Abstract
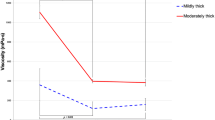
This study reports the viscosity (thickness) of nectar- and honey-thick liquids measured at a typical serving temperature. Centipoise (cP) measurements were compared for three products (two starch and one gum-based thickener) mixed with five beverages that set for three time intervals (manufacturer-recommended time to thicken, 10 min, and 30 min). The serving temperature of the cold beverages was 4°C (water, apple juice, orange juice, and milk), and the hot beverage (coffee) was measured at 70°C. Statistical analysis showed that all factors interacted with one another, meaning that the viscosity of a nectar- or honey-like liquid varies greatly depending on the type of thickening agent and beverage combination in relation to the amount of time it thickens. Simply Thick, the gum-based thickener, typically produced samples that were the least viscous but they maintained a more consistent level of thickness over time. Serving temperature results are contrasted with viscosity measurements collected at room temperature, showing variable thickening patterns especially related to the type of thickening agent.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia JM, Chambers E IV, Molander M: Thickened liquids: Practice patterns of speech-language pathologists. Am J Speech Lang Pathol 14:4–13, 2005
Colodny N: Construction and validation of the mealtime and dysphagia questionnaire: An instrument designed to assess nursing staff reasons for noncompliance with SLP dysphagia and feeding recommendations. Dysphagia 16:263–271, 2001
Mills RH: Rheology overview: Control of liquid viscosities in dysphagia management. Nutr Clin Pract 14:S52–S56, 1999
Steele CM, Van Lieshout PHHM, Goff DH: The rheology of liquids: A comparison of clinicians’ subjective impressions and objective measurement. Dysphagia 18:182–195, 2003
Garcia JM, Chambers E IV, Matta Z, Clark M: Viscosity measurements of nectar and honey-thick liquids: Product, liquid, & time comparisons. Dysphagia 20:325–335, 2005
Lotong V, Chun SS, Chambers E IV, Garcia JM: Texture and flavor characteristics of beverages containing commercial thickening agents for dysphagia diets. J Food Sci 68:1537–1521, 2003
Matta Z, Chambers E IV, Garcia JM, Helverson J: Sensory characteristics of six beverages prepared with commercial thickeners used for dysphagia diets. J Am Diet Assoc 106:1049–1054, 2006
Pelletier CA: A comparison of consistency and taste of five commercial thickeners. Dysphagia 12:74–78, 1997
Glassburn DL, Deem JF: Thickener viscosity in dysphagia management: Variability among speech-language pathologists. Dysphagia 13:218–222, 1998
Bourne M: Food texture and viscosity: Concept and measurement. San Diego: Academic Press, 2002
Rao A: Rheology of fluid and semisolid foods: Principles and applications. Aspen Publication, Gaithersburg, MD, 1999
Bourne M: Effect of temperature on firmness of raw fruits and vegetables. J Food Sci 47:440-444, 1982
Engelen L, de Wijk RA, Prinz JF, van der Bilt A, Janssen AM, Bosman F: The effect of oral temperature on the temperature perception of liquids and semisolids in the mouth. Eur J Oral Sci 110:412–416, 2002
Saravacos GD: Effect of temperature on viscosity of fruit juices and purees. J Food Sci 35:122–125, 1970
Saltmarsh M: Thirst: Or, why do people drink? Nutr Bull 26:53–58, 2001
Crary MA, Groher ME: Introduction to adult swallowing disorders. St. Louis: Butterworth Heinemann, 2003
Logemann JA: Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders, 2nd ed. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed, 1998
Triadafilopoulos G, Tsang HHP, Segall GM: Hot water swallows improve symptoms and accelerate esophageal clearance in esophageal motility disorders. J Clin Gastroenterol 26:239–244, 1998
Mills RH: Evaluation of dysphagia in adults: Expanding the diagnostic options. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed, 2000
National Dysphagia Task Force: National dysphagia diet: Standardization for optimal care. Chicago: American Dietetic Association, 2002
Steele CM, Van Lieshout PHHM: Influence of bolus consistency on lingual behaviors in sequential swallowing. Dysphagia 19:192–206, 2004
Cichero JAY, Jackson O, Halley PJ, Murdoch BE: How thick is thick? Multicenter study of the rheological and material property characteristics of mealtime fluids and videofluoroscopy fluids. Dysphagia 15:188–200, 2000
Kammer R, Baillies A, Gill G, Hind J, Hewitt A, Dunn J, Robbins J: Comparison of Commercial Thickeners for Achieving Diagnostic & Treatment Congruence. Poster session presented at the annual meeting of the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, San Diego, CA, 2005
Brown A: Understanding food: Principles and preparation 2nd ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth, 2004
Akoh CC: Fat replacers. Food Technol 52:47–53, 1998
American Society for Testing and Materials: Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 14.03, 1991
Anonymous: Agglomerated maltodextrin expands uses. Food Dev 15:14–15, 1981
Kuntz LA: Making the most of maltodextrins. Food Prod Design 7:89–104, 1997
Tuason DC Jr, McGinley EJ: Microcrystalline cellulose-based stabilizer system for dry mix instant chocolate drink. U.S. Patent 4980193, 1990
Schuricht H, Schierbaum F, Fleischer LG: The influence of high pressure on gel forming maltodextrins. I. Macro-structure, thermodynamic and fluid dynamic effects. Starch/Stärke 50:499–511, 1998
Hoefler AC: Hydrocolloids: Practical Guides for the Food Industry. St. Paul, MN: Eagan Press, 2004
Thomas DJ, Atwel WA: Starches: Practical Guides for the Food Industry. St. Paul, MN: Eagan Press, 1999
Jeremic K, Markov S, Pekic B, Jovanovic S: The influence of temperature and inorganic salts on the rheological properties of xanthan aqueous solutions. J Serbian Chem Soc 64:109–116, 1999
Liao HJ: Simulation of continuous sterilization of fluid food products: The role of thermorheological behavior of starch dispersion and process. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, 1998
Hamlet S, Choi J, Zormeier M, Shamsa F, Stachler R, Muz J, Jones L: Normal adult swallowing of liquid and viscous material: Scintigraphic data on bolus transit and oropharyngeal residues. Dysphagia 11:41–47, 1996
Cichero JAY: Viscosity testing: Opening pandora’s box. In: Perspectives on swallowing and swallowing disorders newsletter. Rockville, MD: American Speech-Language Hearing Association, 2006, Vol. 15, pp 2–8
Garcia JM, Chambers E IV, Clark M, Helverson J, Matta Z: Nectar & Honey-thick Beverages Prepared by Health Care Providers. Poster session presented at the annual meeting of the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, Miami, FL, 2006
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Kansas Health and Nutrition Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, J.M., Chambers, E., Matta, Z. et al. Serving Temperature Viscosity Measurements of Nectar- and Honey-Thick Liquids. Dysphagia 23, 65–75 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9098-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9098-z