Abstract
Background
Patients with single small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can be managed by surgical resection or radio frequency ablation (RFA), with similar recurrence and survival rates. Recently, minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has been introduced in liver surgery, and the advantage/drawback balance between surgery and RFA needs reassessment.
Methods
Patients with Child-Pugh class A or B cirrhosis, and with single 1–3 cm HCC, undergoing MIS (laparoscopic or robot-assisted) or RFA from July 1998 to December 2012 were compared.
Results
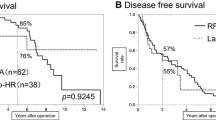
Overall, 45 patients underwent MIS, and 60 underwent RFA. Groups were not statistically different regarding type of underlying liver disease, HCC size, and AFP. However, RFA patients showed worse liver synthetic function with lower albumin and higher bilirubin serum levels, and higher ASA scores. Patients with HCC in segments 2–6 were more often treated by MIS. The incidence of complications was similar between groups (RFA: 6/60, 10 % vs. MIS: 5/45, 11 %, p = 0.854), and there was no measurable difference in the rate of procedure-related blood transfusions (RFA: 1/60, 1.7 % vs. MIS: 3/45, 6.7 %, p = 0.185). Local recurrence was only detected after RFA (11.7 %, p = 0.056, log-rank). Overall survival was higher in the MIS group (p = 0.042), with median survivals of 100 ± 13.5 versus 68 ± 15.9 months.
Conclusion
The present data need further validation. Selected patients with single ≤3-cm HCCs can be safely treated by MIS, without increased risk of perioperative complication, and with a lower risk of local recurrence. MIS should be especially favoured in patients with peripheral HCCs in segments 2–6, and/or when a histological assessment is desirable.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Llovet JM, Ducreux M, Lencioni R, Di Bisceglie AM, Galle PR, Dufour JF, Greten TF, Raymond E, Roskams T, De Baere T, Ducreux M, Mazzaferro V, Bernardi M, Bruix J, Colombo M, Zhu A (2012) EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 56(4):908–943
Wang Y, Luo Q, Li Y, Deng S, Wei S, Li X (2014) Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for small hepatocellular carcinomas: a meta-analysis of randomized and nonrandomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 9(1):e84484. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084484
Feng K, Yan J, Li X, Xia F, Ma K, Wang S, Bie P, Dong J (2012) A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 57(4):794–802. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.05.007
Cucchetti A, Piscaglia F, Cescon M, Colecchia A, Ercolani G, Bolondi L, Pinna AD (2013) Cost-effectiveness of hepatic resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 59(2):300–307. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.009
Weis S, Franke A, Mössner J, Jakobsen JC, Schoppmeyer K (2013) Radiofrequency (thermal) ablation versus no intervention or other interventions for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:CD003046. doi:10.1002/14651858
Huang G, Chen X, Lau WY, Shen F, Wang RY, Yuan SX, Geng WX, Zhou WP (2014) Quality of life after surgical resection compared with radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinomas. Br J Surg 101(8):1006–1015. doi:10.1002/bjs.9539
Yin Z, Fan X, Ye H, Yin D, Wang J (2013) Short- and long-term outcomes after laparoscopic and open hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 20(4):1203–1215. doi:10.1245/s10434-012-2705-8
Buchs NC, Oldani G, Orci LA, Majno PE, Mentha G, Morel P, Toso C (2013) Current status of robotic liver resection: a systematic review. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 14(2):237–246. doi:10.1586/14737140.2014.863155
Afaneh C, Kluger MD (2013) Laparoscopic liver resection: lessons at the end of the second decade. Semin Liver Dis 33(3):226–235. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1351780
Llovet JM, Ducreux M, Lencioni R, Di Bisceglie AM, Galle PR, Dufour JF, Greten TF, Raymond E, Roskams T, De Baere T, Ducreux M, Mazzaferro V, Bernardi M, Bruix J, Colombo M, Zhu A (2012) EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 56(4):908–943
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240(2):205–213
Cherqui D, Laurent A, Mocellin N, Tayar C, Luciani A, Van Nhieu JT, Decaens T, Hurtova M, Memeo R, Mallat A, Duvoux C (2009) Liver resection for transplantable hepatocellular carcinoma, long-term survival and role of secondary liver transplantation. Ann Surg 250:738–746
Bryant R, Laurent A, Tayar C, Cherqui D (2009) Laparoscopic liver resection—understanding its role in current practice :the Henri Mondor Hospital experience. Ann Surg 250:103–111
Salloum C, Subar D, Memeo R, Tayar C, Laurent A, Malek A, Azoulay D (2014) Laparoscopic robotic liver surgery: the Henri Mondor initial experience of 20 cases. J Robot Surg 8:119–124
N’Kontchou G, Aout M, Laurent A, Nahon P, Ganne-Carrié N, Grando V, Baghad I, Roulot D, Trinchet JC, Sellier N, Cherqui D, Vicaut E, Beaugrand M, Seror O (2012) Survival after radiofrequency ablation and salvage transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh A cirrhosis. J Hepatol 56(1):160–166
Terraz S, Constantin C, Majno PE, Spahr L, Mentha G, Becker CD (2007) Image-guided multipolar radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours: initial clinical results. Eur Radiol 17(9):2253–2261
Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Brace CL, Breen DJ, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, Chen MH, Choi BI, de Baère T, Dodd GD 3rd, Dupuy DE, Gervais DA, Gianfelice D, Gillams AR, Lee FT Jr, Leen E, Lencioni R, Littrup PJ, Livraghi T, Lu DS, McGahan JP, Meloni MF, Nikolic B, Pereira PL, Liang P, Rhim H, Rose SC, Salem R, Sofocleous CT, Solomon SB, Soulen MC, Tanaka M, Vogl TJ, Wood BJ, Goldberg SN, International Working Group on Image-Guided Tumor Ablation, Interventional Oncology Sans Frontières Expert Panel, Technology Assessment Committee of the Society of Interventional Radiology, Standard of Practice Committee of the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (2014) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria-a 10-year update. J Vasc Interv Radiol 25(11):1691–1705
Buell JF, Cherqui D, Geller DA, O’Rourke N, Iannitti D, Dagher I, Koffron AJ, Thomas M, Gayet B, Han HS, Wakabayashi G, Belli G, Kaneko H, Ker CG, Scatton O, Laurent A, Abdalla EK, Chaudhury P, Dutson E, Gamblin C, D’Angelica M, Nagorney D, Testa G, Labow D, Manas D, Poon RT, Nelson H, Martin R, Clary B, Pinson WC, Martinie J, Vauthey JN, Goldstein R, Roayaie S, Barlet D, Espat J, Abecassis M, Rees M, Fong Y, McMasters KM, Broelsch C, Busuttil R, Belghiti J, Strasberg S, Chari RS, World Consensus Conference on Laparoscopic Surgery (2009) The international position on laparoscopic liver surgery: the Louisville Statement, 2008. Ann Surg 250(5):825–830
Acknowledgments
Christian Toso was supported by a Professorship from the Swiss National Science Foundation (PP00P3_139021). The work was supported by the Artères Foundation.
Disclosures
Drs. Giulio C. Vitali, Alexis Laurent, Sylvain Terraz, Pietro Majno, Nicolas C. Buchs, Laura Rubbia-Brandt, Alain Luciani, Julien Calderaro, Philippe Morel, Daniel Azoulay, and Christian Toso have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vitali, G.C., Laurent, A., Terraz, S. et al. Minimally invasive surgery versus percutaneous radio frequency ablation for the treatment of single small (≤3 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: a case–control study. Surg Endosc 30, 2301–2307 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4295-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4295-6