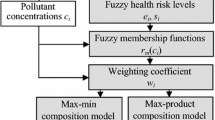
Abstract
Air pollution is one of the most important threats for the humanity. It can damage not only human health but also Earth’s ecosystem. Because of the harmful effects of air pollution, it should be controlled very carefully. To do the risk assessment of air pollution in Istanbul, the process capability indices (PCIs) which are very effective statistics to summarize the performance of process are used in this paper. Fuzzy PCIs are used to determine the levels of the air pollutants which are measured in different nine stations in Istanbul. Robust PCIs (RPCIs) are used when air pollutants have correlation. Fuzzy set theory has been applied for both PCIs and RPCIs to have more sensitive results. More flexible PCIs obtained by using fuzzy specification limits and fuzzy standard deviation are used to evaluate the air pollution’s level of Istanbul. Additionally some evaluation criteria have been constructed for fuzzy PCIs to interpret the air pollution.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buckley JJ (2004) Fuzzy statistics. Studies in fuzziness and soft computing, Springer, Heidelberg
Chan LK, Cheng SW, Spiring FA (1988) A new measure of process capability: Cpm. J Qual Technol 20(3):162–175
Chen KS, Huang ML (2007) Process capability evaluation for the process of product families. Qual Quant 41(1):151–162
Elbir T, Müezzinoğlu A (2004) Estimation of emission strengths of primary air pollutants in the city of Izmir, Turkey. Atmos Environ 38:1851–1857
Elbir T, Müezzinoğlu A, Bayram A (2000) Evaluation of some air pollution indicators in Turkey. Environ Int 26:5–10
EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2008a) What are the six common air pollutants? http://www.epa.gov/air/urbanair/6poll.html
EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (2008b) National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS). http://www.epa.gov/air/criteria.html
Güneş M (2005) A simple evaluation of SO2 and PM data on ambient air quality. Energy Sources 27:729–740
Hsu BM, Shu MH, Pearn WL (2007) Measuring process capability based on Cpmk with gauge measurement errors. Qual Reliability Eng Int 23(5):597–614
IMM-Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality (2008a) The City. http://www.ibb.gov.tr/en-US/Organization/AuthorityArea/Pages/Districts.aspx)
IMM-Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality Department of Environment Protect (2008b) Air quality. http://www.ibb.gov.tr/tr-TR/CevreKoruma/HavaKalitesi/
Kane VE (1986) Process capability indices. J Qual Technol 18:41–52
Karaca F, Alagha O, Ertürk F (2005) Statistical characterization of atmospheric PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations at a non-impacted suburban site of Istanbul, Turkey. Chemosphere 59:1183–1190
Karaca F, Nikov A, Alagha O (2006) NN-AirPol: a neural-network-based method for air pollution evaluation and control. Int J Environ Pollut 28(3–4):310–325
Karademir A (2006) Evaluation of the potential air pollution from fuel combustion in industrial boilers in Kocaeli, Turkey. Fuel 85:1894–1903
Karaöz MO (2003) Air pollution effects on forest trees in Balıkesir, Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut Focus 3:269–279
Kurt A, Gulbagci B, Karaca F, Alagha O (2008) An online air pollution forecasting system using neural networks. Environ Int. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.12.020
Lee KW (2005) First course on fuzzy theory and applications. Advances in soft computing, Springer, Heidelberg
Mathew T, Sebastian G, Kurian KM (2007) Generalized confidence intervals for process capability indices. Qual Reliability Eng Int 23(4):471–481
Montgomery DC (2005) Introduction to statistical quality control. Wiley, New York
NAQWN (National Air Quality Watching Network) (2008) Republic of Turkey Ministry of Environment and Forestry. http://www.havaizleme.gov.tr/
Oğuz E, Kaya MD, Nuhoğlu Y (2003) Interaction between air pollution and meteorological parameters in Erzurum, Turkey. Int J Environ Pollut 19(3):292–300
Özdilek HG (2006) An analogy on assessment of urban air pollution in Turkey over the turn of the millennium (1992–2001). Environmental Monit Assess 122:203–219
Pearn WL, Kotz S, Johnson NL (1992) Distributional and inferential properties of process capability indices. J Qual Technol 24(4):216–231
Prasad S, Bramorski T (1998) Robust process capability indices. Omega 26(3):425–435
Richard AB (2004) Regression analysis: a constructive critique. Sage Publications, Beverly Hills
Şen Z, Altunkaynak A, Özger M (2006) Space-time interpolation by combining air pollution and meteorologic variables. Pure Appl Geophys 163:1435–1451
Tran L, Duckstein L (2002) Comparison of fuzzy numbers using a fuzzy distance measure. Fuzzy Sets Syst 130:331–341
TurkStat-Turkish Statistical Institute (2008). http://www.tuik.gov.tr
Vannman K, Albing M (2007) Process capability induces for one-sided specification intervals and skewed distributions. Qual Reliability Eng Int 23(6):755–765
Wang DS, Koo TY, Chou CY (2007) On the bootstrap confidence intervals of the capability index Cpk for multiple process streams. Eng Comput 24(5):473–485
WHO (World Health Organization) (2005) WHO air quality guidelines for particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide-Global update 2005. Summary of risk assessment, WHO/SDE/PHE/OEH/06.02
WHO (World Health Organization) (2006) Air quality guidelines global update 2005. WHO Regional Office for Europe Publications, German, ISBN 92 890 2192 6
World Bank, Environment Department (2008) Initial Draft of Industrial Pollution Prevention and Abatement Handbook, http://www.worldbank.org/html/fpd/em/power/standards/airqstd.stm#eu
Wu CW (2007) An alternative approach to test process capability for unilateral specification with subsamples. Int J Prod Res 45(22):5397–5415
Wu CW (2008) Assessing process capability based on Bayesian approach with subsamples. Eur J Oper Res 184(1):207–228
Yıldırım Y, Demircioğlu N, Kobya M, Bayramoğlu M (2002) A mathematical modeling of sulphur dioxide pollution in Erzurum City. Environ Pollut 118:411–417
Yu KT, Sheu SH, Chen KS (2007) The evaluation of process capability for a machining center. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 33(5–6):505–510
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaya, I., Kahraman, C. Fuzzy robust process capability indices for risk assessment of air pollution. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23, 529–541 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-008-0238-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-008-0238-2