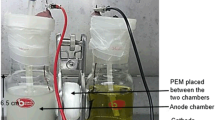
Abstract
A novel nickel oxide/carbon nanotube/polyaniline (NCP) nanocomposite has been prepared and used to modify the electrocatalytic properties of carbon cloth anode in fabricating dual-chamber MFC. The prepared nanocomposite was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The carbon cloth coated with the NCP nanocomposite showed the enhanced electrochemical performance as compared to bare carbon cloth anode. The electrochemical properties of the fabricated MFC with the modified anode have been investigated by linear sweep voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The maximum power density of the MFC using the novel NCP nanocomposite-carbon cloth anode increased by 61.88% compared to that of the bare carbon cloth anode. In comparison to the bare carbon cloth anode, the new composite anode showed 26.8% enhancement of current density output which it can be due to the enhancement of the charge transfer capability.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logan BE, Rabaey K (2012) Conversion of wastes into bioelectricity and chemical by using microbial electrochemical technologies. Science 337:686–690
Alatraktchi FA, Zhang Y, Angelidaki I (2014) Nanomodification of the electrodes in microbial fuel cell: impact of nanoparticle density on electricity production and microbial community. Appl Energy 116:216–222
Richter H, McCarthy K, Nevin KP, Johnson JP, Rotello VM, Lovley DR (2008) Electricity generation by Geobacter sulfurreducens attached to gold electrodes. Langmuir 24:4367–4371
Fan YZ, Hu HQ, Liu H (2007) Enhanced coulombic efficiency and power density of air-cathode microbial fuel cells with an improved cell configuration. J Power Sources 171:348–354
Min B, Logan BE (2004) Continuous electricity generation from domestic wastewater and organic substrates in a flat plate microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 3:5809–5814
Chaudhuri SK, Lovley DR (2003) Electricity generation by direct oxidation of glucose in microbial fuel cells. Nat Biotechnol 21:1229–1232
Liu H, Cheng S, Logan BE (2005) Power generation in fed-batch microbial fuel cells as a function of ionic strength, temperature, and reactor configuration. Environ Sci Technol 39:5488–5493
Tsai H-Y, Wu C-C, Leec C-Y, Shiha EP (2009) Microbial fuel cell performance of multiwall carbon nanotubes on carbon cloth as electrodes. J Power Source 194:199–205
Wong C, Vijayaraghavan V (2012) Nanomechanics of free form and water submerged single layer graphene sheet under axial tension by using molecular dynamics simulation. Mater Sci Eng A 556:420–428
Liu J, He W, Qu Y, Ren N, Feng Y (2014) Enhanced electricity generation for microbial fuel cell by using electrochemical oxidation to modify carbon cloth anode. J Power Source 265:391–396
Y-s Oon, Ong S-A, Ho L-N, Wong Y-S, Oon Y-L, Lehl H, Thung W-E (2016) Long-term operation of double chambered microbial fuel cell for bio-electro denitrification. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39:893–900
Vijayaraghavan V, Castagne S (2016) Computational model for predicting the effect of process parameters on surface characteristics of mass finished components. Eng Comput 33(3):789–805
Fu YB, Liu ZH, Su G, Zai XR, Ying M, Yu J (2016) Modified carbon anode by MWCNTs/PANI used in marine sediment microbial fuel cell and its electrochemical performance. Fuel Cells 16(3):377–383
Huang L, Li X, Ren Y, Wang X (2016) In-situ modified carbon cloth with polyaniline/graphene as anode to enhance performance of microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41(26):11369–11379
Liu X-W, Huang Y-X, Sun X-F, Sheng G-P, Zhao F, Wang S-G, Yu H-Q (2014) Conductive carbon nanotube hydrogel as a bioanode for enhanced microbial electrocatalysis. Appl Mater Interfaces 11:8158–8164
Kang YL, Ibrahim S, Pichiah S (2015) Synergetic effect of conductive polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) with different structural configuration of anode for microbial fuel cell application. Bioresour Technol 189:364–369
Yuan H, Deng L, Chen Y, Yuan Y (2016) MnO2/Polypyrrole/MnO2 multi-walled-nanotube-modified anode for high-performance microbial fuel cells. Electrochim Acta 196:280–285
Vijayaraghavan V, Garg A, Wong C, Tai K (2014) Estimation of mechanical properties of nanomaterials using artificial intelligence methods. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 116(3):1099–1107
Mehdinia A, Ziaeib E, Jabbari A (2014) Multi-walled carbon nanotube/SnO2 nanocomposite: a novel anode material for microbial fuel cells. Electrochim Acta 130:512–518
Katuri KP, Scott K, Head IM, Picioreanu C, Curtis TP (2011) Microbial fuel cells meet with external resistance. Bioresour Technol 102:2758–2766
Feng CH, Ma L, Li FB (2010) A polypyrrole/anthraquinone-2, 6-disulphonic disodium salt (PPy/AQDS)-modified anode to improve performance of microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1516–1520
Yuan Y, Zhou SG, Liu Y, Tang JH (2013) Nanostructured macroporous bioanode based on polyaniline-modified natural loofah sponge for high-performance microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 47:14525–14532
He JB, Lin XQ, Pan J (2005) Multi-wall carbon nanotube paste electrode for adsorptive stripping determination of quercetin: a comparison with graphite paste electrode via voltammetry and chronopotentiometry. Electroanalysis 17:1681–1686
Vijayaraghavan V, Garg A, Gao L, Vijayaraghavan R, Lu G (2016) A finite element based data analytics approach for modeling turning process of Inconel 718 alloys. J Clean Prod 137:1619–1627
Vijayaraghavan V, Garg A, Wong CH, Tai K, Singru PM, Gao L, Sangwan KS (2014) A molecular dynamics based artificial intelligence approach for characterizing thermal transport in nanoscale material. Thermochim Acta 594:39–49
Vijayaraghavan V, Wong CH (2013) Temperature, defect and size effect on the elastic properties of imperfectly straight carbon nanotubes by using molecular dynamics simulation. Comput Mater Sci 71:184–191
Vijayaraghavan V, Wong CH (2014) Torsional characteristics of single walled carbon nanotube with water interactions by using molecular dynamics simulation. Nano Micro Lett 6:268–279
Vijayaraghavan V, Wong CH (2014) Transport characteristics of water molecules in carbon nanotubes investigated by using molecular dynamics simulation. Comput Mater Sci 89:36–44
Wong CH, Vijayaraghavan V (2014) Compressive characteristics of single walled carbon nanotube with water interactions investigated by using molecular dynamics simulation. Phys Lett A 378(5):570–576
HoPark I, Christy M, Kim P, Nahma K-S (2014) Enhanced electrical contact of microbes using Fe3O4/CNT nanocomposite anode in mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 58:75–80
Wang Y, Li B, Cui D, Xiang X, Li W (2014) Nano-molybdenum carbide/carbon nanotubes composite as bifunctional anode catalyst for high-performance Escherichia coli-based microbial fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 51:349–355
Chang HY, Chang HC, Lee KY (2013) Characteristics of NiO coating on carbon nanotubes for electric double layer capacitor application. Vacuum 87:164–168
Qiao Y, Wu X-S, Li CM (2014) Interfacial electron transfer of Shewanella putrefaciens enhanced by nanoflaky nickel oxide array in microbial fuel cells. J Power Sour 266:226–231
Huang J, Zhu N, Yang T, Zhang T, Wu P (2015) Nickel oxide and carbon nanotube composite(NiO/CNT)as a novel cathode non-precious metal catalyst in microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 72:332–339
Lu M, Guo L, Kharkwal S, Wu H, Ng HY, Yau Li S (2013) Manganese-polypyrrole-carbon nanotube, a new oxygen reduction catalyst for air-cathode microbial fuel cells. J Power Source 221:381–386
Qiao Y, Li CM, Bao S-J, Bao Q-L (2007) Carbon nanotube/polyaniline composite as anode material for microbial fuel cells. J Power Source 170:79–84
Logan BE, Aelterman P, Hamelers B, Rozendal R, Schröer U, Keller J, Freguia S, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40:5181–5192
Dong H, Yu H, Wang X, Zhou Q, Sun J (2012) Carbon-supported perovskite oxides as oxygen reduction reaction catalyst in single chambered microbial fuel cells. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:774–778
Lee JY, Liang K, An KH, Lee YH (2005) Nickel oxide/carbon nanotubes nanocomposite for electrochemical capacitance. Synth Met 150:153–157
Qiao Y, Bao S-J, Li CM, Cui X-Q, Lu Z-S, Guo J (2008) Nanostructured polyaniline/titanium dioxide composite anode for microbial fuel cells. ACS Nano 2:113–119
Zou Y, Wang Y (2011) NiO nanosheets grown on graphene nanosheets as superior anode materials for Li-ion batteries. Nanoscale 3:2615–2620
Adekunle AS, Oyekunle J, Oluwafemi OS, Joshua AO, Makinde WO, Ogunfowokan AO, Eleruja MA, Ebenso EE (2014) Comparative catalytic properties of Ni(OH)2 and NiO nanoparticles towards the degradation of nitrite (NO2 −) and nitric Oxide (NO). Int J Electrochem Sci 9:3008–3021
Hsu CH, Mansfeld F (2001) Concerning the conversion of the constant phase element parameter Y0 into a capacitance. Corrosion 57:747–748
Sekar N, Ramasamy RP (2013) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for microbial fuel cell characterization. J Microb Biochem Technol 6:2–14
Zhou M, Chi M, Wang H, Jin T (2012) Anode modification by electrochemical oxi-dation: a new practical method to improve the performance of microbial fuel cells. Biochem Eng J 60:151–155
Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2005) Microbial fuel cells: novel biotechnology for energygeneration. Trends Biotechnol 23:291–298
Karthikeyan R, Krishnaraj N, Selvam A, Wong JW, Lee PK, Leung MK, Berchmans S (2016) Effect of composites based nickel foam anode in microbial fuel cell using Acetobacter aceti and Gluconobacter roseus as a biocatalysts. Bioresour Technol 217:113–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nourbakhsh, F., Mohsennia, M. & Pazouki, M. Nickel oxide/carbon nanotube/polyaniline nanocomposite as bifunctional anode catalyst for high-performance Shewanella-based dual-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40, 1669–1677 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1822-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1822-y