Abstract
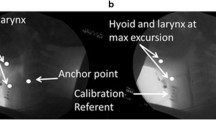
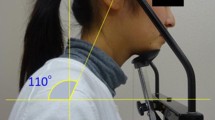
Vertical and anterior displacement of the hyoid bone is a critical biomechanical component of normal swallowing function. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the maximal vertical and anterior displacement of the hyoid bone during oropharyngeal swallowing. A retrospective review of video-fluoroscopic swallowing exams in 40 normal subjects varying by age and gender was performed. Means and standard deviations for both vertical and anterior displacement were analyzed on both 5-ml and 10-ml thin liquids using an ImageJ program. Age and gender differences were submitted to a repeated-measures one-way analysis of variance. There was a significant difference between younger and older subjects for anterior displacement of the hyoid bone during the swallow but not for vertical displacement. No significant differences between male and female subjects were observed. Anterior displacement of the hyoid bone decreased with increasing age. This reduction may be related to muscle weakness. However, older people may adapt to preserve airway protection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logemann JA, Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders. Austin, TX: Pro-ed, 1998.
Robbins JA, Hamilton JW, Lof GL, Kempster GB. Oropharyngeal swallowing in normal adults of different ages. Gastroenterology 1992;103:823–829.
Cook IJ, Dodds WJ, Dantas RO, Kern MK, Massey BT, Shaker R, Hogan WJ. Timing of videofluoroscopic, manometric events, and bolus transit timing during the oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Dysphagia 1998;4:8–15.
Jacob P, Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA, Shah V, Ha T. Upper esophageal sphincter opening and modulation during swallowing. Gastroenterology 1989;97(6):1469–1478.
Ishida R, Palmer JB, Hiemae KM. Hyoid motion during swallowing: factors affecting forward and upward displacement. Dysphagia 2002;17:262–272.
Dodds WJ, Man KM, Cook IJ, Kahrilas PJ, Stewart ET, Kern MK. Influence of bolus volume on swallow-induced hyoid movement in normal subjects. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;150(6):1307–1309, 2002.
Cook IJ, Dodds WJ, Dantas RO, Massey BT, Kern MK, Lang IM, Brasseur JG, Hogan WJ. Opening mechanisms of the human upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol 1989;257(20):G748–G759.
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Colangelo LA, Kahrilas PJ, Smith CH. Temporal and biomechanical characteristics of oropharyngel swallow in younger and older men. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2000;43(5):1264–1274.
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ. Oropharyngeal swallow in younger and older women: videofluoroscopic analysis. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2002;45(3):434–445.
Perlman AL, VanDaele DJ, Otterbacher MS. Quantitative assessment of hyoid bone displacement from video images during swallowing. J Speech Lang Hear Res 1995;38(3):579–585.
McCullough GH, Wertz RT, Rosenbek JC. Age, gender, size, consistency effects on swallowing function in adults between 21 and 99 years of age. Presented to the 10th Annual Meeting of Dysphagia Research Society, Albuquerque, NM, 2001.
Rasband W, ImageJ v1.36b, March 13, 2006. Available at http://www.rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/ [accessed September 1, 2006].
Pauloski BR, Logemann JA, Fox JC, Colangelo LA. Biomechanical analysis of the pharyngeal swallow in postsurgical patients with anterior tongue and floor of mouth resection and distal flap reconstruction. J Speech Lang Hear Res 1995;38:110–123.
Kim Y, McCullough GH, Asp CW. Temporal measurements of pharyngeal swallowing in normal populations. Dysphagia 2005;20:290–296.
Robbins JA, Levine R, Wood J, Roecker EB, Luschei E. Age effects on lingual pressure generation as a risk factor for dysphagia. J Gerontol 1995;50(5):M257–M262.
Campbell MJ, McComas AJ, Petito F. Physiological changes in aging muscles. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1973;36:151–154.
Price PA, Darvell BW. Force and mobility in the aging human tongue. Med J Aust 1981;1:75–78.
Welford AT. Between bodily changes and performance: some possible reasons for slowing with age. Exp Aging Res 1984;10:73–88.
McCullough GH, Rosenbek JC, Wertz RT, Suiter D, McCoy S. Defining swallowing function by age: Promises and pitfalls of pigeonholing. Top Ger Rehabil 2007;23(4):290–307.
Cho YS, Choi MG, Jeong JJ, Chung WC. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: a population-based study in Asan-si, Korea. Am J Gastroenterol 2005;100(4):747–753.
Locke GR, Talley NJ, Fett SL, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology 1997;112(5):1448–1456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y., McCullough, G.H. Maximum Hyoid Displacement in Normal Swallowing. Dysphagia 23, 274–279 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9135-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9135-y