Abstract
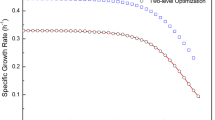
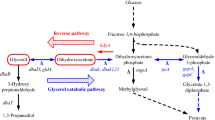
The knowledge of the mechanism of flux distribution will benefit understanding cell physiology and regulation of metabolism. In this study, the measured fluxes obtained under steady-state conditions were used to estimate intracellular fluxes and identify the robustness of branch points of the anaerobic glycerol metabolism in Klebsiella pneumoniae for the production of 1,3-propanediol by metabolic flux analysis. The biomass concentration increased as NADH2/NAD+ decreased at low initial concentration and inversed at high initial glycerol concentration. The flux distribution revealed that the branch points of glycerol and dihydroxyacetonephosphate were rigid to the environmental conditions. However, the pyruvate and acetyl coenzyme A metabolisms gave cells the flexibility to regulate the energy and intermediate fluxes under various environmental conditions. Additionly, it was found that the formation rate of ethanol and the ratio of pyruvate dehydrogenase to pyruvate formate lyase appeared visible fluctuations at high glycerol uptake rate.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biebl H, Menzel K, Zeng AP, Deckwer WD (1999) Microbial production of 1,3-propanediol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:289–297
Nakamura CE, Whited GM (2003) Metabolic engineering for the microbial production of 1,3-propanediol. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:454–459
Menzel K, Zeng AP, Deckwer WD (1997) High concentration and productivity of 1,3-propanediol from continuous fermentation of glycerol by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Enzyme Microb Technol 20:82–86
Zeng AP, Biebl H (2002) Bulk chemicals from biotechnology: the case of 1,3-propanediol production and the new trends. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 74:239–259
Chen X, Xiu ZL, Wang JF, Zhang DJ, Xu P (2003) Stoichiometric analysis and experimental investigation of glycerol bioconversion to 1,3-propanediol by Klebsiella pneumoniae under microaerobic conditions. Enzyme Microb Technol 33:386–394
Cheng KK, Liu DH, Sun Y, Liu WB (2004) 1,3-Propanediol production by Klebsiella pneumoniae under different aeration strategies. Biotechnol Lett 26:911–915
Zhang YP, Li Y, Du CY, Liu M, Cao ZA (2006) Inactivation of aldehyde dehydrogenase: a key factor for engineering 1,3-propanediol production by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Metab Eng 8:578–586
Forage RG, Lin EC (1982) DHA system mediating aerobic and anaerobic dissimilation of glycerol in Klebsiella pneumoniae NCIB 418. J Bacteriol 151:591–599
Tong IT, Liao HH, Cameron DC (1991) 1,3-Propanediol production by Escherichia coli expressing genes from the Klebsiella pneumoniae dha regulon. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3541–3546
Sun JB, Heuvel JVD, Soucaille P, Qu YB, Zeng AP (2003) Comparative genomic analysis of dha regulon and related genes for anaerobic glycerol metabolism in bacteria. Biotechnol Prog 19:263–272
Ahrens K, Menzel K, Zeng AP, Deckwer WD (1998) Kinetic, dynamic, and pathway studies of glycerol metabolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae in anaerobic continuous culture: III. Enzymes and fluxes of glycerol dissimilation and 1,3-propanediol formation. Biotechnol Bioeng 59:544–552
Tobimatsu T, Azuma M, Matsubara H, Takatori H, Niida T, Nishimoto K, Satoh H, Hayashi R, Toraya T (1996) Cloning, sequencing, and high level expression of the genes encoding adenosylcobalamin-dependent glycerol dehydrase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Biol Chem 271:22352–22357
Zeng AP, Menzel K, Deckwer WD (1996) Kinetic, dynamic, and pathway studies of glycerol metabolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae in anaerobic continuous culture: II. Analysis of metabolic rates and pathways under oscillation and steady-state conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng 52:561–571
Fischer E, Sauer U (2005) Large-scale in vivo flux analysis shows rigidity and suboptimal performance of Bacillus subtilis metabolism. Nat Genet 37:636–640
Wiechert W, Mollney M, Petersen S, de Graaf AA (2001) A universal framework for 13C metabolic flux analysis. Metab Eng 3:265–283
Zhao J, Shimizu K (2003) Metabolic flux analysis of Escherichia coli K12 grown on 13C-labeled acetate and glucose using GC-MS and powerful flux calculation method. J Biotechnol 10:101–117
Sauer U (2004) High-throughput phenomics: experimental methods for mapping fluxomes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15:58–63
Stephanopoulos G (1999) Metabolic fluxes and metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 1:1–11
Shirai T, Nakato A, Izutani N, Nagahisa K, Shioya S, Kimura E, Kawarabayasi Y, Yamagishi A, Gojobori T, Shimizu H (2005) Comparative study of flux redistribution of metabolic pathway in glutamate production by two coryneform bacteria. Metab Eng 7:59–69
Ozkan P, sariyar B, Utkur FO, Akman U, Hortacsu A (2005) Metabolic flux analysis of recombinant protein overproduction in Escherichia coli. Biochem Eng J 22:167–195
Maczek J, Junne S, Nowak P, Goetz P (2006) Metabolic flux analysis of the sterol pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 29:241–252
Sanchez AM, Bennett GN, San KY (2006) Batch culture characterization and metabolic flux analysis of succinate-producing Escherichia coli strains. Metab Eng 8:209–226
Sun JB, Zeng AP (2004) IdentiCS—identification of coding sequence and in silico reconstruction of the metabolic network directly from unannotated low-coverage bacterial genome sequence. BMC Bioinformatics 5:112–124
Zeng AP, Biebl H, Schlieker H, Deckwer WD (1993) Pathway analysis of glycerol fermentation by Klebsiella pneumoniae: regulation of reducing equivalent balance and product formation. Enzyme Microb Technol 15:770–779
Menzel K, Zeng AP, Biebl H, Deckwer WD (1996) Kinetic, dynamic, and pathway studies of glycerol metabolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae in anaerobic continuous culture: Ι. The phenomena and characterization of oscillation and hysteresis. Biotechnol Bioeng 52:549–560
Menzel K, Zeng AP, Deckwer WD (1997) Enzymatic evidence of involvement of pyruvate dehydrogenase in anaerobic glycerol metabolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Biotechnol 56:135–142
Menzel K, Ahrens K, Zeng AP, Deckwer WD (1998) Kinetic, dynamic, and pathway studies of glycerol metabolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae in anaerobic continuous culture: IV. Enzymes and fluxes of pyruvate metabolism. Biotechnol Bioeng 60:617–626
Guest J, Green J, Irvine A, Spiro S, (1996) The FNR modulon and FNR-regulated gene expression. In: Lin ECC, Lynch AS (eds) Regulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. RG Landes Company, Austin pp 317–342
Crack J, Green J, Thomson AJ (2004) Mechanism of oxygen sensing by the bacterial transcription factor fumarate-nitrate reduction (FNR). J Biol Chem 279:9278–9286
Salmon K, Hung SP, Mekjian K, Baldi P, Hatfield GW, Gunsalus RP (2003) Global gene expression profiling in Escherichia coli K12: the effects of oxygen availability and FNR. J Biol Chem 278:29837–29855
Kang YS, Weber KD, Qiu Y, Kiley PJ, Blattner FR (2005) Genome-wide expression analysis indicates that FNR of Escherichia coli k-12 regulates a large number of genes of unknown function. J Bacteriol 187:1135–1160
Grabbe R, Kuhn A, Schmitz RA (2001) Cloning, sequencing and characterization of Fnr from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 79:319–326
Grabbe R, Klopprogge K, Schmitz RA (2001) FNR Is required for NifL-dependent oxygen control of nif gene expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 183:1385–1393
Du CY, Yan H, Zhang YP, Li Y, Cao ZA (2006) Use of oxidoreduction potential as an indicator to regulate 1,3-propanediol fermentation by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:554–563
Zeng AP, Deckwer WD (1995) A kinetic model for substrate and energy consumption of microbial growth under substrate-sufficient conditions. Biotechnol Prog 11:71–79
Daniel R, Boenigk R, Gottschalk G (1995) Purification of 1,3-propanediol dehydrogenase from Citrobacter freundii and cloning, sequencing, and overexpression of the corresponding gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177:2151–2156
Barbirato F, Larguier A, Conte T, Astruc S, Bories A (1997) Sensitivity to pH, product inhibition, and inhibition by NAD+ of 1,3-propanediol dehydrogenase purified from Enterobacter agglomerans CNCM 1210. Arch Microbiol 168:160–163
Menzel K (1999) Analyse der Stofffluesse und Metabolic Engineering der Glycerinvergaerung zu 1,3-Propandiol durch Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ph.D. thesis, German Research Center for Biotechnology (GBF), Braunschweig
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20576018) and the grant from the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (No.2007CB714306).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1: List of metabolic reactions
-
1.
Glycerol_ext → Glycerol
-
2.
Glycerol → 3-HPA + H2O
-
3.
3-HPA + NADH2 → 1,3-PD + NAD
-
4.
Glycerol + NAD + ATP → DHAP + NADH2 + ADP
-
5.
DHAP → GA3P
-
6.
GA3P + NAD + PI + ADP → PEP + ATP + NADH2 + H2O
-
7.
PEP + ADP → PYR + ATP
-
8.
PYR + COA + NAD → ACCOA + CO2 + NADH2
-
9.
PYR + COA → ACCOA + Formate
-
10.
Formate → CO2 + H2
-
11.
ACCOA + 2 NADH2 → Ethanol + 2 NAD + COA
-
12.
ACCOA + ADP → AC + ATP + COA
-
13.
2PYR → Acetoin + 2CO2
-
14.
Acetoin + NADH2 → 2,3-BD + NAD
-
15.
PYR + NADH2 → LAC + NAD
-
16.
GA3P + DHAP + ADP → F6P + ATP
-
17.
F6P → G6P
-
18.
G6P + 2 NADP + H2O → R5P + CO2 + 2 NADPH
-
19.
R5P → RIB5P
-
20.
R5P → XYL5P
-
21.
RIB5P + XYL5P → S7P + GA3P
-
22.
S7P + GA3P → E4P + F6P
-
23.
XYL5P + E4P → F6P + GA3P
-
24.
ACCOA + OA → CIT + COA
-
25.
CIT + NAD → AKG + NADH2 + CO2
-
26.
OA + 2 NADH2 → SUCC + 2 NAD
-
27.
PEP + ADP + CO2 → OA + ATP
-
28.
0.35 G6P + 0.523 F6P + 0.952 RIB5P + 0.4075EP + 0.383 PEP + 3.13 PYR + 1.346AKG + 1.6 OA + 1.13 ACCOA + 16.3 ATP + 6.75 NAD + 17.8 NADPH → 1g Biomass + 16.3 ADP + 6.75 NADH2 + 17.8 NADP
-
29.
PYR → PYR_ext
-
30.
Formate → Formate_ext
-
31.
CIT_ext → CIT
-
32.
Acetoin → Acetoin_ext
-
33.
CO2 → CO2_ext
Appendix 2: Summary of abbreviations for the list of metabolic reactions
Table 1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Teng, H., Sun, Y. et al. Metabolic flux and robustness analysis of glycerol metabolism in Klebsiella pneumoniae . Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 31, 127–135 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-007-0155-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-007-0155-7