Abstract
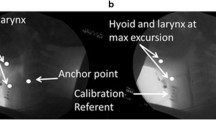
The aim of this study is to develop an index to assess swallowing function by ultrasonography to evaluate the relationship between movements of the hyoid bone and the larynx while swallowing water. Forty-two younger participants (mean age, 20.3 ± 3.4 years) and 42 older participants (mean age, 75.1 ± 10.6 years) with normal swallowing function were included in the study. Movements of the hyoid bone and the larynx while swallowing 5 mL of water were observed using ultrasonography. Two-dimensional distances from the starting points of the hyoid bone and the larynx to their points of maximum movement were measured as displacements. The hyoid bone–laryngeal motion ratio was defined as the hyoid bone displacement divided by the laryngeal displacement. Parameters were compared among four groups: younger male, younger female, older male, and older female. The hyoid bone displacement differed significantly between the younger and older groups, and the laryngeal displacement differed significantly between age groups and sexes. The hyoid bone–laryngeal motion ratio was not significantly correlated with age, height, or body weight, and did not show a significant difference between the four groups. Thus, the hyoid bone–laryngeal motion ratio is an index that evaluates swallowing movement and is independent of physique and physiological changes associated with aging.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Colangelo LA, Kahrilas PJ, Smith CH. Temporal and biomechanical characteristics of oropharyngeal swallow in younger and older men. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2000;43(5):1264–74.
Martino R, Pron G, Diamant N. Screening for oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke: insufficient evidence for guidelines. Dysphagia. 2000;15(1):19–30.
Ekberg O. The normal movements of the hyoid bone during swallow. Investig Radiol. 1986;22(1):92.
Bours GJ, Speyer R, Lemmens J, Limburg M, de Wit R. Bedside screening tests vs. videofluoroscopy or fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing to detect dysphagia in patients with neurological disorders: systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2009;65(3):477–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2008.04915.x.
Shanley C, O’Loughlin G. Dysphagia among nursing home residents: an assessment and management protocol. J Gerontol Nurs. 2000;26(8):35–48.
Sonies BC, Wang C, Sapper DJ. Evaluation of normal and abnormal hyoid bone movement during swallowing by use of ultrasound duplex-Doppler imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1996;22(9):1169–75.
Kuhl V, Eicke BM, Dieterich M, Urban PP. Sonographic analysis of laryngeal elevation during swallowing. J Neurol. 2003;250(3):333–7.
Yabunaka K, Sanada H, Sanada S, Konishi H, Hashimoto T, Yatake H, Yamamoto K, Katsuda T, Ohue M. Sonographic assessment of hyoid bone movement during swallowing: a study of normal adults with advancing age. Radiol Phys Technol. 2011;4(1):73–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-010-0107-9.
Hsiao MY, Chang YC, Chen WS, Chang HY, Wang TG. Application of ultrasonography in assessing oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38(9):1522–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2012.04.017.
Lee YS, Lee KE, Kang Y, Yi TI, Kim JS. Usefulness of submental ultrasonographic evaluation for dysphagia patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(2):197–205. https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.197.
Steele CM, Bailey GL, Chau T, Molfenter SM, Oshalla M, Waito AA, Zoratto DC. The relationship between hyoid and laryngeal displacement and swallowing impairment. Clin Otolaryngol. 2011;36(1):30–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-4486.2010.02219.x.
Chi-Fishman G, Sonies BC. Effects of systematic bolus viscosity and volume changes on hyoid movement kinematics. Dysphagia. 2002;17(4):278–87.
Chen Y-C, Hsiao M-Y, Wang Y-C, Fu C-P, Wang T-G. Reliability of ultrasonography in evaluating hyoid bone movement. J Med Ultrasound. 2017;25:90–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmu.2017.01.002.
Dodds WJ, Stewart ET, Logemann JA. Physiology and radiology of the normal oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990;154(5):953–63.
Okada T, Aoyagi Y, Inamoto Y, Saitoh E, Kagaya H, Shibata S, Ota K, Ueda K. Dynamic change in hyoid muscle length associated with trajectory of hyoid bone during swallowing: analysis using 320-row area detector computed tomography. J Appl Physiol. 2013;115(8):1138–45. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00467.2013.
Kim Y, McCullough GH. Maximum hyoid displacement in normal swallowing. Dysphagia. 2008;23(3):274–9.
Dantas RO, Kern MK, Massey BT, Dodds WJ, Kahrilas PJ, Brasseur JG, Cook IJ, Lang IM. Effect of swallowed bolus variables on oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Am J Physiol. 1990;258(5 Pt 1):G675–G681681.
Sundgren P, Maly P, Gullberg B. Elevation of the larynx on normal and abnormal cineradiogram. Br J Radiol. 1993;66(789):768–72.
Kahrilas PJ, Dodds WJ, Dent J, Logemann JA, Shaker R. Upper esophageal sphincter function during deglutition. Gastroenterology. 1988;95(1):52–62.
Leonard R, Kendall KA, McKenzie S. Structural displacements affecting pharyngeal constriction in nondysphagic elderly and nonelderly adults. Dysphagia. 2004;19(2):133–41.
Funding
This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) Grant Number JP17K18264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were performed in accordance with the Research Ethics Committee of Kansai University of Welfare Sciences (Approval number: 17-64) and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants for publication of this case report and accompanying images.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuo, T., Matsuyama, M., Nakatani, K. et al. Evaluation of swallowing movement using ultrasonography. Radiol Phys Technol 13, 62–68 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-019-00547-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-019-00547-1