Abstract
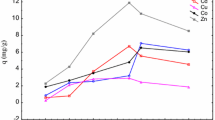
A number of preparations of residual non-living brewery yeast were examined for their ability to remove lead from solution. Those preparations included washed and un-washed intact yeast and washed and un-washed homogenates of the yeast cells. Using biosorption isotherm analysis it was found that the washed and un-washed preparations of intact, non-living yeast exhibited maximum biosorption capacities for lead of 127 and 99 mg/g dry weight biomass, respectively. The washed and un-washed cell homogenates exhibited maximum biosorption capacities of 38 and 139 mg lead/g dry weight biomass, respectively. Since it had previously been shown that these preparations of biomass were capable of removing uranium from solution by combined biosorption and precipitation processes, it was decided to examine removal of lead from solution using a form of equilibrium dialysis in which the biomass was retained within a semi-permeable membrane during contact reactions. The results suggest that precipitation plays an important role during removal of lead from solution, and this is partially due to membrane-permeable substances released from the biomass into the membrane-excluded solution. The results demonstrate that removal of lead from solution by some of the yeast preparations used in this study involves combined biosorption and precipitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riordan, C., McHale, A. Removal of lead from solution using non-living residual brewery yeast. Bioprocess Engineering 19, 277–280 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004490050519
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004490050519