Abstract
Background
There is very scant literature on the impact of inguinal hernia mesh repair on testicular functions and sexual functions following open and laparoscopic repair. The present randomized study compares TAPP and TEP repairs in terms of testicular functions, sexual functions, quality of life and chronic groin pain.
Methods
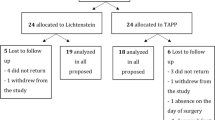
This study was conducted from April 2012 to October 2014. A total of 160 patients with uncomplicated groin hernia were randomized to either trans-abdominal pre-peritoneal (TAPP) repair or totally extra-peritoneal (TEP) repair. Testicular functions were assessed by measuring testicular volume, testicular hormone levels preoperatively and at 3 months postoperatively. Sexual functions were assessed using BMSFI, and quality of life was assessed using WHO-QOL BREF scale preoperatively and at 3 and 6 months postoperatively. Chronic groin pain was evaluated using the VAS scale at 3 months, 6 months and at 1 year.
Results
The median duration of follow-up was 13 months (range 6–18 months). The mean preoperative pain scores (p value 0.35) as well as the chronic groin pain were similar between TEP and TAPP repairs at 3 months (p value 0.06) and 6 months (p value 0.86). The testicular resistive index and testicular volume did not show any significant change at follow-up of 3 months (p value 0.9) in the study population. No significant difference was observed in testicular resistive index and testicular volume when comparing TEP and TAPP groups at at follow-up of 3 months (p value >0.05). There was a statistically significant improvement in the sexual drive score, erectile function and overall satisfaction over the follow-up period following laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. However, sexual function improvement was similar in patients undergoing both TEP and TAPP repairs. All the domains of quality of life in the study population showed a significant improvement at a follow-up of 3 and 6 months. Subgroup analysis of all the domains of quality of life in both TAPP and TEP groups showed a similar increment as in the study population (p value <0.001); however, the mean scores of all the domains were comparable between the two subgroups (p value >0.05), preoperatively and 3 and 6 months follow-up.
Conclusions
Laparoscopic groin hernia repair improves the testicular functions, sexual functions and quality of life, but TEP and TAPP repairs are comparable in terms of these long-term outcomes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gass M, Banz V, Rosella L, Adamina M, Candinas D, Guller U (2012) TAPP or TEP? Population-based analysis of prospective data on 4,552 patients undergoing endoscopic inguinal hernia repair. World J Surg 36:2782–2786
Neumayer L, Hurdcr AG, Jonasson O, Fitzgibbons R, Dunlop D, Gibbs J, Reda D, Henderson W (2004) Open mesh vs laparoscopic mesh repair of inguinal hernia. N Engl J Med 350:1819–1827
Agnihotri K, Awasthi S, Chandra H, Singh U, Thakur S (2010) Validation of WHO QOL-BREF instrument in Indian adolescents. Indian J Pediatr 77:381–386
Myers E, Katherine M, Kavanagh D, Hurley M (2010) Laparoscopic (TEP) versus lichtenstein inguinal hernia repair: a comparison of quality-of-life outcomes. World J Surg 34:3059–3064
Tekatli H, Schouten N, van Dalen T, Burgmans I, Smakman N (2012) Mechanism, assessment, and incidence of male infertility after inguinal hernia surgery: a review of the preclinical and clinical literature. Am J Surg 204:503–509
Bittner R, Montgomery MA, Arregui E, Bansal V, Bingener J, Bisgaard T, Buhck H, Dudai M, Ferzli GS, Fitzgibbons RJ, Fortelny RH, Grimes KL, Klinge U, Koeckerling F, Kumar S, Kukleta J, Lomanto D, Misra MC, Morales-Conde S, Reinpold W, Rosenberg J, Singh K, Timoney M, Weyhe D, Chowbey P (2015) Update of guidelines on laparoscopic (TAPP) and endoscopic (TEP) treatment of inguinal hernia (International Endohernia Society). Surg Endosc 29:289–321
Melissa CS, Bun TA, Wing CK, Chung TY, Wai NE, Tat LH (2014) Randomized double-blinded prospective trial of fibrin sealant spray versus mechanical stapling in laparoscopic total extraperitoneal hernioplasty. Ann Surg 259:432–437
O’Reilly EA, Burke JP, Ronan O’Connell P (2012) A meta-analysis of surgical morbidity and recurrence after laparoscopic and open repair of primary unilateral inguinal hernia. Ann Surg 2012(255):846–853
Wang W-J, Chen J-Z, Fang Q, Li J-F, Jin P-F, Li Z-T (2013) Comparison of the effects of laparoscopic hernia repair and Lichtenstein tension-free hernia repair. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 23:301–305
Elster EA, Hale DA, Mannon RB (2005) Surgical transplant physical examination: correlation of renal resistance index and biopsy-proven chronic allograft nephropathy. J Am Coll Surg 200:552–556
Bignell M, Partridge G, Mahon D, Rhodes M (2012) Prospective randomized trial of laparoscopic (trans-abdominal pre-peritoneal-TAPP) versus open (mesh) repair for bilateral and recurrent inguinal hernia: incidence of chronic groin pain and impact on quality of life: results of 10-year follow-up. Hernia 16:635–640
Abbas AE, Abd Ellatif ME, Noaman N, Negm A, El-Morsy G, Amin M, Moatamed A (2012) Patient-perspective quality of life after laparoscopic and open hernia repair: a controlled randomized trial. Surg Endosc 26:2465–2470
Bright E, Reddy VM, Wallace D, Garcea G, Dennison AR (2010) The incidence and success of treatment for severe chronic groin pain after open, transabdominal preperitoneal, and totally extraperitoneal hernia repair. World J Surg 34:692–696
Zheng B, Nan W, Qiao Q (2014) Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing Lichtenstein and totally extraperitoneal laparoscopic hernioplasty in treatment of inguinal hernias. J Surg Res 192:409–420
Krishna A, Misra MC, Bansal VK, Kumar S, Rajeshwari S, Chabra A (2012) Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) versus totally extraperitoneal (TEP) approach—a prospective randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc 26:639–649
International Association for the Study of Pain (1986) Subcommittee on taxonomy. classification of chronic pain: description of chronic pain syndromes and definition of pain terms. Pain 3:S1–S226
Reid I, Devlin HE (1994) Testicular atrophy as a consequence of inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 81:91–93
Uzzo RG, Lemack GE, Morissey KP, Goldstein M (1999) The effect of mesh prosthesis on the spermatic cord structures: a preliminary report in a canine model. J Urol 161:1344–1349
Peiper C, Junge K, Klinge U, Strehlau E, Ottinger A, Schumpelick V (2006) Is there a risk of infertility after inguinal mesh repair? Experimental studies in the pig and the rabbit. Hernia 10:7–12
Akbulut G, Serteser M, Yücel A, Değirmenci B, Yilmaz S, Polat C, San O, Dilek ON (2013) Can laparoscopic hernia repair alter function and volume of testis? Randomized clinical trial. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 13:377–381
Ersin S, Aydin D, Makay O, Icoz G, Tamsel S, Sozbilen M, Killi R (2006) Is testicular perfusion influenced during laparoscopic inguinal hernia surgery? Surg Endosc 20:685–689
Singh AN, Bansal VK, Misra MC, Kumar S, Rajeshwari S, Kumar A, Sagar R, Kumar A (2012) Testicular functions, chronic groin pain, and quality of life after laparoscopic and open mesh repair of inguinal hernia: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc 2012(26):1304–1317
Štula I, Družijanić N, Sapunar A, Perko Z, Bošnjak N, Kraljević D (2014) Antisperm antibodies and testicular blood flow after inguinal hernia mesh repair. Surg Endosc 28:3413–3420
Bischoff JM, Linderoth G, Aasvang EK, Werner MU, Kehlet H (2012) Dysejaculation after laparoscopic inguinal herniorrhaphy: a nationwide questionnaire study. Surg Endosc 26:979–983
McCormack K, Wake BL (2005) Transabdominal pre-peritoneal (TAPP) versus totally extraperitoneal (TEP) laparoscopic techniques for inguinal hernia repair: a systematic review. Hernia 9:109–114
Bansal VK, Misra MC, Babu D, Victor J, Kumar S, Sagar R, Rajeshwari S, Krishna A, Rewari V (2013) A prospective, randomized comparison of long-term outcomes: chronic groin pain and quality of life following totally extraperitoneal (TEP) and transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. Surg Endosc 27:2373–2382
Bracale U, Melillo P, Pignata G, Di Salvo E, Rovani M, Merola G, Pecchia L (2012) Which is the best laparoscopic approach for inguinal hernia repair: TEP or TAPP? A systematic review of the literature with a network meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 26:3355–3366
Poobalan A, Bruce T, King PM, Chambers WA, Krukowski ZH, Smith WCS (2001) Chronic pain and quality of life following open inguinal hernia repair. BJS 88:1122–1126
Cunningham J, Temple WJ, Mitchell P (1996) Co-operative study: pain in the post repair patient. Ann Surg 224:598–602
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Virinder Kumar Bansal, Asuri Krishna, Pratik Manek, Subodh Kumar, Omprakash Prajapati, Rajeshwari Subramaniam, Anand Kumar, Atin Kumar, Rajesh Sagar, M. C. Misra have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, V.K., Krishna, A., Manek, P. et al. A prospective randomized comparison of testicular functions, sexual functions and quality of life following laparoscopic totally extra-peritoneal (TEP) and trans-abdominal pre-peritoneal (TAPP) inguinal hernia repairs. Surg Endosc 31, 1478–1486 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5142-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5142-0