Abstract
Background
This study investigated the feasibility of endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy (ERAT) for the treatment of acute appendicitis.
Methods
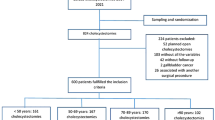
There were 210 patients included who were admitted to our hospital from January 2017 to October 2019 with a diagnosis of acute appendicitis. According to the method of treatment, patients were stratified into the ERAT group, laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) group, or open appendectomy (OA) group for comparison of perioperative information extracted from the medical records of the patients.
Results
The operations were successfully completed in all patients. The length of operation in the ERAT group (median: 48 min, range: 34–78 min) was significantly shorter compared to the LA group (median: 67 min, range: 47–90 min) or OA group (median: 85 min, range: 58–120 min). Postoperatively, the length of the hospital stay, the amount of time spent bedridden following surgery, surgery-related complications, and in-patient expenses were all significantly less than those in both the LA and OA groups (all p < 0.05). Moreover, the recurrence rate of appendicitis after ERAT was 2.86% during the first six months of postoperative follow-up. Thirteen patients in the ERAT group were diagnosed with appendicular abscesses, all of which successfully proceeded by colonoscopically incising the most protruding or fluctuating place around the appendix opening without procedure-related complications during the follow-up period.
Conclusion
ERAT is a safe and effective endoscopic treatment method for acute appendicitis and abscesses of the appendix. The advantages include reduced trauma, faster recovery times, and lower costs in comparison with either OA or LA procedures. ERAT with internal incision and drainage can be safely performed with immediate effect, especially in patients with acute uncomplicated appendicitis accompanied by either fecal stones or stenosis of the appendix cavity, or an abscess within the appendix cavity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addiss DG, Shaffer N, Fowler BS, Tauxe RV (1990) The epidemiology of appendicitis and appendectomy in the United States. Am J Epidemiol 132(5):910–925
McBurney C IV (1894) The incision made in the abdominal wall in cases of appendicitis, with a description of a new method of operating. Ann Surg 20(1):38–43
Halim I, Tavakkolizadeh A (2008) NOTES: the next surgical revolution. Int J Surg 6(4):273–276
Ruffolo C, Fiorot A, Pagura G et al (2013) Acute appendicitis: what is the gold standard of treatment. World J Gastroenterol 19(47):8799–8807
Liu BR, Song JT, Han FY, Li H, Yin JB (2012) Endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy: a pilot minimally invasive technique (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 76(4):862–866
Liu BR, Ma X, Feng J et al (2015) Endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy (ERAT): a multicenter retrospective study in China. Surg Endosc 29(4):905–909
Li Y, Mi C, Li W, She J (2016) Diagnosis of acute appendicitis by endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy (ERAT): combination of colonoscopy and endoscopic retrograde appendicography. Dig Dis Sci 61(11):3285–3291
de Oliveira Machado SL, Bagatini MD, da Costa P et al (2016) Evaluation of mediators of oxidative stress and inflammation in patients with acute appendicitis. Biomarkers 21(6):530–537
Rong HM (2017) Retrospective analysis of surgical diagnosis and treatment of patients with abscess around the appendix. World’s Latest Med Inform Digest 17(25):24–25
Podda M, Gerardi C, Cillara N et al (2019) Antibiotic treatment and appendectomy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults and children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 270(6):1028–1040
Sallinen V, Akl EA, You JJ et al (2016) Meta-analysis of antibiotics versus appendicectomy for non-perforated acute appendicitis. Br J Surg 103(6):656–667
Huston JM, Kao LS, Chang PK et al (2017) Antibiotics vs. appendectomy for acute uncomplicated appendicitis in adults: review of the evidence and future directions. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 18(5):527–535
Salminen P, Tuominen R, Paajanen H et al (2018) Five-year follow-up of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in the APPAC randomized clinical trial. JAMA 320(12):1259–1265
Acknowledgements
Thanks to professor Yunming Li for his guidance on data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Drs. Wenjuan Ding, Zhiqiang Du, and Xiongrong Zhou have no conficts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, W., Du, Z. & Zhou, X. Endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy for management of acute appendicitis. Surg Endosc 36, 2480–2487 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08533-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08533-8