Abstract
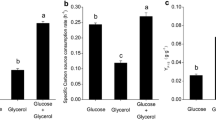
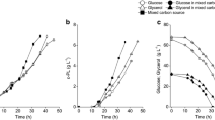
ε-Poly-l-lysine (ε-PL), one of the only two homo-poly amino acids known in nature, is used as a preservative. In this study, strategies of feeding precursor l-lysine into 5 L laboratory scale fermenters, including optimization of l-lysine concentration and time, was investigated to optimize the production of ε-PL by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18. The optimized strategy was then used in ε-PL fed-batch fermentation in which glucose and glycerol served as mixed carbon sources. In this way, a novel ε-PL production strategy involving precursor l-lysine coupled with glucose–glycerol co-fermentation was developed. Under optimal conditions, ε-PL production reached 37.6 g/l, which was 6.2 % greater than in a previous study in which glucose and glycerol co-fermentation was performed without added l-lysine (35.14 g/l). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the enhancement of ε-PL production through l-lysine feeding to evaluate the use of fermenters. Meanwhile, the role of l-lysine in the promotion of ε-PL production, participating ε-PL synthesis as a whole, was first determined using the l-[U–13C] lysine labeling method. It has been suggested that the bottleneck of ε-PL synthesis in Streptomyces sp. M-Z18 is in the biosynthesis of precursor l-lysine. The information obtained in the present work may facilitate strain improvement and efficient large-scale ε-PL production.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shima S, Sakai H (1977) Polylysine produced by Streptomyces. Agric Biol Chem 41:1807–1809
Saimura M, Takehara M, Mizukami S, Kataoka K, Hirohara H (2008) Biosynthesis of nearly monodispersed poly(ε-l-lysine) in Streptomyces species. Biotechnol Lett 30:377–385
Hiraki J, Masakazu H, Hiroshi M, Yoshikazu I (1998) Improved ε-poly-l-lysine production of an S-(2-aminoethyl)-l-cysteine resistant mutant of Streptomyces albulus. Seibutu Kougaku Kaishi 76:487–493
Shih IL, Shen MH (2006) Application of response surface methodology to optimize production of poly-ε-lysine by Streptomyces albulus IFO 14147. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:15–21
Kobayashi K, Nishikawa M (2007) Promotion of ε-poly-l-lysine production by iron in Kitasatospora Kifunense. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1033–1036
Kahar P, Iwata T, Hiraki J, Park EY, Okabe M (2001) Enhancement of ε-polylysine production by Streptomyces albulus strain 410 using pH control. J Biosci Bioeng 91:190–194
Hiraki J, Suzuki E (1999) Process for producing ε-poly-l-lysine with immobilized Streptomyces albulus. US Patent 5900363
Liu S, Wu Q, Zhang J, Mo S (2011) Production of ε-poly-l-lysine by Streptomyces sp. using resin-based, in situ product removal. Biotechnol Lett 33:1581–1585
Chen XS, Li S, Liao LJ, Ren XD, Li F, Tang L, Zhang JH, Mao ZG (2011) Production of ε-poly-l-lysine using a novel two-stage pH control strategy by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18 from glycerol. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 34:561–567
Chen XS, Ren XD, Dong N, Li S, Li F, Zhao FL, Tang L, Zhang JH, Mao ZG (2012) Culture medium containing glucose and glycerol as a mixed carbon source improves ε-poly-l-lysine production by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35:469–475
Bankar SB, Singhal RS (2011) Improved poly-ε-lysine biosynthesis using Streptomyces noursei NRRL 5126 by controlling dissolved oxygen during fermentation. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:652–658
Mao XZ, Wang F, Zhang JG, Chen S, Deng ZX, Shen YL, Wei DZ (2009) The pH shift and precursor feeding strategy in a low-toxicity FR-008/candicidin derivative CS103 fermentation bioprocess by a mutant of Streptomyces sp. FR-008. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 159:673–686
Zhou WW, Ma B, Tang YJ, Zhong JJ, Zheng XD (2012) Enhancement of validamycin A production by addition of ethanol in fermentation of Streptomyces hygroscopicus 5008. Bioresour Technol 114:616–621
Chen XL, Xu YH, Zheng YG, Shen YC (2010) Improvement of tautomycin production in Streptomyces spiroverticillatus by feeding glucose and maleic anhydride. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 15:969–974
Shima S, Oshima S, Sakai H (1983) Biosynthesis of ε-poly-l-lysine by washed mycelium of Streptomyces albulus no. 346. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 57:221–226
Kawai T, Kubota T, Hiraki J, Izumi Y (2003) Biosynthesis of ε-poly-l-lysine in a cell-free system of Streptomyces albulus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:635–640
Yamanaka K, Maruyama C, Takagi H, Hamano Y (2008) ε-Poly-l-lysine dispersity is controlled by a highly unusual nonribosomal peptide synthetase. Nat Chem Biol 4:766–772
Hirohara H, Takehara M, Saimura M, Masayuki A, Miyamoto M (2006) Biosynthesis of poly(ε-l-lysine)s in two newly isolated strains of Streptomyces sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:321–331
Bankar SB, Singhal RS (2011) Metabolic precursors enhance the production of poly-ε-lysine by Streptomyces noursei NRRL 5126. Eng Life Sci 11:253–258
Jia SR, Mo ZW, Tan ZL, Wang GL, Fan BQ, Wang T, Li L, Zhou B (2010) A new method for enhancing ε-poly-l-lysine production. China patent CN101671703A
Zhang Y, Feng XH, Xu H, Yao Z, Ouyang PK (2010) ε-Poly-l-lysine production by immobilized cells of Kitasatospora sp. MY 5–36 in repeated fed-batch cultures. Bioresour Technol 101:5523–5527
Itzhaki RF (1972) Colorimetric method for estimating polylysine and polyarginine. Anal Biochem 50:569–574
Rahulan R, Dhar KS, Madhavan Nampoothiri K, Pandey A (2011) Production of leucine amino peptidase in lab scale bioreactors using Streptomyces gedanensis. Bioresour Technol 102:8171–8178
Hamano Y, Nicchu I, Shimizu T, Onji Y, Hiraki J, Takagi H (2007) epsilon-Poly-l-lysine producer, Streptomyces albulus, has feedback-inhibition resistant aspartokinase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:873–882
Anne-Marie C, Gross RA (1995) Investigation by NMR of metabolic routes to bacterial γ-poly(glutamic acid) using 13C-labeled citrate and glutamate as media carbon sources. Can J Microbiol 41:902–909
Maeda S, Kunimoto KK, Sasaki C, Kuwae A, Hanai K (2003) Characterization of microbial poly (ε-l-lysine) by FT-IR, Raman and solid state 13C NMR spectroscopies. J Mol Struct 655:149–155
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Jiangsu Key Project of Scientific and Technical Supporting Program (BE2012616), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP11217), the Wuxi Science and Technology Support Program (CYE21N1107), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and the 111 Project (111-2-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, XS., Ren, XD., Zeng, X. et al. Enhancement of ε-poly-l-lysine production coupled with precursor l-lysine feeding in glucose–glycerol co-fermentation by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36, 1843–1849 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0958-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0958-7