Abstract
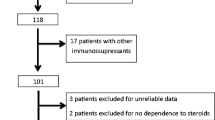
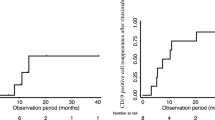
Rituximab (RTX) has a significant steroid-sparing effect in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS). However, patients are likely to relapse with the recovery of CD20+ cells. We conducted a small prospective cohort study with a historical control to evaluate the effect of RTX infusion followed by mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) as a maintenance therapy. Nine patients with SDNS who stopped their steroid treatment but were treated with MMF after RTX infusion were prospectively observed (group A). Seven patients with SDNS who discontinued steroid and immunosuppressive agents after RTX administration served as a control (group B). During the first year after the administration of RTX, six patients in group A and one patient in group B did not suffer a relapse (p < 0.05). The number of patients who relapsed during the 1 year preceding RTX treatment did not differ between the two groups [4.1 (A) vs. 5.7 (B)], but it was significantly lower in the MMF-treated group 1 year after the RTX treatment [0.4 (A) vs. 2.3 (B), p < 0.005]. The daily amount of prednisolone after the RTX treatment was lower in group A than in group B (0.11 vs. 0.46 mg/kg/day, respectively; p < 0.05). Three patients in group A and five patients in group B relapsed to SDNS and needed additional RTX treatment(s) within 1 year (odds ratio 5.0). Based on these results, we conclude that maintenance therapy with MMF after RTX is a good clinical option.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPA:
-
Cyclophosphamide
- MMF:
-
Mycophenolate mofetil
- MPA:
-
Mycophenolic acid
- MZR:
-
Mizoribine
- PSL:
-
Prednisolone
- RTX:
-
Rituximab
- SDNS:
-
Steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome
References
Benz K, Dötsch J, Rascher W, Stachel D (2004) Change of the course of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 19:794–797
Nozu K, Iijima K, Fujisawa M, Nakagawa A, Yoshikawa N, Matsuo M (2005) Rituximab treatment for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) induces complete remission of recurrent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 20:1660–1663
Kamei K, Ito S, Nozu K, Fujinaga S, Nakayama M, Sako M, Saito M, Yoneko M, Iijima K (2009) Single dose of rituximab for refractory steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1321–1328
Fujinaga S, Hirano D, Nishizaki N, Kamei K, Ito S, Ohtomo Y, Shimizu T, Kaneko K (2010) Single infusion of rituximab for persistent steroid-dependent minimal-change nephrotic syndrome after long-term cyclosporine. Pediatr Nephrol 25:539–544
Guigonis V, Dallocchio A, Baudouin V, Dehennault M, Hachon-Le Camus C, Afanetti M, Groothoff J, Llanas B, Niaudet P, Nivet H, Raynaud N, Taque S, Ronco P, Bouissou F (2008) Rituximab treatment for severe steroid- or cyclosporine-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentric series of 22 cases. Pediatr Nephrol 23:1269–1279
(1981) The primary nephrotic syndrome in children: identification of patients with minimal change nephrotic syndrome from initial response to prednisone—a report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. J Pediatr 98:561–564
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Macher MA, Loirat C, Guérin V, Watier H, Peuchmaur M, Baudouin V, Deschênes G (2010) Rituximab efficiency in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 25:1109–1115
Kyrieleis HA, Löwik MM, Pronk I, Cruysberg HR, Kremer JA, Oyen WJ, van den Heuvel BL, Wetzels JF, Levtchenko EN (2009) Long-term outcome of biopsy-proven, frequently relapsing minimal-change nephrotic syndrome in children. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1593–1600
Trompeter RS, Evans PR, Barratt TM (1981) Gonadal function in boys with steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome treated with cyclophosphamide for short periods. Lancet 30:1177–1179
Hogg RJ, Fitzgibbons L, Bruick J, Bunke M, Ault B, Baqi N, Trachtman H, Swinford R (2006) Mycophenolate mofetil in children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome: a report from the Southwest Pediatric Nephrology Study Group. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:1173–1178
Fujinaga S, Ohtomo Y, Umino D, Takemoto M, Shimizu T, Yamashiro Y, Kaneko K (2007) A prospective study on the use of mycophenolate mofetil in children with cyclosporine-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 22:71–76
Dorresteijn EM, Kist-van Holthe JE, Levtchenko EN, Nauta J, Hop WC, van der Heijden AJ (2008) Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclosporine for remission maintenance in nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 23:2013–2020
Sharma AP, Filler G (2009) Role of mycophenolate mofetil in remission maintenance after a successful response to rituximab. Pediatr Nephrol 24:423–424
Iijima K, Hamahira K, Tanaka R, Kobayashi A, Nozu K, Nakamura H, Yoshikawa N (2002) Risk factors for cyclosporine-induced tubulointerstitial lesions in children with minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 61:1801–1805
Carson KR, Evens AM, Richey EA, Habermann TM, Focosi D, Seymour JF, Laubach J, Bawn SD, Gordon LI, Winter JN, Furman RR, Vose JM, Zelenetz AD, Mamtani R, Raisch DW, Dorshimer GW, Rosen ST, Muro K, Gottardi-Littell NR, Talley RL, Sartor O, Green D, Major EO, Bennett CL (2009) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy after rituximab therapy in HIV-negative patients: a report of 57 cases from the Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports project. Blood 113:4834–4840
Bitzan M, Anselmo M, Carpineta L (2009) Rituximab (B-cell depleting antibody) associated lung injury (RALI): a pediatric case and systematic review of the literature. Pediatr Pulmonol 44:922–934
Chaumais MC, Garnier A, Chalard F, Peuchmaur M, Dauger S, Jacqz-Agrain E, Deschênes G (2009) Fatal pulmonary fibrosis after rituximab administration. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1753–1755
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Mari Saito for her statistical expertise and guidance.
Conflicts of interest
There is no financial support or conflict of interest concerning this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, S., Kamei, K., Ogura, M. et al. Maintenance therapy with mycophenolate mofetil after rituximab in pediatric patients with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 26, 1823–1828 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1886-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-1886-x