Abstract
Background
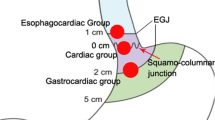
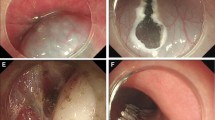
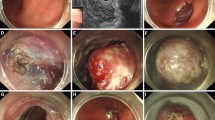
The esophagogastric junction (EGJ) is a difficult location for endoscopic resection due to its narrow lumen and sharp angle. Potential increased risks of perforation and mediastinal infection exist, especially for submucosal tumors (SMTs) originating from the muscularis propria (MP) layer. We previously demonstrated the safety and efficacy of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection (STER) for upper gastrointestinal SMTs, but the feasibility of STER for the removal of SMTs at the EGJ requires systematic investigation. The aim of the investigation was to evaluate the clinical impact of STER on the removal of SMTs at the EGJ.
Methods
A prospective study was carried out which included a consecutive cohort of 57 patients who underwent STER for 57 SMTs of the EGJ originating from the MP layer between July 2010 and August 2012 in a single academic medical center. Adverse events, en bloc resection rate, and local recurrence were evaluated.
Results
The average maximum diameter of the lesions was 21.5 mm (range 6–35 mm). The en bloc resection rate was 100 % (57/57). No delayed hemorrhage or severe adverse events occurred in any of the 57 patients following STER. No local recurrence and distant metastasis occurred during 24 months’ follow-up. Less subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum absorption time (p = 0.005) occurred with CO2 versus air insufflations.
Conclusions
Our study showed that STER was safe and effective, provided accurate histopathologic evaluation, and was curative for SMTs of the deep MP layers at the EGJ. CO2 gas insufflation is recommended.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ponsaing LG, Kiss K, Hansen MB (2007) Classification of submucosal tumors in the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol 13(24):3311–3315
Miettinen M, Sobin LH, Lasota J (2005) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the stomach: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 1,765 cases with long-term follow-up. Am J Surg Pathol 29(1):52–68
Miettinen M, Makhlouf H, Sobin LH, Lasota J (2006) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the jejunum and ileum: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 906 cases before imatinib with long-term follow-up. Am J Surg Pathol 30(4):477–489
Miettinen M, Lasota J (2001) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: definition, clinical, histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and differential diagnosis. Virchows Arch 438(1):1–12
Levy RM, Wizorek J, Shende M, Luketich JD (2010) Laparoscopic and thoracoscopic esophagectomy. Adv Surg 44:101–116
Kent M, d’Amato T, Nordman C, Schuchert M, Landreneau R, Alvelo-Rivera M et al (2007) Minimally invasive resection of benign esophageal tumors. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 134(1):176–181
Hirasawa K, Kokawa A, Oka H, Yahara S, Sasaki T, Nozawa A et al (2010) Superficial adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction: long-term results of endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc 72(5):960–966
Yoshinaga S, Gotoda T, Kusano C, Oda I, Nakamura K, Takayanagi R (2008) Clinical impact of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial adenocarcinoma located at the esophagogastric junction. Gastrointest Endosc 67(2):202–209
Lee IL, Lin PY, Tung SY, Shen CH, Wei KL, Wu CS (2006) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of intraluminal gastric subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer. Endoscopy 38(10):1024–1028
Xu MD, Cai MY, Zhou PH, Qin XY, Zhong YS, Chen WF et al (2012) Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection: a new technique for treating upper GI submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 75(1):195–199
Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, Sato Y, Kaga M, Suzuki M et al (2010) Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy 42(4):265–271
Stein HJ, Feith M, Siewert JR (2000) Cancer of the esophagogastric junction. Surg Oncol 9(1):35–41
Li QL, Yao LQ, Zhou PH, Xu MD, Chen SY, Zhong YS et al (2012) Submucosal tumors of the esophagogastric junction originating from the muscularis propria layer: a large study of endoscopic submucosal dissection (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 75(6):1153–1158
Li ZS, Li Q (2011) The latest 2010 WHO classification of tumors of digestive system. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 40(5):351–354 (in Chinese)
Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Antonescu CR, DeMatteo RP, Ganjoo KN, Maki RG et al (2007) NCCN Task Force report: update on the management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 8(Suppl 2):S1–s41 quiz S42-44
Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, Gorstein F, Lasota J, Longley BJ et al (2002) Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a consensus approach. Hum Pathol 33(5):459–465
Beham AW, Schaefer IM, Schuler P, Cameron S, Ghadimi BM (2012) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Int J Colorectal Dis 27(6):689–700
Gold JS, Gonen M, Gutierrez A, Broto JM, Garcia-del-Muro X, Smyrk TC et al (2009) Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram for recurrence-free survival after complete surgical resection of localised primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol 10(11):1045–1052
Gong W, Xiong Y, Zhi F, Liu S, Wang A, Jiang B (2012) Preliminary experience of endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors. Endoscopy 44(3):231–235
Chun SY, Kim KO, Park DS, Lee IJ, Park JW, Moon SH et al (2013) Endoscopic submucosal dissection as a treatment for gastric subepithelial tumors that originate from the muscularis propria layer: a preliminary analysis of appropriate indications. Surg Endosc 27(9):3271–3279
Shi Q, Zhong YS, Yao LQ, Zhou PH, Xu MD, Wang P (2012) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for treatment of esophageal submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer. Gastrointest Endosc 74(6):1194–1200
Catalano F, Rodella L, Lombardo F, Silano M, Tomezzoli A, Fuini A et al (2013) Endoscopic submucosal dissection in the treatment of gastric submucosal tumors: results from a retrospective cohort study. Gastric Cancer 16(4):563–570
Maeda Y, Hirasawa D, Fujita N, Obana T, Sugawara T, Ohira T et al (2012) A pilot study to assess mediastinal emphysema after esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection with carbon dioxide insufflation. Endoscopy 44(6):565–571
Dellon ES, Hawk JS, Grimm IS, Shaheen NJ (2009) The use of carbon dioxide for insufflation during GI endoscopy: a systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc 69(4):843–849
Higashiyama M, Oka S, Tanaka S, Sanomura Y, Imagawa H, Shishido T et al (2011) Risk factors for bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric epithelial neoplasm. Dig Endosc 23(4):290–295
Acknowledgment
This study was supported as a project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 1071046) and a major project of the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Committee (09DZ1950102, 11411950500, and 11DZ2280400), and Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2011211B30).
Disclosures
Xiao-Yun Wang, Li-Qing Yao, Ping-Hong Zhou, Douglas Pleskow, Quan-Lin Li, Yi-Qun Zhang, Wei-Feng Chen and Yun-Shi Zhong have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Video 1. Locating the tumor site to guide the direction of the submucosal tunnel (WMV 5130 kb)
Video 2. Creation of the submucosal tunnel to expose the tumor using the hybrid knife (WMV 9873 kb)
Video 3. Resection of the submucosal tumor under direct endoscopic view using the hook knife and insulated-tip knife (WMV 12568 kb)
Video 4. Closure of the mucosal incision site with the hemostatic clips (WMV 2318 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XY., Xu, MD., Yao, LQ. et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for submucosal tumors of the esophagogastric junction originating from the muscularis propria layer: a feasibility study (with videos). Surg Endosc 28, 1971–1977 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3420-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3420-2