Abstract
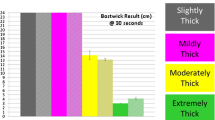
Texture-modified diets are commonly prescribed for patients with dysphagia; it is therefore important to demonstrate that clinicians form accurate impressions of the rheological (flow) properties of the items that they recommend for their clients. We explored the correlation between objective rheological measurement and clinicians’ subjective impressions of liquid consistency, rated on the bases of product labeling and sampling. Ten liquids, ranging from thin through nectar-thick and honey-thick to spoon-thick consistencies, were selected for study. Rheological analysis was conducted using a Carri-Med CSL Controlled Stress Rheometer. Fifty speech-language pathologists ranked the liquids in order of perceived viscosity, based on their interpretation of the product packaging and label. Product nomenclature proved insufficient to accurately represent the consistency class to which each liquid belonged. A second group of 16 speech-language pathologists rated the perceived relative viscosity and density of nectar-thick and honey-thick juice items in blinded two-point discrimination tests of stirring-resistance, oral manipulation, and vessel weight. Physical sampling of these two products enabled clinicians to reliably perceive relative viscosity and density differences between the nectar- and honey-thick items.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
RP Borwankar (1992) ArticleTitleFood texture: A tutorial review. J Food Eng 16 1–16
MC Bourne (1982) Viscosity and consistency. MC Bourne (Eds) Food texture and viscosity: Concept and measurement. Academic Press New York 199–246
ST Coster WH Schwarz (1987) ArticleTitleRheology and the swallow-safe bolus. Dysphagia 1 113–118
EE Finney Jr (1973) Elementary concepts of rheology relevant to food texture studies. A Kramer AS Szczesniak (Eds) Texture measurements of foods: Psychophysical fundamentals; Sensory, mechanical and chemical procedures, and their interrelationships. D. Reidel Publishing Co. Boston 33–51
B Launay (1996) Rheological techniques. G Linden WJ Hurst (Eds) Analytical techniques for food and agricultural products. VCH Publishers, Inc. New York 195–228
MA Rao (1992) Measurement of viscoelastic properties of fluid and semisolid foods. MA Rao JF Steffe (Eds) Viscoelastic properties of foods. Elsevier London 207–232
CF Shoemaker (1992) Instrumentation for the measurement of viscoelasticity. MA Rao JF Steffe (Eds) Viscoelastic properties of foods. Elsevier London 233–246
AS Szczesniak (1973) Instrumental methods of texture measurements. A Kramer AS Szczesniak (Eds) Texture measurements of foods: Psychophysical fundamentals; Sensory, mechanical and chemical procedures, and their interrelationships. D. Reidel Publishing Co. Boston 71–104
MA Tung AT Paulson (1995) Rheological concepts for probing ingredient interactions in food systems. AG Gaonkar (Eds) Ingredient interactions: Effects on food quality. Marcel Dekker New York 45–84
JN Yeatman BK Drake (1973) Physiological aspects of texture perception, including mastication. A Kramer AS Szczesniak (Eds) Texture measurements of foods: Psychophysical fundamentals; Sensory, mechanical and chemical procedures, and their interrelationships. D. Reidel Publishing Co. Boston 10–15
B Jones BW Donner (1989) ArticleTitleHow I do it: Examination of the patient with dysphagia. Dysphagia 4 162–172 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BA383otlU%3D Occurrence Handle2640191
ML Huckabee CA Pelletier (1999) Management of adult neurogenic dysphagia. Singular Publishing Group, Inc. San Diego, CA
JA Logemann (1983) Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. College Hill Press, Inc. San Diego, CA
JA Logemann (1989) Guidelines for safe and efficient feeding of patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. Northern Speech Services Gaylord, MI
J Curran ME Groher (1990) ArticleTitleDevelopment and dissemination of an aspiration risk reduction diet. Dysphagia 5 6–12 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BA28%2FmsVA%3D Occurrence Handle2202558
AW Martin (1991) ArticleTitleDietary management of swallowing disorders. Dysphagia 6 129–134 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2D3cnntFU%3D Occurrence Handle1914540
EM Pardoe (1993) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a multistage diet for dysphagia. J Am Diet Assoc 93 568–571 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA3c7jtFM%3D Occurrence Handle8315168
IR Odderson JC Keaton BS McKenna (1990) ArticleTitleSwallow management in patients on an acute stroke pathway: Quality is cost effective. Arch Phy Med Rehabil 76 1130–1133
CM Steele (2002) ArticleTitleEmergency room assessment and intervention for dysphagia: A pilot project. J Speech Lang Pathol Audiol XX XXX–XXX
BR Garon M Engle C Ormiston (1996) ArticleTitleSilent aspiration: results of 1,000 videofluoroscopic swallow evaluations. J Neurol Rehabil 10 121–126
HM Finestone NC Foley MG Woodbury L Greene–Finestone (2001) ArticleTitleQuantifying fluid intake in dysphagic stroke patients: A preliminary comparison of oral and nonoral strategies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 82 IssueID2 1774–1746
JAY Cichero O Jackson PJ Halley BE Murdoch (2000) ArticleTitleWhich one of these is not like the others? An inter-hospital study of the viscosity of thickened fluids. J Speech Lang Hear Res 43 537–547 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3hvVKmsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10757702
DL Glassburn DF Deem (1998) ArticleTitleThickener viscosity in dysphagia management: Variability among speech-language pathologists. Dysphagia 13 218–222 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czosVejsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9716753
CA Pelletier (1997) ArticleTitleA comparison of consistency and taste of five commercial thickeners. Dysphagia 12 74–78 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB38rksVA%3D Occurrence Handle9071806
P Felt (1999) ArticleTitleThe national dysphagia diet project: The science and practice. Nutr Clin Pract 14 S60–S63
RH Mills (1999) ArticleTitleRheology overview: Control of liquid viscosities in dysphagia management. Nutr Clin Pract 14 S52–S56
CH Smith JA Logemann WR Burghardt TD Carrell SG Zecker (1997) ArticleTitleOral sensory discrimination of fluid viscosity. Dysphagia 12 68–73 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB38rksVc%3D Occurrence Handle9071805
Belvito L: Novartis Nutrition, Personal communication, February 2001
InstitutionalAuthorNameAmerican Dietetic Association (2000) Diet for Dysphagia. Manual of Clinical Dietetics, 6th ed. Author Chicago, IL 668–693
Toronto Dysphagia Interest Group members: Personal communication, May 2001
EM Bisch JA Logemann AW Rademaker PJ Kahrilas CL Lazarus (1994) ArticleTitlePharyngeal effects of bolus volume, viscosity, and temperature in patients with dysphagia resulting from neurologic impairment and in normal subjects. J Speech Hear Res 37 1041–1049 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqC38zovV0%3D Occurrence Handle7823550
RO Dantas MK Kern BT Massey WJ Dodds PJ Kahrilas JG Brasseur IJ Cook IM Lang (1990) ArticleTitleEffect of swallowed bolus variables on oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Am J Physiol 258 G675–G681 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BB2c%2FksVI%3D Occurrence Handle2333995
CL Lazarus JA Logemann AW Rademaker PJ Kahrilas T Pajak R Lazar A Halper (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of bolus volume, viscosity, and repeated swallows in nonstroke subjects and stroke patients. Arch Phys Rehabil 74 1066–1070 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD38bltFQ%3D
AL Perlman DJ Van Daele MS Otterbacher (1995) ArticleTitleQuantitative assessment of hyoid bone displacement from video images during swallowing. J Speech Hear Res 38 IssueID3 579–585 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqH3cvpslY%3D Occurrence Handle7674650
JAY Cichero G Hay BE Murdoch PJ Halley (1997) ArticleTitleVideofluroscopic fluids versus mealtime fluids: Differences in viscosity and density made clear. J Med Speech Lang Pathol 5 IssueID3 203–215
RO Dantas WJ Dodds BT Massey MK Kern (1989) ArticleTitleThe effect of high- vs. low-density barium preparations on the quantitative features of swallowing. Am J Roentgenol 153 1191–1195 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BD2MzgsFc%3D
Miller JL: The influence of volume and viscosity during oral stage swallowing. Masters thesis, McGill University, Ann Arbor, MI: University Microfilms International, 1994
JL Miller KL Watkin (1996) ArticleTitleThe influence of bolus volume and viscosity on anterior lingual force during the oral stage of swallowing. Dysphagia 11 117–124 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymA3sbgt1E%3D Occurrence Handle8721070
AL Perlman JG Schultz DJ Van Daele (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of age, gender, bolus volume and bolus viscosity on oropharyngeal pressure during swallowing. J Appl Physiol 74 33–37
L Reimers–Neils J Logemann C Larson (1994) ArticleTitleViscosity effects on EMG activity in normal swallowing. Dysphagia 9 101–106 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuB2szlsVM%3D Occurrence Handle8005004
CM Christensen (1979) ArticleTitleOral perception of solution viscosity. J Texture Studies 10 153–164
HR Moskowitz (1972) ArticleTitleScales of subjective viscosity and fluidity of gum solutions. J Texture Studies 3 89–100
C Parkinson P Sherman (1971) ArticleTitleThe influence of turbulent flow on the sensory assessment of viscosity in the mouth. J Texture Studies 2 451–459
F Sharma P Sherman (1973) ArticleTitleIdentification of stimuli controlling the sensory evaluation of viscosity. J Texture Studies 4 111–118
SS Stevens M Guirao (1964) ArticleTitleScaling of apparent viscosity. Science 144 1157–1158 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CCuC3cnjslc%3D Occurrence Handle14148443
FW Wood (1968) Psychophysical studies on the consistency of liquid foods. FW Wood (Eds) Society of chemical industry monograph no. 27: Rheology and texture of foodstuffs. Rochester Staples printers limited Kent 40–49
M Li JG Brasseur MK Kern WJ Dodds (1992) ArticleTitleViscosity measurements of barium sulfate mixtures for use in motility studies of the pharynx and esophagus. Dysphagia 7 17–30 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyD2cfhvFQ%3D Occurrence Handle1424824
S Hamlet J Choi M Zormeier F Shamsa R Stachler J Muz L Jones (1996) ArticleTitleNormal adult swallowing of liquid and viscous material: Scintigraphic data on bolus transit and oropharyngeal residues. Dysphagia 11 41–47 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC2cfhvV0%3D Occurrence Handle8556878
HM Robertson MS Patillo (1993) ArticleTitleA strategy for providing food to the patient with neurologically based dysphagia. J Can Diet Assoc 54 198–201
K Stanek C Hensley C Van Riper (1992) ArticleTitleFactors affecting use of food and commercial agents to thicken liquids for individuals with swallowing disorders. J Am Diet Assoc 92 IssueID4 488–490 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2B3M%2FpsF0%3D Occurrence Handle1556355
Goff HD: Personal communication, April 2001
JA Logemann BR Pauloski L Colangelo C Lazarus M Fujiu PJ Kahrilas (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of a sour bolus on oropharyngeal swallowing measures in patients with neurogenic dysphagia. J Speech Hear Res 38 556–563 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqH3cvps10%3D Occurrence Handle7674647
L Newman R Armstrong T Rogers S Walsh C Keckley M Petersen (2002) ArticleTitleThe effect of carbonation on sensory dysphagia in the pediatric population [abstract]. Abstracts of the 9th Annual Dysphagia Research Society Meeting, October 2000, Savannah, GA. Dysphagia 16 IssueID2 148–149
G Lazzara C Lazarus JA Logemann (1986) ArticleTitleImpact of thermal stimulation on the triggering of the swallowing reflex. Dysphagia 1 73–77
J Rosenbek J Robbins B Fishback R Levine (1991) ArticleTitleEffects of thermal application on dysphagia after stroke. J Speech Hear Res 34 1257–1268 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2C2MjlvFQ%3D Occurrence Handle1787707
J Rosenbek EB Roecker JL Wood J Robbins (1996) ArticleTitleThermal application reduces the duration of stage transition in dysphagia after stroke. Dysphagia 11 IssueID4 225–233 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiD38vgtlQ%3D Occurrence Handle8870348
JC Rosenbek J Robbins WO Willford G Kirk A Schiltz TW Sowell SE Deutsch FJ Milanti J Ashford GD Gramigna A Fogarty K Dong MT Rau TE Prescott AM Lloyd MT Sterkel JE Hansen (1998) ArticleTitleComparing treatment intensities of tactile-thermal application. Dysphagia 13 IssueID1 1–9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FlsVWlsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9391220
CM Steele . Van Lieshout (2002) ArticleTitleKinematics of swallowing measured using electromagnetic midsagittal articulography [abstract]. Abstracts .of the 10th Annual Dysphagia Research Society Meeting, October 2001, Albuquerque, NM. Dysphagia 17 IssueID2 176
JA Logemann BR Pauloski AW Rademaker LA Colangelo PJ Kahrilas CH Smith (2000) ArticleTitleTemporal and biomechanical characteristics of oropharyngeal swallow in younger and older men. J Speech Lang Hear Res 43 1264–1274 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzgsV2qsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11063246
MA Nicosia JA Hind EB Roecker M Carnes J Doyle GA Dengel J Robbins (2000) ArticleTitleAge effects on the temporal evolution of isometric and swallowing pressure. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 55 M634–M640
J Robbins (1999) ArticleTitleOld swallowing and dysphagia: Thoughts on intervention and prevention. Nutr Clin Pract 14 821–826
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Jamie Patmore in conducting the rheological measurement portion of this research. Preparation of this manuscript was supported by a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada postgraduate scholarship held by the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix Clinician Survey
Appendix Clinician Survey
I am currently conducting a study to determine how clinicians perceive the relative consistency of a variety of liquids (listed below in alphabetical order).
Please rank the following liquid items in order of consistency (1 being the “thinnest” and 10 being the “thickest”). Do NOT use the same number twice (i.e., please rank each of the three honey-thick liquids with a different number).
—— Apple Juice
—— Applesauce (President’s Choice “Just Apples Appletreet)
—— Chocolate Milk
—— JELL-O Chocolate Pudding
—— Novartis RESOURCE® Chocolate Dairy Thick (Honey Consistency)
—— Novartis RESOURCE® Original Dairy Thick (Honey Consistency)
—— Novartis RESOURCE® Thickened Apple Juice (Honey Consistency)
—— Novartis RESOURCE® Thickened Apple Juice (Nectar Consistency)
—— Water
—— Yogurt (Minigo Fromage Frais by Yoplait)
Thank you VERY MUCH for your contribution.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steele, C.M., Van Lieshout, P.H. & Goff, D.H. The Rheology of Liquids: A Comparison of Clinicians’ Subjective Impressions and Objective Measurement . Dysphagia 18, 182–195 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-002-0104-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-002-0104-1