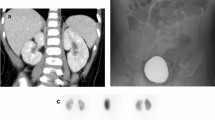
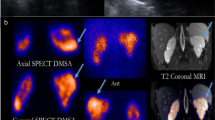
Abstract
To assess renal inflammation and its sequelae in Kawasaki disease (KD) patients, we conducted a prospective study in a university medical center setting in Taiwan. From June 2002 to January 2005, 50 children with KD were enrolled, and after admission, all received technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy single photon emission computed tomography (DMSA renal SPECT), the results of which were used as the reference standard for determining renal inflammation. Patients with renal inflammation underwent another DMSA renal SPECT more than 6 months later to evaluate the sequelae. We found that 26 of the 50 patients (52%) had renal inflammatory foci. There were no significant relationships between clinical or laboratory parameters and renal involvement in KD, except the presence of coronary artery lesions [P < 0.01; odds ratio (OR) 5.18; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.52–17.65]. Although all patients were free of clinical symptoms, the 6-month follow-up DMSA renal SPECT showed renal scarring in 11 of the 24 patients (46%). Patients with an initial abnormal renal ultrasound did predict a greatly increased risk of scarring (P < 0.05; OR 16.2; 95% CI 1.27–206.20). In conclusion, this study demonstrated that the potential long-term clinical impact of KD is not limited to coronary artery lesion sequelae but also includes renal scar formation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawasaki T (1967) Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children: Clinical Observation of 50 Cases (In Japanese). Jpn J Allergol 16:178–222
Brogan PA, Bose A, Burgner D, Shingadia D, Tulloh R, Michie C, Klein N, Booy R, Levin M, Dillon MJ (2002) Kawasaki disease: an evidence based approach to diagnosis, treatment, and proposals for future research. Arch Dis Child 86:286–290
Burns JC, Glode MP (2004) Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet 364:533–544
Amano S, Hazama F, Hamashima Y (1979) Pathology of Kawasaki disease: I. Pathology and morphogenesis of the vascular changes. Jpn Circ J 43:633–643
Amano S, Hazama F, Kubagawa H, Tasaka K, Haebara H, Hamashima Y (1980) General pathology of Kawasaki disease: On the morphological alterations corresponding to the clinical manifestations. Acta Pathol Jpn 30:681–694
Dajani AS, Taubert KA, Takahashi M, Bierman FZ, Freed MD, Ferrieri P, Gerber M, Shulman ST, Karchmer AW, Wilson W (1994) Guidelines for long-term management of patients with Kawasaki disease. Report from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation 89:916–922
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, Wilson WR, Baddour LM, Levison ME, Pallasch TJ, Falace DA, Taubert KA (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 114:1708–1733
Melish ME, Hicks RM, Larson EJ (1976) Mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome in the United States. Am J Dis Child 130:599–607
Nardi PM, Haller JO, Friedman AP, Slovis TL, Schaffer RM (1985) Renal manifestations of Kawasaki’s disease. Pediatr Radiol 15:116–118
Ferriero DM, Wolfsdorf JI (1981) Hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 68:405–406
Foster BJ, Bernard C, Drummond KN (2000) Kawasaki disease complicated by renal artery stenosis. Arch Dis Child 83:253–255
Bonany PJ, Bilkis MD, Gallo G, Lago N, Dennehy MV, Sosa del Valle JM, Vallejo G, Canepa C (2002) Acute renal failure in typical Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Nephrol 17:329–331
Veiga PA, Pieroni D, Baier W, Feld LG (1992) Association of Kawasaki disease and interstitial nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 6:421–423
Mac Ardle BM, Chambers TL, Weller SD, Tribe CR (1983) Acute renal failure in Kawasaki disease. J R Soc Med 76:615–616
Roberti I, Reisman L, Churg J (1993) Vasculitis in childhood. Pediatr Nephrol 7:479–489
Jakobsson B, Nolstedt L, Svensson L, Soderlundh S, Berg U (1992) 99mTechnetium-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan in the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children: relation to clinical and radiological findings. Pediatr Nephrol 6:328–334
Majd M, Rushton HG, Chandra R, Andrich MP, Tardif CP, Rashti F (1996) Technetium-99m-DMSA renal cortical scintigraphy to detect experimental acute pyelonephritis in piglets: comparison of planar (pinhole) and SPECT imaging. J Nucl Med 37:1731–1734
Linne T, Fituri O, Escobar-Billing R, Karlsson A, Wikstad I, Aperia A, Tullus K (1994) Functional parameters and 99mtechnetium-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan in acute pyelonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 8:694–699
Stokland E, Hellstrom M, Jakobsson B, Sixt R (1999) Imaging of renal scarring. Acta Paediatr Suppl 88:13–21
Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, American Heart Association (2001) Diagnostic guidelines for Kawasaki disease. Circulation 103:335–336
Dajani AS, Taubert KA, Gerber MA, Shulman ST, Ferrieri P, Freed M, Takahashi M, Bierman FZ, Karchmer AW, Wilson W (1993) Diagnosis and therapy of Kawasaki disease in children. Circulation 87:1776–1780
Nicholson JF, Pesce MA (2004) Reference ranges for laboratory tests and procedure. In Behrman RE, Kliegman RM, Jenson HB (eds) Nelson textbook of pediatrics, 17th edn, WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 2396–2426
Chiou YY, Wang ST, Tang MJ, Lee BF, Chiu NT (2001) Renal fibrosis: Prediction from acute pyelonephritis focus volume measured at 99mTc Dimercaptosuccinic acid SPECT. Radiology 221:366–370
Wang YT, Chiu NT, Chen MJ, Huang JJ, Chou HH, Chiou YY (2005) Correlation of renal ultrasonographic findings with inflammatory volume from dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scans in children with acute pyelonephritis. J Urol 173:190–194
Jakobsson B, Svensson L (1997) Transient pyelonephritic changes on 99mTechnetium-dimercaptosuccinic acid scan for at least five months after infection. Acta Paediatr 86:803–807
Report of the Subcommittee on Standardization of Diagnostic Criteria and Reporting of Coronary Artery Lesions in Kawasaki Disease (1984) Tokyo, Japan: Research Committee on Kawasaki disease, Ministry of Health and Welfare
Salcedo JR, Greenberg L, Kapur S (1988) Renal histology of mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (Kawasaki disease). Clin Nephrol 29:47–51
Ogawa H (1985) Kidney pathology in muco-cutaneous lymphnode syndrome. Jpn J Nephrol 27:1229–1237
Rowley AH, Shulman ST, Mask CA, Finn LS, Terai M, Baker SC (2000) IgA plasma cell infiltration of proximal respiratory tract, pancreas, kidney, and coronary artery in acute Kawasaki disease. J Infect Dis 182:1183–1191
Grunebaum E, Blank M, Cohen S, Afek A, Kopolovic J, Meroni PL, Youinou P, Shoenfeld Y (2002) The role of anti-endothelial cell antibodies in Kawasaki disease-in vitro and in vivo studies. Clin Exp Immunol 130:233–240
Watanabe T, Abe Y, Sato S, Uehara Y, IKeno K, Abe T (2006) Hyponatremia in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Nephrol 21:778–781
Ohta K, Seno A, Shintani N, Kato E, Yachie A, Seki H, Miyawaki T, Taniguchi N (1993) Increased levels of urinary interleukin-6 in Kawasaki disease. Eur J Pediatr 152:647–649
Jibiki T, Terai M, Kohno Y (2004) High concentrations of interleukin-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in urine of patients with acute Kawasaki disease. Eur J Pediatr 163:749–750
Hellerstein S (2000) Long-term consequences of urinary tract infections. Curr Opin Pediatr 12:125–128
Rushton HG (1997) Urinary tract infections in children. Epidemiology, evaluation, and management. Pediatr Clin North Am 44:1133–1169
Resch M, Banas B, Endemann D, Mack M, Riegger GAJ, Gröne HJ, Kramer BK (2006) Exanthema and acute anuric renal failure. Clin Nephrol 65:361–363
Kato H, Sugimura T, Akagi T, Sato N, Hashino K, Maeno Y, Kazue T, Eto G, Yamakawa R (1996) Long-term consequences of Kawasaki disease. A 10- to 21-year follow-up study of 594 patients. Circulation 94:1379–1385
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Financial support: Grants from the National Cheng Kung University Medical Center.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JN., Chiou, YY., Chiu, NT. et al. Renal scarring sequelae in childhood Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Nephrol 22, 684–689 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-006-0385-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-006-0385-y