Abstract
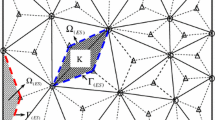
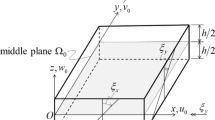
The cell-based strain smoothing technique is combined with the well-known three-node Mindlin plate element (MIN3) to give a so-called the cell-based smoothed MIN3 (CS-MIN3) for static and free vibration analyses of plates. In the process of formulating the system stiffness matrix of the CS-MIN3, each triangular element will be divided into three sub-triangles, and in each sub-triangle, the stabilized MIN3 is used to compute the strains and to avoid the transverse shear locking. Then the strain smoothing technique on whole the triangular element is used to smooth the strains on these three sub-triangles. The numerical examples demonstrated that the CS-MIN3 is free of shear locking, passes the patch test and shows four superior properties such as: (1) be a strong competitor to many existing three-node triangular plate elements in the static analysis, (2) can give high accurate solutions for problems with skew geometries in the static analysis, (3) can give high accurate solutions in free vibration analysis, (4) can provide accurately the values of high frequencies of plates by using only coarse meshes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zienkiewicz OC, Taylor RL (2000) The finite element method, vol. 2. Solid mechanics. 5. Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford
Bathe KJ (1996) Finite element procedures. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River
Henry Yang TY, Saigal S, Masud A, Kapania RK (2000) A survey of recent shell finite elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 47: 101–127
Mackerle J (1997) Finite element linear and nonlinear, static and dynamic analysis of structural elements: a bibliography (1992–1995). Eng Comput 14(4): 347–440
Mackerle J (2002) Finite element linear and nonlinear, static and dynamic analysis of structural elements: a bibliography (1999–2002). Eng Comput 19(5): 520–594
Leissa AW (1969) Vibration of plates. NASA, SP-160, Washington, DC
Leissa AW (1987) A review of laminated composite plate buckling. Appl Mech Rev 40(5): 575–591
Robert DB (1979) Formulas for natural frequency and mode shape. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Liew KM, Xiang Y, Kitipornchai S (1995) Research on thick plate vibration: a literature survey. J Sound Vib 180(1): 163–176
Reddy JN (2006) Theory and analysis of elastic plates and shells. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, New York
Gruttmann F, Wagner W (2004) A stabilized one-point integrated quadrilateral Reissner–Mindlin plate element. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61: 2273–2295
Brasile S (2008) An isostatic assumed stress triangular element for the Reissner–Mindlin plate-bending problem. Int J Numer Methods Eng 74: 971–995
Cen S, Long YQ, Yao ZH, Chiew SP (2006) Application of the quadrilateral area co-ordinate method: a new element for Mindlin–Reissner plate. Int J Numer Methods Eng 66: 1–45
Nguyen-Xuan H, Liu GR, Thai-Hoang C, Nguyen-Thoi T (2009) An edge-based smoothed finite element method with stabilized discrete shear gap technique for analysis of Reissner–Mindlin plates. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199: 471–489
Ayad R, Dhatt G, Batoz JL (1998) A new hybrid-mixed variational approach for Reissner–Mindlin plates. The MiSP model. Int J Numer Methods Eng 42: 1149–1179
Ayad R, Rigolot A (2002) An improved four-node hybrid-mixed element based upon Mindlin’s plate theory. Int J Numer Methods Eng 55: 705–731
Soh AK, Cen S, Long YQ, Long ZF (2001) A new twelve DOF quadrilateral element for analysis of thick and thin plate. Eur J Mech A 20(2): 299–326
Cen S, Long YQ, Yao ZH (2002) A new hybrid-enhanced displacement-based element for the analysis of laminated composite plates. Comput Struct 80((9–10): 819–833
Cen S, Soh AK, Long YQ, Yao ZH (2002) A new 4-node quadrilateral FE model with variable electrical degrees of freedom for the analysis of piezoelectric laminated composite plates. Compos Struct 58(4): 583–599
Zienkiewicz OC, Taylor RL, Too JM (1971) Reduced integration techniques in general of plates and shells. Int J Numer Methods Eng 3: 275–290
Hughes TJR, Taylor RL, Kanoknukulchai W (1977) A simple and efficient finite element for plate bending. Int J Numer Methods Eng 11: 1529–1543
Hughes TJR, Cohen M, Haroun M (1978) Reduced and selective integration techniques in finite element method of plates. Nucl Eng Des 46: 203–222
Belytschko T, Tsay CS, Liu WK (1981) A stabilization matrix for the bilinear Mindlin plate element. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 29: 313–327
Belytschko T, Tsay CS (1983) A stabilization procedure for the quadrilateral plate element with one point quadrature. Int J Numer Methods Eng 19: 405–419
Bergan PG, Wang X (1984) Quadrilateral plate bending elements with shear deformations. Comput Struct 19(1–2): 25–34
Hinton E, Huang HC (1986) A family of quadrilateral Mindlin plate element with substitute shear strain fields. Comput Struct 23(3): 409–431
Lee SW, Pian THH (1978) Finite elements based upon Mindlin plate theory with particular reference to the four-node isoparametric element. AIAA J 16: 29–34
Lee SW, Wong C (1982) Mixed formulation finite elements for Mindlin theory plate bending. Int J Numer Methods Eng 18: 1297–1311
Lovadina C (1998) Analysis of a mixed finite element method for the Reissner–Mindlin plate problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 163: 71–85
Miranda SD, Ubertini F (2006) A simple hybrid stress element for shear deformable plates. Int J Numer Methods Eng 65: 808–833
Hughes TJR, Tezduzar TE (1981) Finite elements based upon Mindlin plate theory with particular reference to the four-node bilinear isoparametric element. J Appl Mech 48(3): 587–596
Bathe KJ, Brezzi F (1985) On the convergence of a four-node plate bending element based on Mindlin–Reissner plate theory and a mixed interpolation. In: Whiteman J (ed) Proceedings of the conference on mathematics of finite elements and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 491–503
Bathe KJ, Brezzi F (1987) A simplified analysis of two plate bending elements—the MITC4 and MITC9 elements. Proceedings of the conference NUMETA, University College of Swansea, Wales
Brezzi F, Bathe KJ, Fortin M (1989) Mixed-interpolated elements for Reissner–Mindlin plates. Int J Numer Methods Eng 28: 1787–1801
Bathe KJ, Dvorkin EN (1985) A four-node plate bending element based on Mindlin–Reissner plate theory and a mixed interpolation. Int J Numer Methods Eng 21: 367–383
Dvorkin EN, Bathe KJ (1984) A continuum mechanics based four-node shell element for general non-linear analysis. Eng Comput 1: 77–78
Bathe KJ, Dvorkin EN (1986) A formulation of general shell elements—the use of mixed interpolation of tensorial components. Int J Numer Methods Eng 22: 697–722
Bathe KJ, Cho SW, Buchalem ML (1989) On our MITC plate bending shell elements. In: Noor AK, Belytschko T, Simo JC (eds) Analytical and computational models for shells, CED. ASME, New York, pp 261–278
Onate E, Zienkiewicz OC, Suarez B, Taylor RL (1992) A general methodology for deriving shear constrained Reissner–Mindlin plate elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 33: 345–367
Onate E, Castro J (1992) Derivation of plate based on assumed shear strain_elds. In: Ladev_eze P, Zienkiewicz OC (eds) New Advances in computational structural mechanics. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 237–288
Zienkiewicz OC, Xu Z, Zeng LF, Samuelson A, Wiberg NE (1993) Linked interpolation for Reissner–Mindlin plate elements. Part I—a simple quadrilateral. Int J Numer Methods Eng 36: 3043–3056
Taylor RL, Auricchio F (1993) Linked interpolation for Reissner–Mindlin plate element. Part II—a simple triangle. Int J Numer Methods Eng 36: 3057–3066
Batoz JL, Bathe KJ, Ho LW (1980) A study of three-node triangular plate bending elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 15: 1771–1812
Batoz JL, Tahar MB (1982) Evaluation of a new quadrilateral thin plate bending element. Int J Numer Methods Eng 18: 1655–1677
Katili I (1993) A new discrete Kirchhoff–Mindlin element based on Mindlin–Reissner plate theory and assumed shear strain fields—Part I: an extended DKT element for thick-plate bending analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 36: 1859–1883
Katili I (1993) A new discrete Kirchhoff–Mindlin element based on Mindlin–Reissner plate theory and assumed shear strain fields—Part II: an extended DKQ element for thick-plate bending analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 36: 1885–1908
Bletzinger KU, Bischoff M, Ramm E (2000) A unified approach for shear-locking free triangular and rectangular shell finite elements. Comput Struct 75: 321–334
Tessler A, Hughes TJR (1985) A three-node mindlin plate element with improved transverse shear. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 50: 71–101
Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T (2010) Smoothed finite element methods. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, NewYork
Chen JS, Wu CT, Yoon S, You Y (2001) A stabilized conforming nodal integration for Galerkin mesh-free methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50: 435–466
Liu GR, Dai KY, Nguyen-Thoi T (2007) A smoothed finite element for mechanics problems. Comput Mech 39: 859–877
Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Dai KY, Lam KY (2007) Theoretical aspects of the smoothed finite element method (SFEM). Int J Numer Methods Eng 71: 902–930
Cui XY, Liu GR, Li GY, Zhao X, Nguyen-Thoi T, Sun GY (2008) A smoothed finite element method (SFEM) for linear and geometrically nonlinear analysis of plates and shells. Comput Model Eng Sci 28(2): 109–125
Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Thoi T (2009) A stabilized smoothed finite element method for free vibration analysis of Mindlin–Reissner plates. Commun Numer Methods Eng 25: 882–906
Dai KY, Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T (2007) An n-sided polygonal smoothed finite element method (nSFEM) for solid mechanics. Finite Elem Anal Des 43: 847–860
Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Nguyen-Xuan H, Lam KY (2009) A node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM) for upper bound solutions to solid mechanics problems. Comput Struct 87: 14–26
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H (2009) Additional properties of the node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM) for solid mechanics problems. Int J Comput Methods 6: 633–666
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Tran C (2009) Adaptive analysis using the node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM). Commun Numer Methods Eng 27(2): 198–218
Nguyen-Thoi T, Vu-Do HC, Nguyen-Xuan H (2010) A node-based smoothed finite element method (NS-FEM) for upper bound solution to visco-elastoplastic analyses of solids using triangular and tetrahedral meshes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199: 3005–3027
Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Lam KY (2008) A novel Alpha Finite Element Method (αFEM) for exact solution to mechanics problems using triangular and tetrahedral elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197: 3883–3897
Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Lam KY (2009) An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) for static, free and forced vibration analyses of solids. J Sound Vib 320: 1100–1130
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H (2010) An n-sided polygonal edge-based smoothed finite element method (nES-FEM) for solid mechanics. Commun Numer Methods Eng. doi:10.1002/cnm.1375
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Vu-Do HC, Nguyen-Xuan H (2009) An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) for visco-elastoplastic analyses of 2D solids using triangular mesh. Comput Mech 45: 23–44
Nguyen-Xuan H, Liu GR, Nguyen-Thoi T, Nguyen-Tran C (2009) An edge–based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) for analysis of two–dimensional piezoelectric structures. Smart Mater Struct 18: 065015
Nguyen-Xuan H, Liu GR, Thai-Hoang C, Nguyen-Thoi T (2009) An edge-based smoothed finite element method with stabilized discrete shear gap technique for analysis of Reissner–Mindlin plates. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199: 471–489
Tran Thanh N, Liu GR, Nguyen-Xuan H, Nguyen-Thoi T (2010) An edge-based smoothed finite element method for primal-dual shakedown analysis of structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 82: 917–938
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Lam KY, Zhang GY (2009) A Face-based Smoothed Finite Element Method (FS-FEM) for 3D linear and nonlinear solid mechanics problems using 4-node tetrahedral elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 78: 324–353
Nguyen-Thoi T, Liu GR, Vu-Do HC, Nguyen-Xuan H (2009) A face-based smoothed finite element method (FS-FEM) for visco-elastoplastic analyses of 3D solids using tetrahedral mesh. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198: 3479–3498
Liu GR, Quek SS (2002) The finite element method: a practical course. Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford
Bischoff M, Bletzinger KU (2001) Stabilized DSG plate and shell elements, trends in computational structural mechanics. CIMNE, Barcelona
Lyly M, Stenberg R, Vihinen T (1993) A stable bilinear element for the Reissner–Mindlin plate model. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 110: 343–357
Morley LSD (1963) Skew plates and structures. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Abbassian F, Dawswell DJ, Knowles NC (1987) Free vibration benchmarks softback. Atkins Engineering Sciences, Glasgow
Karunasena W, Liew KM, Al-Bermani FGA (1996) Natural frequencies of thick arbitrary quadrilateral plates using the pb-2 Ritz method. J Sound Vib 196: 371–385
Nguyen-Thanh N, Timon R, Nguyen-Xuan H, Stéphane PAB (2008) A smoothed finite element method for shell analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198: 165–177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen-Thoi, T., Phung-Van, P., Luong-Van, H. et al. A cell-based smoothed three-node Mindlin plate element (CS-MIN3) for static and free vibration analyses of plates. Comput Mech 51, 65–81 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-012-0705-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-012-0705-y