Abstract
Background
Laparoscopic antireflux surgery (LARS) represents the gold standard in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease with or without hiatal hernia. It offers excellent long-term results and high patient satisfaction. Nevertheless, several studies have reported a high rate of intrathoracic wrap migration or paraesophageal hernia recurrence. To reduce the incidence of this complication, the use of prosthetic meshes has been advocated. This study retrospectively evaluated the long-term results of LARS with or without the use of a mesh in a series of patients treated from 1992 to 2007.
Methods
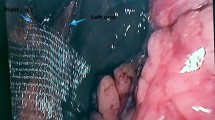
From November 1992 to May 2007, 297 patients underwent laparoscopic antireflux surgery in the authors’ department. Crural closure was performed by means of two or three interrupted nonabsorbable sutures for 93 patients (group A), by tailored 3 × 4-cm polypropylene mesh placement for 113 patients (group B), and by nonabsorbable suture plus superimposed tailored mesh for 91 patients (group C).
Results
The mean follow-up period for the entire group was 95.1 ± 38.7 months, specifically 95.2 ± 49 months for group A, 117.6 ± 18 months for group B, and 69.3 ±.17.6 months for group C. Intrathoracic Nissen wrap migration or hiatal hernia recurrence occurred for nine patients (9.6%) in group A, two patients (1.8%) in group B, and only one patient (1.1%) in group C. Esophageal erosion occurred in only one case (0.49%). Functional results and the long-term quality-of-life evaluation after surgery showed a significant and durable improvement with no significant differences related to the type of hiatoplasty.
Conclusion
Over a long-term follow-up period, the use of a prosthetic polypropylene mesh in the crura for hiatal hernia proved to be effective in reducing the rate of postoperative intrathoracic wrap migration or hernia recurrence, with a very low incidence of mesh-related complications.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dallemagne B, Weerts JM, Jehaes C et al (1991) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc 1:138–142
Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Schweiger UM, Pasiut M, Wykypiel H, Pointner R (2002) Surgical outcome and analysis of failure after 500 laparoscopic antireflux procedures. Surg Endosc 16:753–757
Granderath FA, Carlson MA, Champion JK, Basso N, Szold A, Frantzides CT (2006) Prosthetic closure of the esophageal hiatal hernia repair and laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Surg Endosc 20:367–379
Granderath FA, Schweiger UM, Kamolz T, Pointner R (2005) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in patients with nonerosive reflux disease. Surg Endosc 19:494–500
Granderath FA, Kamolz T (2002) Quality of life, surgical outcome, and patients’ satisfaction three years after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. World J Surg 26:1234–1238
Leeder PC, Smith G, Dehn TCB (2003) Laparoscopic management of large paraesophageal hiatal hernia. Surg Endosc 17:1372–1375
Taragona EM, Novell J, Vela S (2004) Midterm analysis of safety and quality of life after the laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal hiatal hernia. Surg Endosc 18:1045–1050
Carlson MA, Frantzides CT (2001) Complications and results of primary minimally invasive antireflux procedures: a review of 10,735 reported cases. J Am Coll Surg 193:428–437
Johnson JM, Carbonell AM, Carmody BJ, Jamal MK, Maher JW (2006) Laparoscopic mesh hiatoplasty for paraesophageal hernias and fundoplications: a critical analysis of the available literature. Surg Endosc 20:362–366
Keidar A, Szold A (2003) Laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal hernia with selective use of mesh. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 13:149–154
Hunter JG, Smith D, Branum GD, Waring JP, Thadeus LT (1999) Laparoscopic fundoplication failures: patterns of failure and response to fundoplication revision. Ann Surg 230:595–606
Granderath FA, Schweiger UM, Kamolz T, Pointner R (2002) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery with routine mesh-hiatoplasty in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Gastrointest Surg 6:347–353
Targarona EM, Bendaham G, Balague C, Garriga J, Trias M (2004) Mesh in the hiatus. Arch Surg 139:1286–1296
Frantzides CT, Madan AT, Carlson MA, Stavropoulos GP (2002) A prospective randomized trial of laparoscopic polytetrafluorethylene (PTFE) patch repair vs. simple cruroplasty for large hiatal hernia. Arch Surg 137:649–652
Hasemi M, Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Huprich JE (2000) Laparoscopic repair of large type iii hiatal hernia: objective follow-up reveals high recurrence rate. J Am Coll Surg 190:553–560
Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Bammer T, Pasiut M, Pointner R (2002) Dysphagia and quality of life after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in patients with and without prosthetic reinforcement of the hiatal crura. Surg Endosc 16:572–577
Granderath FA, Schweiger UM, Kamolz T, Pointner R (2005) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with prosthetic hiatal closure reduces postoperative intrathoracic wrap herniation. Arch Surg 140:40–48
Carlson MA, Richards CG, Frantzides CT (1999) Laparoscopic prosthetic reinforcement of hiatal herniorraphy. Dig Surg 16:407–410
Champion JK, Rock D (2003) Laparoscopic mesh cruroplasty for large paraesophageal hernias. Surg Endosc 17:551–553
Jansen M, Otto J, Anurov M, Titkova S (2007) Mesh migration into the esophageal wall after mesh hiatoplasty: comparison of two alloplastic materials. Surg Endosc 21:2298–2303
Tatum RP, Shalhub S, Pellegrini CA et al (2008) Complications of PTFE mesh at the diaphragmatic hiatus. J Gastrointest Surg 12:953–957
Dally E, Falk GL (2004) Teflon pledget reinforced fundoplication causes symptomatic gastric and esophageal lumenal penetration. Am J Surg 187:226–229
Baladas HG, Smith GS, Richardson MA et al (2000) Esophagogastric fistula secondary to teflon pledget: a rare complication following laparoscopic fundoplication. Dis Esophagus 13:72–74
Stadlhuber RJ, Sherif AE, Mittal SK et al (2008) Mesh complications after prosthetic reinforcement of hiatal closure: a 28 case series. Surg Endosc (online first). doi:10.1007/s00464-008-0205-5
Velanovich V (1998) Comparison of generic (SF-36) vs. disease-specific (GERD-HRQL) quality-of-life scales for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Gastrointest Surg 2:141–145
Eypasch E, Neugebauer E, Fischer F, Troidl H (1997) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): results of a Consensus Development Conference. Surg Endosc 11:413–426
Papasavas PK, Keenan W (2003) Effectiveness of laparoscopic fundoplication in relieving the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and eliminating antireflux medical therapy. Surg Endosc 17:1200–1205
Anvari M, Allen C (2003) Five-year comprehensive outcome evaluation in 181 patients after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Am Coll Surg 196:51–59
Ciovica R, Gadenstatter M (2006) Quality of life in GERD patients: medical treatment versus antireflux surgery. J Gastroint Surg 10:934–939
Parameswaran R, Ali A, Velmurugan S et al (2006) Laparoscopic repair of large paraesophageal hiatus hernia: quality of life and durability. Surg Endosc 20:1221–1224
Samir M, Bennet J (2006) Prospective trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication versus proton pump inhibitor therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease: seven years follow-up. J Gastrointest Surg 10:1312–1317
Cookson R, Flood C, Koo B et al (2005) Short-term cost effectiveness and long-term cost analysis comparing laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with proton pump inhibitor maintenance for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg 92:700–706
Lundell L, Miettinen P, Myrvold HE et al (2007) Seven-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial comparing proton pump inhibition with surgical therapy for reflux esophagitis. Br J Surg 94:198–203
Basso N, De Leo A, Genco A, Rosato P, Rea S, Spaziani E, Primavera A (2000) 360º Laparoscopic fundoplication with tension-free hiatoplasty in the treatment of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 14:164–169
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soricelli, E., Basso, N., Genco, A. et al. Long-term results of hiatal hernia mesh repair and antireflux laparoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc 23, 2499–2504 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0425-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0425-3