Abstract
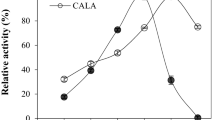
Lipase (EC 3.1.1.3) is a popular enzyme used as an ingredient in detergents and biocatalyst in many biochemical reactions. Lipase is usually expressed in Escherichia coli as an inactive inclusion body and at a low level. In this study, Candida antarctica lipase B (CalB) was fused with various polycationic amino acid tags and expressed in E. coli in order to increase a soluble expression level. By induction with 1.0 mM IPTG, the authentic and fused CalBs were expressed at 27–56% of total protein. The 10-arginine and 10-lysine tags fused at the C-terminal of CalB significantly increased the solubility of CalB by five- to ninefold, relative to the case of the authentic CalB expressed in a recombinant E. coli Origami 2TM (DE3) strain. Among a series of the C-terminal poly-arginine tags, the recombinant CalB combined with the 10-arginine tag (CalB-R10) possessed the highest lipase specific activity of 9.5 ± 0.03 U/mg protein, corresponding to a fourfold enhancement compared with the authentic CalB.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmid RD, Verger R (1998) Lipases: interfacial enzymes with attractive applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 37:1608–1633
Blank K, Morfill J, Gumpp H, Gaub HE (2006) Functional expression of Candida antarctica lipase B in Eschericha coli. J Biotechnol 125:474–483
Hoegh I, Patkar S, Halkier T, Hansen MT (1995) Two lipases from Candida antarctica: cloning and expression in Aspergillus oryzae. Can J Bot 73:S869–S875
Rotticci D, Rotticci-Mulder JC, Denman S, Norin T, Hult K (2001) Improved enantioselectivity of a lipase by rational protein engineering. ChemBioChem 2:766–770
Zhang N, Suen WC, Windsor W, Xiao L, Madison V, Zaks A (2003) Improving tolerance of Candida antarctica lipase B towards irreversible thermal inactivation through directed evolution. Protein Eng 16:599–605
Park HJ, Kim YH (2009) Functional expression of Candida antarctica lipase A in Pichia pastoris and Escherichia coli. Kor J Biotechnol Bioeng 24:341–346
Liu D, Schmid R, Rusnak M (2006) Functional expression of Candida antarctica lipase B in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm—a screening system for a frequently used biocatalyst. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:1024–1032
Seo HS, Kim SE, Han KY, Park JS, Kim YH, Sim SJ, Jw Lee (2009) Functional fusion mutant of Candida antarctica lipase B (CalB) expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794:519–525
Esposito D, Chatterjee DK (2006) Enhancement of soluble protein expression through the use of fusion tags. Curr Opin Biotech 17:353–358
Kato A, Maki K, Ebina T, Kuwajima K, Soda K, Kuroda Y (2007) Mutational analysis of protein solubility enhancement using short peptide tags. Biopolymers 85:12–18
Ashraf SS, Benson RE, Payne ES, Halbleib CM, Gr H (2004) A novel multi-affinity tag system to produce high levels of soluble and biotinylated proteins in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 33:238–245
Kim S-G, Kim J-A, Yu H-A, Lee D-H, Kweon D-H, Seo J-H (2006) Application of poly-arginine fused minichaperone to renaturation of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase expressed in recombinant Escherichia coli. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:459–465
Kweon DH, Kim SG, Han NS, Lee JH, Chung KM, Seo JH (2005) Immobilization of Bacillus macerans cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase fused with poly-lysine using cation exchanger. Enzyme Microb Technol 36:571–578
Lee DH, Kim SG, Kweon DH, Seo JH (2009) Folding machineries displayed on a cation-exchanger for the concerted refolding of cysteine- or proline-rich proteins. BMC Biotechnol 9:27
Lee DH, Lee YJ, Ryu YW, Seo JH (2010) Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of a novel erythrose reductase from Candida magnoliae JH110. Microb Cell Fac 9:43
Jung SM, Park YC, Park KM (2010) Effects of environmental conditions and methanol feeding strategy on lipase-mediated biodiesel production using soybean oil. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 15:614–619
Prinz WA, Åslund F, Holmgren A, Beckwith J (1997) The role of the thioredoxin and glutaredoxin pathways in reducing protein disulfide bonds in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm. J Biol Chem 272:15661–15667
Xu Y, Yasin A, Tang R, Scharer J, Moo-Young M, Chou C (2008) Heterologous expression of lipase in Escherichia coli is limited by folding and disulfide bond formation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:79–87
Smith JC, Derbyshire RB, Cook E, Dunthorne L, Viney J, Brewer SJ, Sassenfeld HM, Bell LD (1984) Chemical synthesis and cloning of a poly(arginine)-coding gene fragment designed to aid polypeptide purification. Gene 32:321–327
Hossain MA, Belgi A, Lin F, Zhang S, Shabanpoor F, Chan L, Belyea C, Truong H-T, Blair AR, Andrikopoulos S, Tregear GW, Wade JD (2009) Use of a temporary “solubilizing” peptide tag for the FMOC solid-phase synthesis of human insulin glargine via use of regioselective disulfide bond formation. Bioconjugate Chem 20:1390–1396
Jung S, Park S (2008) Improving the expression yield of Candida antarctica lipase B in Escherichia coli by mutagenesis. Biotechnol Lett 30:717–722
Qing G, Ma L-C, Khorchid A, Swapna GVT, Mal TK, Takayama MM, Xia B, Phadtare S, Ke H, Acton T, Montelione GT, Ikura M, Inouye M (2004) Cold-shock induced high-yield protein production in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotech 22:877–882
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program (2010-0015928) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), and the Advanced Biomass R&D Center (ABC) of Korea Grant (2010-0029799) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, and in part by the new faculty research program 2009 of Kookmin University in Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, HJ., Kim, SK., Min, WK. et al. Polycationic amino acid tags enhance soluble expression of Candida antarctica lipase B in recombinant Escherichia coli . Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 34, 833–839 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0533-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0533-z