Abstract
Background
This study aimed to assess the prognostic significance of endoluminal ultrasound-defined total length of disease and endoluminal ultrasound defined tumor volume (EDTV) in esophageal cancer. The hypothesis was that endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-defined total length of disease and EDTV are both significant prognostic indicators and better predictors of outcome than endoscopic tumor length.
Methods
In this study, 174 consecutive patients (median age, 64 years and 128 months) underwent specialist EUS, and the maximum potential EDTV was calculated (πr 2 L, where r is the tumor thickness and L is the total length of disease) including proximal and distal lymph node metastases. Of the 174 patients, 104 underwent surgery (70 had neoadjuvant chemotherapy), 60 underwent definitive chemoradiotherapy, and 10 had palliative therapy.
Results
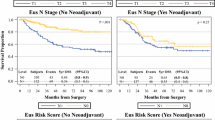
Survival was related to EUS T stage (p = 0.013), EUS N stage (p = 0.001), EUS M1a stage (p = 0.004), EUS disease length (<8 cm; p = 0.001), and EDTV (all patients <25 cm3, p = 0.001; surgical patients <40 cm3, p = 0.036). Forward conditional multivariate analysis showed three factors to be associated with survival: EUS N stage (hazard ratio [HR], 1.646; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.041–2.602; p = 0.033), EUS M1a stage (HR, 2.702; 95% CI, 1.069–6.830; p = 0.036), and EDTV (HR, 2.702; 95% CI, 1.069–6.830; p = 0.025). Median and 2-year survival for EDTV <25 cm3 versus >25 cm3 was 43.4 months and 56%, respectively, compared with 23.5 months and 35%.
Conclusions
In this study, EDTV based on total EUS-defined length of disease emerged as a new and important prognostic indicator for patients with esophageal cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly S, Harris KM, Berry E, Hutton J, Roderick P, Cullingworth J, Gathercole L, Smith MA (2001) A systematic review of the staging performance of endoscopic ultrasound in gastro-oesophageal carcinoma. Gut 49:534–539
Weaver SR, Blackshaw GR, Lewis WG, Edwards P, Roberts SA, Thomas GV, Allison MC (2004) Comparison of special interest computed tomography, endosonography, and histopathological stage of oesophageal cancer. Clin Radiol 59:499–504
Peters JH, Hoeft SF, Heimbucher J, Bremner RM, DeMeester TR, Bremner CG, Clark GW, Kiyabu M, Parisky Y (1994) Selection of patients for curative or palliative resection of esophageal cancer based on preoperative endoscopic ultrasonography. Arch Surg 129:534–539
Griffiths EA, Brummell Z, Gorthi G, Pritchard SA, Welch IM (2006) Tumor length as a prognostic factor in esophageal malignancy: univariate and multivariate survival analyses. J Surg Oncol 93:258–267
Mennigen R, Tuebergen D, Koehler G, Sauerland C, Senninger N, Bruewer M (2008) Endoscopic ultrasound with conventional probe and miniprobe in preoperative staging of esophageal cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 12:256–262
Ishikawa H, Sakurai H, Yamakawa M, Saito Y, Nakayama Y, Kitamoto Y, Okamoto M, Harada K, Hasegawa M, Nakano T (2005) Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with definitive radiation therapy alone. J Clin Gastroenterol 39:495–500
Morgan MA, Lewis WG, Casbard A, Roberts SA, Adams R, Clark G W, Havard TJ, Crosby TD (2008) Stage-for-stage comparison of definitive chemoradiation, surgery alone, and neoadjuvant chemotherapy for oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Surg (in Press)
Stahl M, Stuschke M, Lehmann N, Meyer HJ, Walz MK, Seeber S, Klump B, Budach W, Teichmann R, Schmitt M, Schmitt G, Franke C, Wilke H (2005) Chemoradiation with and without surgery in patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J Clin Oncol 23:2310–2317
Crosby TD, Brewster AE, Borley A, Perschky L, Kehagioglou P, Court J, Maughan TS (2004) Definitive chemoradiation in patients with inoperable oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Cancer 90:70–75
Bowrey DJ, Clark GW, Roberts SA, Maughan TS, Hawthorne AB, Williams GT, Carey PD (1999) Endosonographic staging of 100 consecutive patients with esophageal carcinoma: introduction of the 8-mm esophagoprobe. Dis Esophagus 12:258–263
Stephens MR, Lewis WG, Brewster AE, Lord I, Blackshaw GR, Hodzovic I, Thomas GV, Roberts SA, Crosby TD, Gent C, Allison MC, Shute K (2006) Multidisciplinary team management is associated with improved outcomes after surgery for esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus 19:164–171
Orringer MB (1984) Transhiatal esophagectomy without thoracotomy for carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg 200:282–288
Lewis I (1964) The surgical treatment of carcinoma of the oesophagus, with special reference to a new operation for growths of the middle third. Br J Surg 51:53–68
Tanner IC (1947) The present position of carcinoma of the oesophagus. Postgrad Med J 23:109–139
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 58:457–481
Landis JR, Kock GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc B 18:7–200
Eloubeidi MA, Desmond R, Arguedas MR, Reed CE, Wilcox CM (2002) Prognostic factors for the survival of patients with esophageal carcinoma in the U.S.: the importance of tumor length and lymph node status. Cancer 95:1434–1443
Rizk N, Venkatraman E, Park B, Flores R, Bains MS, Rusch V (2006) The prognostic importance of the number of involved lymph nodes in esophageal cancer: implications for revisions of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 132:1374–1381
Tachibana M, Yoshimura H, Kinugasa S, Dhar DK, Shibakita M, Ohno S, Ueda S, Fujii T, Nagasue N (2001) Clinicopathologic factors correlated with number of metastatic lymph nodes in oesophageal cancer. Dig Liver Dis 33:534–538
van Vliet EP, Heijenbrok-Kal MH, Hunink MG, Kuipers EJ, Siersema PD (2008) Staging investigations for oesophageal cancer: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer 98:547–557
Gheorghe C, Stanescu C, Gheorghe L, Bancila I, Herlea V, Becheanu G, Voinea D, Iacob R, Lupescu I, Anghel R, Croitoru A, Popescu I (2006) Preoperative noninvasive EUS evaluation in patients with esophageal cancer considered for esophagectomy. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 15:137–141
Moorjani N, Junemann-Ramirez M, Judd O, Fox B, Rahamim JS (2007) Endoscopic ultrasound in oesophageal carcinoma: comparison with multislice computed tomography and importance in the clinical decision-making process. Minerva Chir 62:217–223
Zhang X, Watson DI, Lally C, Bessell JR (2005) Endoscopic ultrasound for preoperative staging of esophageal carcinoma. Surg Endosc 19:1618–1621
Zuccaro G Jr, Rice TW, Vargo JJ, Goldblum JR, Rybicki LA, Dumot JA, Adelstein DJ, Trolli PA, Blackstone EH (2005) Endoscopic ultrasound errors in esophageal cancer. Am J Gastroenterol 100:601–606
Al-Sarira AA, David G, Willmott S, Slavin JP, Deakin M, Corless DJ (2007) Oesophagectomy practice and outcomes in England. Br J Surg 94:585–591
Medical Research Council Oesophageal Cancer Working Group (2002) Surgical resection with or without preoperative chemotherapy in oesophageal cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 359:1727–1733
Crehange G, Bosset M, Lorchel F, Buffet-Miny J, Dumas JL, Mercier M, Puyraveau M, Maingon P, Bosset JF (2006) Tumor volume as outcome determinant in patients treated with chemoradiation for locally advanced esophageal cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 29:583–587
Shinkai M, Niwa Y, Arisawa T, Ohmiya N, Goto H, Hayakawa T (2000) Evaluation of prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus by endoscopic ultrasonography. Gut 47:120–125
Bedenne L, Michel P, Bouche O, Milan C, Mariette C, Conroy T, Pezet D, Roullet B, Seitz JF, Herr JP, Paillot B, Arveux P, Bonnetain F, Binquet C (2007) Chemoradiation followed by surgery compared with chemoradiation alone in squamous cancer of the esophagus: FFCD 9102. J Clin Oncol 25:1160–1168
Lagarde SM, Reitsma JB, de Castro SM, Ten Kate FJ, Busch OR, van Lanschot JJ (2007) Prognostic nomogram for patients undergoing oesophagectomy for adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus or gastro-oesophageal junction. Br J Surg 94:1361–1368
Ruol A, Castoro C, Portale G, Cavallin F, Sileni VC, Cagol M, Alfieri R, Corti L, Boso C, Zaninotto G, Peracchia A, Ancona E (2009) Trends in management and prognosis for esophageal cancer surgery: twenty-five years of experience at a single institution. Arch Surg 144:247–254
Hayano K, Okazumi S, Shuto K, Matsubara H, Shimada H, Nabeya Y, Kazama T, Yanagawa N, Ochiai T (2007) Perfusion CT can predict the response to chemoradiation therapy and survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: initial clinical results. Oncol Rep 18:901–908
Mamede M, El FG, Abreu-e-Lima P, Gandler W, Nose V, Gerbaudo VH (2007) Preoperative estimation of esophageal tumor metabolic length in FDG-PET images with surgical pathology confirmation. Ann Nucl Med 21:553–562
Mamede M, Abreu-e-Lima P, Oliva MR, Nose V, Mamon H, Gerbaudo VH (2007) FDG-PET/CT tumor segmentation-derived indices of metabolic activity to assess response to neoadjuvant therapy and progression-free survival in esophageal cancer: correlation with histopathology results. Am J Clin Oncol 30:377–388
Guha C, Alfieri A, Blaufox MD, Kalnicki S (2008) Tumor biology-guided radiotherapy treatment planning: gross tumor volume versus functional tumor volume. Semin Nucl Med 38:105–113
Riddell AM, Allum WH, Thompson JN, Wotherspoon AC, Richardson C, Brown G (2007) The appearances of oesophageal carcinoma demonstrated on high-resolution, T2-weighted MRI, with histopathological correlation. Eur Radiol 17:391–399
Korst RJ, Rusch VW, Venkatraman E, Bains MS, Burt ME, Downey RJ, Ginsberg RJ (1998) Proposed revision of the staging classification for esophageal cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 115:660–669
Wijnhoven BP, Tran KT, Esterman A, Watson DI, Tilanus HW (2007) An evaluation of prognostic factors and tumor staging of resected carcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Surg 245:717–725
Greenstein AJ, Litle VR, Swanson SJ, Divino CM, Packer S, Wisnivesky JP (2008) Prognostic significance of the number of lymph node metastases in esophageal cancer. J Am Coll Surg 206:239–246
Hofstetter W, Correa AM, Bekele N, Ajani JA, Phan A, Komaki RR, Liao Z, Maru D, Wu TT, Mehran RJ, Rice DC, Roth JA, Vaporciyan AA, Walsh GL, Francis A, Blackmon S, Swisher SG (2007) Proposed modification of nodal status in AJCC esophageal cancer staging system. Ann Thorac Surg 84:365–373
Dhar DK, Hattori S, Tonomoto Y, Shimoda T, Kato H, Tachibana M, Matsuura K, Mitsumoto Y, Little AG, Nagasue N (2007) Appraisal of a revised lymph node classification system for esophageal squamous cell cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 83:1265–1272
Mariette C, Piessen G, Briez N, Triboulet JP (2008) The number of metastatic lymph nodes and the ratio between metastatic and examined lymph nodes are independent prognostic factors in esophageal cancer regardless of neoadjuvant chemoradiation or lymphadenectomy extent. Ann Surg 247:365–371
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mr. G. Clark and Mr. T. Havard, consultant general surgeons who treated patients in this study and kindly allowed access to their patients’ details.
Disclosure
Drs. Christopher P. Twine, S. Ashley Roberts, Wyn G. Lewis, B. Vicki Dave, Claire E. Rawlinson, David Chan, Mark Robinson, and Tom D. Crosby have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Twine, C.P., Ashley Roberts, S., Lewis, W.G. et al. Prognostic significance of endoluminal ultrasound-defined disease length and tumor volume (EDTV) for patients with the diagnosis of esophageal cancer. Surg Endosc 24, 870–878 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0681-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0681-2