Abstract
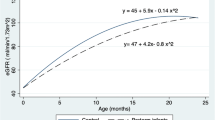
Serum creatinine (SeCr), creatinine clearance (CrCl), and fractional excretion of sodium (FeNa) were measured in 83 preterm neonates divided into four groups according to gestational age (GA). At birth, there were no differences in mean SeCr values in the four groups nor any significant correlation between initial values and GA. In all groups there was an initial SeCr increase; an inverse correlation between SeCr and GA was observed from the 3rd day of life to the 5th week (p<0.001). CrCl showed a positive correlation to GA from the first week onwards (p<0.001); in each group CrCl values correlated positively to days of life (p=0.0001). Rate of CrCl increase correlated positively to GA(p=0.0005). FeNa showed an inverse correlation to GA from the first week (p<0.001). In each group, the FeNa value correlated negatively to postnatal age (p<0.001) and the velocity of decrease was directly correlated to GA (p=0.0358). Our findings indicate that glomerular function shows a progression directly correlated to GA and postnatal age, while tubular function correlates inversely to the same parameters. The values reported could be useful for following renal function in very low birth weight infants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 19 May 1999 / Revised: 1 February 2000 / Accepted: 2 February 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallini, F., Maggio, L., Romagnoli, C. et al. Progression of renal function in preterm neonates with gestational age ≤32 weeks. Pediatr Nephrol 15, 119–124 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670000356
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670000356