Umschmelzen unter Schutzgas. Berg Huettenmaenn Monatsh 157, 174–180 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00501-012-0068-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00501-012-0068-x