Abstract
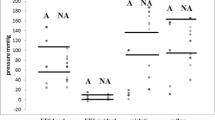
The goal of our study was to verify the clinical applicability of an original balloon sensor probe for the manofluorographic study of oropharyngeal dysphagia. A prototype apparatus for manofluorography was developed and a standard perfused probe for esophageal manometry was modified by applying fluid-filled floppy balloons 0.5-, 1-, and 2.5-cm long. A group of healthy volunteers and a group of patients affected by oropharyngeal dysphagia underwent manofluorography. Statistically significant differences were calculated between the groups with regard to the upper esophageal sphincter (UES) basal and postrelaxation contraction pressures (p < 0.05, Student’s t test, 2.5- vs. 1-cm-long balloon sensors). In the group of patients versus the group of healthy volunteers, statistically significant differences were calculated with regard to pharyngeal intrabolus pressure, UES residual and UES postrelaxation contraction pressures, and mean diameter of the UES during maximal opening (p < 0.05, Student’s t test). A strong negative correlation (r = −0.92, p = 0.001; r = −0.93, p = 0.006 linear regression analysis) was observed between intrabolus pressure and UES diameter during maximum opening in the group of patients. The balloon probe demonstrated its reliability and clinical adequacy for the study of swallowing disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
IJ Cook M Gabb V Panagopoulos GG Jamieson WJ Dodds J Dent DJ Shearman (1992) ArticleTitlePharyngeal (Zenker’s) diverticulum is a disorder of upper esophageal sphincter opening. Gastroenterology 103 1229–1235 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyD3M3mvFI%3D Occurrence Handle1397879
RO Dantas IJ Cook WJ Dodds MK Kern IM Lang JG Brasseur (1990) ArticleTitleBiomechanics of cricopharyngeal bars. Gastroenterology 99 1269–1274 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6D3cjgslA%3D Occurrence Handle2210235
PJ Kahrilas (1993) ArticleTitleVolume accommodation during swallowing. Dysphagia 8 259–265 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA28rjtFU%3D Occurrence Handle8359048
P Jacob PJ Kahrilas JA Logemann V Shah T Ha (1989) ArticleTitleUpper esophageal sphincter opening and modulation during swallowing. Gastroenterology 97 1469–1478 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BD28%2FlvVc%3D Occurrence Handle2583413
PJ Kahrilas JA Logemann S Lin A Ergun (1992) ArticleTitlePharyngeal clearance during swallowing: a combined manometric and videofluoroscopic study. Gastroenterology 103 128–136 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2A3cjivVE%3D Occurrence Handle1612322
D Cerenko FMS McConnel RT Jackson (1989) ArticleTitleQuantitative assessment of pharyngeal bolus driving forces. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 100 57–63 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaC28%2FgsFY%3D Occurrence Handle2493617
PJ Kahrilas JA Logemann C Drugler E Flanagan (1991) ArticleTitleVolitional augmentation of upper esophageal sphincter opening during swallowing. Am J Physiol 5 6450–6456
FMS McConnel P Cerenko MS Mendelsohn (1988) ArticleTitleManofluorographic analysis of swallowing. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 21 IssueID6 1149–1171
FMS McConnel A O’Connor (1994) ArticleTitleDysphagia secondary to head and neck cancer surgery. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg 48 165–170 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuB2s%2FhsVA%3D
FMS McConnel MS Mendelsohn JA Logemann (1987) ArticleTitleManofluorography of deglutition after supraglottic laryngectomy. Head Neck Surg 9 142–150 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiA3cjjvFY%3D Occurrence Handle3623944
IJ Cook P Kahrilas (1999) ArticleTitleAmerican Gastroenterological Association Technical Review on Management of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Gastroenterology 116 455–478 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7it12ksw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9922328
PJ Kahrilas G Shi (1998) ArticleTitleFirst measurement standard, then catheter standards, for manofluorography. Dysphagia 13 111–112 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7nsVCqsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9513307
DO Castell (Eds) (1992) The Esophagus. Little, Brown Boston
PJ Kahrilas RE Clouse WJ Hogan (1994) ArticleTitleAmerican Gastroenterological Association technical review on the clinical use of esophageal manometry. Gastroenterology 107 1865–1884 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqD2cjhslY%3D
J Dent (1976) ArticleTitleA new technique for continuous sphincter pressure measurements. Gastroenterology 71 263–267 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSmB3sngt1E%3D Occurrence Handle939387
S Mattioli ML Lugaresi R Zannoli S Brusori F D’Ovidio (2003) ArticleTitleBalloon sensors for the manometric recording of the pharyngoesophageal tract: an experimental study. Dysphagia 18 249–254
S Mattioli V Felice FG Pearson R Zannol G Gozetti (1993) ArticleTitleBalloon sensors versus perfused side hole sensors for oesophageal manometry. A study in healthy volunteers. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 5 133–139
JA Castell CB Dalton DO Castell (1990) ArticleTitlePharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter in humans. Am J Physiol 258 G173–G178 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BC28vns1M%3D Occurrence Handle2305883
TE Knuff SB Benjamin DO Castell (1982) ArticleTitlePharyngoesophageal (Zenker’s) diverticulum: a reappraisal. Gastroenterology 82 734–736 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi2C3sbpsVE%3D Occurrence Handle6800871
JA Wilson A Pryde A Cecilia CC Macintyre RC Heading (1989) ArticleTitleNormal pharyngoesophageal motility. A study of 50 healthy subjects. Dig Dis Sci 10 1590–1599
JA Castell (1987) The computer in the motility laboratory. DO Castell JE Richter C Boag Dalton (Eds) . Elsevier New York 91–103
KA Kendall RJ Leonard (2001) ArticleTitleHyoid movement during swallowing in older patients with dysphagia. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127 IssueID10 1224–1229 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MngvVKnsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11587603
IJ Cook WJ Dodds RO Dantas B Massey MK Kern IM Lang JG Brasseur WJ Hogan (1989) ArticleTitleOpening mechanisms of the human upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol 257 G748–G759 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BD1cjgslQ%3D Occurrence Handle2596608
M Atkinson P Kramer S Wyman et al. (1957) ArticleTitleThe dynamics of swallowing: normal pharyngeal mechanisms. J Clin Invest 36 581–588 Occurrence Handle13416388
C DiRe S Guoxiang M Manka P Kahrilas (2001) ArticleTitleManometric characteristics of the upper esophageal sphincter recorded with a microsleeve. Am J Gastroenterol 96 1383–1389 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3psVOnsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11379603
GN Ali KL Wallace R Schwartz DJ DeCarle AS Zagami IJ Cook (1996) ArticleTitleMechanisms of oral-pharyngeal dysphagia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Gastroenterology 110 383–392 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC2Mngtl0%3D Occurrence Handle8566584
BR Cohen BS Wolf (1968) Cineradiographic and intraluminal correlations in the pharynx and esophagus. CF Code (Eds) Handbook of Physiology: Alimentary Canal Motility. American Physiological Society Washington, DC 1841–1860
P Jacob PJ Kahrilas JA Logemann V Shah T Ha (1989) ArticleTitleUpper esophageal sphincter opening and modulation during swallowing. Gastroenterology 97 1469–1478 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BD28%2FlvVc%3D Occurrence Handle2583413
PJ Kahrilas WJ Dodds J Dent JA Logemann R Shaker (1988) ArticleTitleUpper esophageal sphincter function during deglutition. Gastroenterology 95 52–62 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieB38rptlY%3D Occurrence Handle3371625
JA Wilson A Pryde CCA Macintyre AGD Maran RC Heading (1990) ArticleTitleThe effects of age, sex, and smoking on normal pharyngoesophageal motility. Am J Gastroenterol 85 IssueID6 686–691 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BB1c3itV0%3D Occurrence Handle2353687
WJ Dodds WJ Hogan SB Lydon ET Stewart JJ Stef RC Arndorfer (1975) ArticleTitleQuantitation of pharyngeal motor function in normal subjects. J Appl Physiol 39 IssueID4 692–696 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSmD28fpsFM%3D Occurrence Handle1194163
J Robbins JW Hamilton GL Lof GB Kempster (1992) ArticleTitleOropharyngeal swallowing in normal adults of different ages. Gastroenterology 103 823–829 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2A28zhsFM%3D Occurrence Handle1499933
W Dodds KM Man IJ Cook PJ Kahrilas ET Stewart MK Kern (1988) ArticleTitleInfluence of bolus volume on swallow-induced hyoid movement in normal subjects. AJR Am J Roentgenol 150 1203
M Yokoyama N Mitomi K Tetsuka N Tayama S Niimi (2000) ArticleTitleRole of laryngeal movement and effect of aging on swallowing pressure in the pharynx and upper esophageal sphincter. Laryngoscope 3 Pt 1 434–439
DC Gotley CP Barham R Miller R Arnold D Alderson (1991) ArticleTitleThe sphinctometer: a new device for measurement of lower oesophageal sphincter function. Br J Surg 78 933–935 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2D3cvmsFM%3D Occurrence Handle1913108
NJ Trudgill SA Riley (1999) ArticleTitleMonitoring the lower oesophageal sphincter: sphinctometer or sleeve? Neurogastroenterol Motil 11 173–178 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3ot1yjsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10354342
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattioli, S., Lugaresi, M., Zannoli, R. et al. Pharyngoesophageal Manometry with an Original Balloon Sensor Probe for the Study of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia . Dysphagia 18, 242–248 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0010-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0010-1