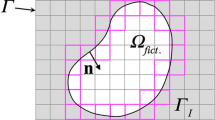
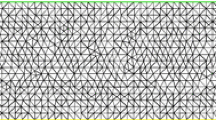
Abstract
This paper presents a variational multiscale stabilized finite element method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. The formulation is written in an Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian (ALE) frame to model problems with moving boundaries. The structure of the stabilization parameter is derived via the solution of the fine-scale problem that is furnished by the variational multiscale framework. The projection of the fine-scale solution onto the coarse-scale space leads to the new stabilized method. The formulation is integrated with a mesh moving scheme that adapts the computational grid to the evolving fluid boundaries and fluid-solid interfaces. Several test problems are presented to show the accuracy and stability of the new formulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks AN, Hughes TJR (1982) Streamline upwind/Petrov–Galerkin formulations for convection dominated flows with particular emphasis on the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 32: 199–259
Hughes TJR, Tezduyar TE (1984) Finite element methods for first-order hyperbolic systems with particular emphasis on the compressible Euler equations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 45: 217–284
Hughes TJR, Franca LP, Balestra M (1986) A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: V. Circumventing the Babuska-Brezzi condition: a stable Petrov-Galerkin formulation of the Stokes problem accommodating equal-order interpolations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 59: 85–99
Hughes TJR, Franca LP, Hulbert GM (1989) A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: VIII. The Galerkin/least-squares method for advective diffusive equations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 73(2): 173–189
Hughes TJR (1995) Multiscale phenomena: Green’s functions, the Dirichlet-to-Neumann formulation, subgrid scale models, bubbles and the origins of stabilized methods. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 127: 387–401
Hughes TJR, Feijoo GR, Mazzei Quincy JB (1998) The variational multiscale method—a paradigm for computational mechanics. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 166(1–2): 3–24
Franca LP, Hauke G, Masud A (2006) Revisiting stabilized finite element methods for the advective-diffusive equation. Comp Methods Appl Mech Eng 195: 1560–1572
Masud A, Hughes TJR (2002) A stabilized mixed finite element method for Darcy flow. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191: 4341–4370
Ayub M, Masud A (2003) A new stabilized formulation for convective-diffusive heat transfer. Numer Heat Transf Part B 44: 1–23
Masud A, Khurram R (2004) A multiscale/stabilized finite element method for the advection-diffusion equation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193: 1997–2018
Masud A, Xia K (2005) A stabilized mixed finite element method for nearly incompressible elasticity. J Appl Mech 72: 711–720
Masud A, Khurram R (2006) A multiscale finite element method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195: 1750–1777
Tezduyar TE, Aliabadi S, Behr M, Johnson A, Mittal S (1993) Parallel finite element computation of 3D flows. Computer 26: 27–36
Johnson AA, Tezduyar TE (1994) Mesh update strategies in parallel finite element computations of flow problems with moving boundaries and interfaces. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 119: 73–94
Johnson AA, Tezduyar TE (1999) Advanced mesh generation and update methods for 3D flow simulations. Comput Mech 23: 130–143
Masud A, Hughes TJR (1997) A space–time Galerkin/least-squares finite element formulation of the Navier-Stokes equations for moving domain problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 146: 91–126
Masud A (2006) Effects of mesh motion on the stability and convergence of ALE based formulations for moving boundary flows. Comput Mech 38: 430–439
Hughes TJR, Liu WK, Zimmermann TK (1981) Lagrangian–Eulerian finite element formulation for incompressible viscous flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 29: 329–349
Belytschko T, Kennedy JM, Schoeberie DF (1980) Quasi-Eulerian finite element formulation for fluid–structure interaction. ASME J Pressure Vessel Technol 102: 62–69
Tezduyar TE, Behr M, Liou J (1992) A new strategy for finite element computations involving moving boundaries and interfaces—the deforming-spatial-domain/space–time procedure. I. The concept and the preliminary numerical tests. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 94: 339–351
Tezduyar TE, Behr M, Mittal S, Liou J (1992) A new strategy for finite element computations involving moving boundaries and interfaces – the deforming-spatial-domain/space-time procedure: II. Computation of free-surface flows, two-liquid flows, and flows with drifting cylinders. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 94: 353–371
Lesoinne M, Farhat C (1996) Geometric conservation laws for flow problems with moving boundaries and deformable meshes, and their impact on aeroelastic computations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 134(1–2): 71–90
Oñate E, Garcia J, Idelsohn SR, Del Pin F (2004) Finite calculus formulations for finite element analysis of incompressible flows. Eulerian, ALE and Lagrangian approaches. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195(23–24): 3001–3037
Farhat C, Geuzaine P (2004) Design and analysis of robust ALE time-integrators for the solution of unsteady flow problems on moving grids. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(39–41): 4073–4095
Khurram R, Masud A (2006) A multiscale/stabilized formulation of the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations for moving boundary flows and fluid–structure interaction. Comput Mech 38(4–5): 403–416
Masud A, Calderer R (2009) A variational multiscale stabilized formulation for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput Mech 44: 145–160
Masud A, Bhanabhagvanwala M, Khurram R (2007) An adaptive mesh rezoning scheme for moving boundary flows and fluid– structure interaction. Comput Fluids 36: 77–91
Kanchi H, Masud A (2007) A 3D adaptive mesh moving scheme. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 54: 923–944
Masud A, Franca LP (2008) A hierarchical multiscale framework for problems with multiscale source terms. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197: 2692–2700
Masud A, Kwack J (2008) A stabilized mixed finite element method for the first-order form of convection-diffusion equation. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 57: 1321–1348
Bazilevs Y, Calo VM, Cottrell JA, Hughes TJR, Reali A, Scovazzi G (2007) Variational multiscale residual-based turbulence modeling for large eddy simulation of incompressible flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197: 173–201
Behr M, Hastreiter D, Mittal S, Tezduyar TE (1995) Incompressible flow past a circular cylinder: dependence of the computed flow field on the location of the lateral boundaries. Methods Appl Mech Eng 123: 309–316
Hauke G, Hughes TJR (1998) A comparative study of different sets of variables for solving compressible and incompressible flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 153: 1–44
Mittal S, Tezduyar TE (1992) A finite element study of incompressible flows past oscillating cylinders and airfoils. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 15: 1073–1118
Wall WA, Ramm E (1998) Fluid–Structure interaction based upon a stabilized (ALE) finite element method. In: Idelsohn S, Oñate E, Dvorkin E (eds) Computational mechanics—new trends and applications (Proceedings of WCCM IV), CIMNE, Barcelona
Kalro V, Tezduyar TE (1997) Parallel 3D computation of unsteady flows around circular cylinders. Parallel Comput. 23: 1235–1248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calderer, R., Masud, A. A multiscale stabilized ALE formulation for incompressible flows with moving boundaries. Comput Mech 46, 185–197 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0487-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0487-z