Abstract
Background
The use of laparoscopic and robotic procedures has increased in general surgery. Minimally invasive robotic surgery has made tremendous progress in a relatively short period of time, realizing improvements for both the patient and surgeon. This has led to an increase in the use and development of robotic devices and platforms for general surgery. The purpose of this review is to explore current and emerging surgical robotic technologies in a growing and dynamic environment of research and development.
Methods
This review explores medical and surgical robotic endoscopic surgery and peripheral technologies currently available or in development. The devices discussed here are specific to general surgery, including laparoscopy, colonoscopy, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, and thoracoscopy. Benefits and limitations of each technology were identified and applicable future directions were described.
Results
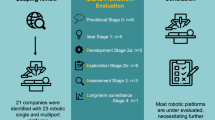
A number of FDA-approved devices and platforms for robotic surgery were reviewed, including the da Vinci Surgical System, Sensei X Robotic Catheter System, FreeHand 1.2, invendoscopy E200 system, Flex® Robotic System, Senhance, ARES, the Single-Port Instrument Delivery Extended Research (SPIDER), and the NeoGuide Colonoscope. Additionally, platforms were reviewed which have not yet obtained FDA approval including MiroSurge, ViaCath System, SPORT™ Surgical System, SurgiBot, Versius Robotic System, Master and Slave Transluminal Endoscopic Robot, Verb Surgical, Miniature In Vivo Robot, and the Einstein Surgical Robot.
Conclusions
The use and demand for robotic medical and surgical platforms is increasing and new technologies are continually being developed. New technologies are increasingly implemented to improve on the capabilities of previously established systems. Future studies are needed to further evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each robotic surgical device and platform in the operating suite.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar A, Yadav N, Singh S, Chauhan N (2016) Minimally invasive (endoscopic-computer assisted) surgery: technique and review. Ann Maxillofac Surg 6:159
Walker AS, Steele SR (2016) The future of robotic instruments in colon and rectal surgery, vol 27. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 144–149
Oleynikov D (2008) Robotic surgery. Surg Clin North Am 88:1121–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2008.05.012
Rassweiler JJ, Teber D (2016) Advances in laparoscopic surgery in urology. Nat Rev Urol 13:387–399. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2016.70
Simorov A, Otte RS, Kopietz CM, Oleynikov D (2012) Review of surgical robotics user interface: what is the best way to control robotic surgery? Surg Endosc 26:2117–2125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2182-y
DACH Medical Group—English (2017). https://www.dach-medical-group.com/en. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Rivera-Serrano CM, Johnson P, Zubiate B, Kuenzler R, Choset H, Zenati M, Tully S, Duvvuri U (2012) A transoral highly flexible robot. Laryngoscope 122:1067–1071
World’s First Use of Miniaturized Robot in Human Surgery—Virtual Incision Corporation (2017). https://www.virtualincision.com/fim-surgery/. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
van den Bedem LJM (2010) Realization of a demonstrator slave for robotic minimally invasive surgery. Doctoral degree 22-09-2010; Department of Mechanical Engineering; Supervisors: M. Steinbuch and I.A.M.J. Broeders; Co-promotor: P.C.J.N. Rosielle; Eindhoven: Technische Universiteit Eindhoven. https://doi.org/10.6100/IR684835
Hanly EJ, Talamini MA (2004) Robotic abdominal surgery. Am J Surg 188:19–26
Armijo PR, Pagkratis S, Boilesen E, Tanner T, Oleynikov D (2017) Growth in robotic-assisted procedures is from conversion of laparoscopic procedures and not from open surgeons’ conversion: a study of trends and costs. Surg Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5908-z
Tsui C, Klein R, Garabrant M (2013) Minimally invasive surgery: national trends in adoption and future directions for hospital strategy. Surg Endosc 27:2253–2257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2973-9
Alli VV, Yang J, Xu J, Bates AT, Pryor AD, Talamini MA, Telem DA (2017) Nineteen-year trends in incidence and indications for laparoscopic cholecystectomy: the NY State experience. Surg Endosc 31:1651–1658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5154-9
Rodriguez-Sanjuan JC, Gomez-Ruiz M, Trugeda-Carrera S, Manuel-Palazuelos C, Lopez-Useros A, Gomez-Fleitas M (2016) Laparoscopic and robot-assisted laparoscopic digestive surgery: present and future directions. World J Gastroenterol 22:1975–2004. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1975
Ghezzi TL, Corleta OC (2016) 30 Years of robotic surgery. World J Surg 40(10):1–8
Higgins RM, Frelich MJ, Bosler ME, Gould JC (2017) Cost analysis of robotic versus laparoscopic general surgery procedures. Surg Endosc 31:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4954-2
Beasly RA (2012) Medical robots: current systems and research directions. J Robot 2012:1–14
Al-Ahmad A, Grossman JD, Wang PJ (2005) Early experience with a computerized robotically controlled catheter system. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 12:199–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-005-0325-y
Hansen Medical (2017). http://www.hansenmedical.com/us/en/why-robotics. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Rafii-Tari H, Payne CJ, Yang GZ (2014) Current and emerging robot-assisted endovascular catheterization technologies: a review. Ann Biomed Eng 42:697–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0946-8
Russo AD, Fassini G, Conti S, Casella M, Di Monaco A, Russo E, Riva S, Moltrasio M, Tundo F, De Martino G (2016) Analysis of catheter contact force during atrial fibrillation ablation using the robotic navigation system: results from a randomized study. J Interv Cardiac Electrophysiol 46:97–103
Hlivák P, Mlčochová H, Peichl P, ČIHÁK R, Wichterle D, Kautzner J (2011) Robotic navigation in catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: midterm efficacy and predictors of postablation arrhythmia recurrences. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 22:534–540
Datino T, Arenal A, Pelliza M, Hernandez-Hernandez J, Atienza F, Gonzalez-Torrecilla E, Avila P, Bravo L, Fernandez-Aviles F (2014) Comparison of the safety and feasibility of arrhythmia ablation using the Amigo Robotic Remote Catheter System versus manual ablation. Am J Cardiol 113:827–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.11.030
Stolzenburg JU, Franz T, Kallidonis P, Minh D, Dietel A, Hicks J, Nicolaus M, Al-Aown A, Liatsikos E (2011) Comparison of the FreeHand(R) robotic camera holder with human assistants during endoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 107:970–974. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09656.x
Sbaih M, Arulampalam TH, Motson RW (2016) Rate of skill acquisition in the use of a robotic laparoscope holder (FreeHand®). Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 25:196–202
Tran H (2011) Robotic single-port hernia surgery. JSLS 15:309–314. https://doi.org/10.4293/108680811X13125733356198
Groth S, Rex DK, Rosch T, Hoepffner N (2011) High cecal intubation rates with a new computer-assisted colonoscope: a feasibility study. Am J Gastroenterol 106:1075–1080. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2011.52
Kurniawan N, Keuchel M (2017) Flexible gastro-intestinal endoscopy—clinical challenges and technical achievements. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 15:168–179
Sterile single-use endoscopy; invendo medical GmbH (2017). http://www.invendo-medical.com/. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Remacle M, Prasad V, Lawson G, Plisson L, Bachy V, Van der Vorst S (2015) Transoral robotic surgery (TORS) with the Medrobotics Flex™ System: first surgical application on humans. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272:1451–1455
Schuler PJ, Duvvuri U, Friedrich DT, Rotter N, Scheithauer MO, Hoffmann TK (2015) First use of a computer-assisted operator-controlled flexible endoscope for transoral surgery. Laryngoscope 125:645–648
Funk E, Goldenberg D, Goyal N (2017) Demonstration of transoral robotic supraglottic laryngectomy and total laryngectomy in cadaveric specimens using the Medrobotics Flex System. Head Neck 39(6):1218–1225
Johnson PJ, Serrano CMR, Castro M, Kuenzler R, Choset H, Tully S, Duvvuri U (2013) Demonstration of transoral surgery in cadaveric specimens with the medrobotics flex system. Laryngoscope 123:1168–1172
Mattheis S, Hasskamp P, Holtmann L, Schafer C, Geisthoff U, Dominas N, Lang S (2017) Flex robotic system in transoral robotic surgery: the first 40 patients. Head Neck 39:471–475. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.24611
Fanfani F, Monterossi G, Fagotti A, Rossitto C, Alletti SG, Costantini B, Gallotta V, Selvaggi L, Restaino S, Scambia G (2016) The new robotic TELELAP ALF-X in gynecological surgery: single-center experience. Surg Endosc 30:215–221
Fanfani F, Restaino S, Rossitto C, Alletti SG, Costantini B, Monterossi G, Cappuccio S, Perrone E, Scambia G (2016) Total laparoscopic (S-LPS) versus TELELAP ALF-X robotic-assisted hysterectomy: a case-control study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol 23:933–938
Rassweiler JJ, Autorino R, Klein J, Mottrie A, Goezen AS, Stolzenburg J, Rha KH, Schurr M, Kaouk J, Patel V (2017) Future of robotic surgery in urology. BJU Int 120(6):822–841
Stark M, Pomati S, D’Ambrosio A, Giraudi F, Gidaro S (2015) A new telesurgical platform–preliminary clinical results. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 24:31–36
Spinelli A, David G, Gidaro S, Carvello M, Sacchi M, Montorsi M, Montroni I (2017) First experience in colorectal surgery with a new robotic platform with haptic feedback. Colorectal Dis. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.13882
Miller NS (2017) Florida Hospital 1st in nation to use new robotic surgery system. Orlando Sentinel. http://www.orlandosentinel.com/health/os-florida-hospital-TransEnterix-robotic-surgery-20171114-story.html. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Auris Surgical Robotics (2017) Auris indications for use statement and 510 k summary bronchscopy v4 052616 ra. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf15/k152319.pdf. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Romo E, Bogusky J (2014) Auris Surgical Robotics Inc. Endoscopic device with helical lumen design. US Patent 20,150,164,594
Harris M (2016) First surgical robot from secretive startup Auris cleared for use. IEEE Spectr. https://spectrum.ieee.org/the-human-os/biomedical/devices/first-surgical-robot-from-secretive-startup-auris-cleared-for-use. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Eickhoff A, van Dam J, Jakobs R, Kudis V, Hartmann D, Damian U, Weickert U, Schilling D, Riemann JF (2007) Computer-assisted colonoscopy (the NeoGuide Endoscopy System): results of the first human clinical trial (“PACE study”). Am J Gastroenterol 102:261–266
Gudeloglu A, Brahmbhatt J, Parekattil S (2014) Robotic microsurgery in male infertility and urology—taking robotics to the next level. Transl Androl Urol 3:102
Prendergast JM, Rentschler ME (2016) Towards autonomous motion control in minimally invasive robotic surgery. Expert Rev Med Devices 13:741–748
Henry B, Novarro G, Santo G (2017) Peering Behind The Veil of Secrecy In Surgical Robotics & 2016 Market Outlook
Hagn U, Konietschke R, Tobergte A, Nickl M, Jörg S, Kübler B, Passig G, Gröger M, Fröhlich F, Seibold U (2010) DLR MiroSurge: a versatile system for research in endoscopic telesurgery. Int J Comp Assist Radiol Surg 5:183–193
Konietschke R, Hagn U, Nickl M, Jorg S, Tobergte A, Passig G, Seibold U, Le-Tien L, Kubler B, Groger M, Frohlich F, Rink C, Albu-Schaffer A, Grebenstein M, Ortmaier T, Hirzinger G (2009) The DLR MiroSurge—A robotic system for surgery. Robotics and Automation, 2009 ICRA ‘09 IEEE International Conference on 1589–1590. https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2009.5152361
Tobergte A, Helmer P, Hagn U, Rouiller P, Thielmann S, Grange S, Albu-Schaffer A, Conti F, Hirzinger G (2011) The sigma.7 haptic interface for MiroSurge: a bi-manual surgical console, pp 3023–3029
Klibansky D, Rothstein RI (2012) Robotics in endoscopy. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 28:477–482. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0b013e328356ac5e
Yeung BP, Gourlay T (2012) A technical review of flexible endoscopic multitasking platforms. Int J Surg 10:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2012.05.009
ViaCath diagnostic catheters (2016). https://www.biotronik.com/sixcms/media.php/136/ViaCath_EN.pdf. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
SPORT™ Surgical System (2017) Titan Medical Inc. http://www.titanmedicalinc.com/product/. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
SurgiBot (2017) http://www.transenterix.com/SurgiBot
Haskins O (2015) TransEnterix completes SurgiBot pre-clinical FDA work Bariatric News. http://www.bariatricnews.net/?q=node/1856. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Pryor AD, Tushar JR, DiBernardo LR (2010) Single-port cholecystectomy with the TransEnterix SPIDER: simple and safe. Surg Endosc 24:917–923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0695-9
Haber G, Autorino R, Laydner H, Yang B, White MA, Hillyer S, Altunrende F, Khanna R, Spana G, Wahib I (2012) SPIDER surgical system for urologic procedures with laparoendoscopic single-site surgery: from initial laboratory experience to first clinical application. Eur Urol 61:415–422
Thibault M (2016) Finally, details on Medtronic’s robotics platform. Medical Device Business. http://www.mddionline.com/blog/devicetalk/finally-details-medtronics-robotics-platform-06-08-16. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
CMR reveals versus robotic surgery system. (2016)
Kume K (2016) Flexible robotic endoscopy: current and original devices. Comp Assisted Surg 21:150–159
Lomanto D, Wijerathne S, Ho LKY, Phee LSJ (2015) Flexible endoscopic robot. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 24:37–44
Verb surgical delivers digital surgery prototype demonstration to collaboration partners (2017). http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/verb-surgical-delivers-digital-surgery-prototype-demonstration-to-collaboration-partners-300397192.html. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Simonite T (2016) The recipe for the perfect robot surgeon. https://www.technologyreview.com/s/602595/the-recipe-for-the-perfect-robot-surgeon/. MIT Technology Review 2017. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Here’s the Latest from Verb Surgical|MDDI Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry News Products and Suppliers (2017). http://www.mddionline.com/blog/devicetalk/heres-latest-verb-surgical-10-03-16. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Khateeb OM (2016) Democratizing Surgery Part 1: What Verb surgical is creating. Robotics Buisness Review. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/democratizing-surgery-how-verb-surgical-invented-new-category. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Wortman TD (2011) Design, analysis, and testing of in vivo surgical robots. Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Nebraska—Lincoln. http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/mechengdiss/28. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Rentschler ME, Oleynikov D (2007) Recent in vivo surgical robot and mechanism developments. Surg Endosc 21:1477–1481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9338-1
Feussner H (2017) Surgery 4.0. In: Thuemmler C, Bai C (eds) Health 4.0: How Virtualization and Big Data are Revolutionizing healthcare. Springer, Cham, pp 91–107
Berci G, Forde K (2000) History of endoscopy. Surg Endosc 14:5–15
McMurray J, Strudwick G, Forchuk C, Morse A, Lachance J, Baskaran A, Allison L, Booth R (2017) The importance of trust in the adoption and use of intelligent assistive technology by older adults to support aging in place: scoping review protocol. JMIR Res Protoc 6:e218. https://doi.org/10.2196/resprot.8772
Yan A (2017) How a robot passed China’s medical licensing exam: Machine shows capacity to learn, reason and make judgments but is not quite ready to go into solo practice, developers say. South China Morning Post. http://www.scmp.com/news/china/society/article/2120724/how-robot-passed-chinas-medical-licensing-exam. Accessed 20 Dec 2017
Moukarzel LA, Fader AN, Tanner EJ (2017) Feasibility of robotic-assisted laparoendoscopic single-site surgery in the gynecologic oncology setting. J Minim Invasive Gynecol 24:258–263
Tsukamoto S, Nishizawa Y, Ochiai H, Tsukada Y, Sasaki T, Shida D, Ito M, Kanemitsu Y (2017) Surgical outcomes of robot-assisted rectal cancer surgery using the da Vinci Surgical System: a multi-center pilot Phase II study. Jpn J Clin Oncol:1–6, https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyx141
Galvez D, Sorber R, Javed AA, He J (2017) Technical considerations for the fully robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Vis Surg 3:81. https://doi.org/10.21037/jovs.2017.05.08
Randell R, Honey S, Hindmarsh J, Alvarado N, Greenhalgh J, Pearman A, Long A, Cope A, Gill A, Gardner P, Kotze A, Wilkinson D, Jayne D, Croft J, Dowding D (2017) https://doi.org/10.3310/hsdr05200
Ozyurtkan MO, Kaba E, Toker A (2017) What happens while learning robotic lobectomy for lung cancer? J Vis Surg 3:27. https://doi.org/10.21037/jovs.2017.02.02
Criss CN, Gadepalli SK (2017) Sponsoring surgeons; an investigation on the influence of the da Vinci robot. Am J Surg, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2017.08.017
Jeong IG, Khandwala YS, Kim JH, Han DH, Li S, Wang Y, Chang SL, Chung BI (2017) Association of robotic-assisted vs laparoscopic radical nephrectomy with perioperative outcomes and health Care costs, 2003 to 2015. JAMA 318:1561–1568. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.14586
Vasudevan V, Reusche R, Wallace H, Kaza S (2016) Clinical outcomes and cost–benefit analysis comparing laparoscopic and robotic colorectal surgeries. Surg Endosc 30:5490–5493
Waite KE, Herman MA, Doyle PJ (2016) Comparison of robotic versus laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) inguinal hernia repair. J Robot Surg 10:239–244
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial and material support of the Center for Advanced Surgical Technology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Dr. Dmitry Oleynikov has an equity interest in the company, Virtual Incision. Songita a. Choudhury, Priscila R. Armijo, Crystal Krause, and Brian S. Peters have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, B.S., Armijo, P.R., Krause, C. et al. Review of emerging surgical robotic technology. Surg Endosc 32, 1636–1655 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6079-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6079-2