Abstract
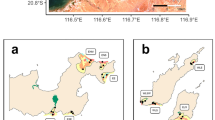
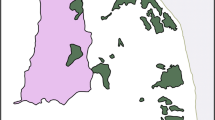
Habitat variability at multiple spatial scales may affect community structure within a given habitat patch, even within seemingly homogenous landscapes. In this context, we tested the importance of habitat variables at two spatial scales (patch and landscape) in driving fish community assembly using experimental artificial reefs constructed across a gradient of seagrass cover in a coastal bay of The Bahamas. We found that species richness and benthic fish abundance increased over time, but eventually reached an asymptote. The correlation between habitat variables and community structure strengthened over time, suggesting deterministic processes were detectable in community assembly. Abundance of benthic fishes, as well as overall community structure, were predicted by both patch- and landscape-scale variables, with the cover of seagrass at the landscape-scale emerging as the most important explanatory variable. Results of this study indicate that landscape features can drive differences in community assembly even within a general habitat type (i.e., within seagrass beds). A primary implication of this finding is that human activities driving changes in seagrass cover may cause significant shifts in faunal community structure well before complete losses of seagrass habitat.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alevizon WS, Gorham JC, Richardson R, Mccarthy SA (1985) Use of man-made reefs to concentrate snapper (Lutjanidae) and grunts (Haemulidae) in Bahamian waters. Bull Mar Sci 37:3–10
Almany GR (2003) Priority effects in coral reef fish communities. Ecology 84:1920–1935
Ansari ZA, Rivonker CU, Ramani P, Parulekar AH (1991) Seagrass habitat complexity and macroinvertebrate abundance in lakshadweep coral-reef lagoons, Arabian Sea. Coral Reefs 10:127–131
Arrington DA, Winemiller KO, Layman CA (2005) Community assembly at the patch scale in a species rich tropical river. Oecologia 144:157–167
Atema J, Kingsford M, Gerlach G (2002) Larval reef fish could use odour for detection, retention and orientation to reefs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 241:151–160
Beck M et al (2001) The identification, conservation, and management of estuarine and marine nurseries for fish and invertebrates. Bioscience 51:633–641
Bell SS, Brooks RA, Robbins BD, Fonseca MS, Hall MO (2001) Faunal response to fragmentation in seagrass habitats: implications for seagrass conservation. Biol Conserv 100:115–123
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER v6. PRIMER-E, UK
Cocheret de la Moriniere E, Pollux BJA, Nagelkerken I, van der Velde G (2003) Diet shifts of Caribbean grunts (Haemulidae) and snappers (Lutjanidae) and the relation with nursery-to-coral reef migrations. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 57:1079–1089
Debinski DM, Holt RD (2000) Review: a survey and overview of habitat fragmentation experiments. Conserv Biol 14:342–355
Draper N, Smith H (1998) Applied regression analysis, 30th edn. Wiley, USA
ERSI (2008) ArcGIS v 9. Redlands, USA
Faunce CH, Layman CA (2009) Sources of variation that affect perceived nursery function in mangroves. In: Nagelkerken I (ed) Ecological linkages across tropical coastal ecosystems. Springer, USA, pp 401–421
Fonseca MS, Bell SS (1998) Influence of physical setting on seagrass landscapes near Beaufort, North Carolina, USA. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 171:109–121
Fonseca M, Whitfield PE, Kelly NM, Bell SS (2002) Modeling seagrass landscape pattern and associated ecological attributes. Ecol Appl 12:218–237
Fourqurean JW, Willsie A, Rose CD, Rutten LM (2001) Spatial and temporal pattern in seagrass community composition and productivity in south Florida. Mar Biol 138:341–354
Gladfelter WB, Ogden JC, Gladfelter EH (1980) Similarity and diversity among coral reef fish communities a comparison between tropical Western Atlantic (Virgin Islands) and tropical Central Pacific (Marshall Islands) patch reefs. Ecology 61:1156–1168
Google (2010) Google Earth®, v 5.1
Grabowski JH, Hughes AR, Kimbro DL, Dolan MA (2005) How habitat setting influences restored oyster reef communities. Ecology 86:1926–1935
Grober-Dunsmore R, Frazer TK, Beets JP, Lindberg WJ, Zwick P, Funicelli NA (2008) Influence of landscape structure on reef fish assemblages. Landsc Ecol 23:37–53
Grober-Dunsmore R, Pittman SJ, Caldow C, Kendall MS, Frazer TK (2009) A landscape ecology approach for the study of ecological connectivity across tropical marine seascapes. In: Nagelkerken I (ed) Ecological connectivity among tropical coastal ecosystems. Springer, New York, pp 493–530
Gunst RF, Mason RL (1980) Regression analysis and its application: a data-oriented approach. Marcel Dekker, USA
Heck K, Hays G, Orth RJ (2003) Critical evaluation of the nursery role hypothesis for seagrass meadows. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 253:123–136
Hixon MA, Beets JP (1989) Shelter characteristics and Caribbean fish assemblages: experiments with artificial reefs. Bull Mar Sci 44:666–680
Hovel KA, Fonseca MS (2005) Influence of seagrass landscape structure on the juvenile blue crab habitat–survival function. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 300:179–191
Hovel KA, Lipcius RN (2002) Effects of seagrass habitat fragmentation on juvenile blue crab survival and abundance. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 271:75–98
Huijbers C, Mollee E, Nagelkerken I (2008) Post-larval French grunts (Haemilon flavolineatum) distinguish between seagrass, mangrove and coral reef water: implicaltions for recognition of potential nursery habitats. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 357:134–139
Ims RA (2005) The role of experiments in landscape ecology. In: Wiens JA, Moss MR (eds) Issues and perspectives in landscape ecology. Cambridge University Press, UK, pp 70–78
Irlandi EA (1994) Large-scale and small-scale effects of habitat structure on rates of predation: how percent coverage of seagrass affects rates of predation and siphon nipping on an infaunal bivalve. Oecologia 98:176–183
Irlandi EA, Crawford MK (1997) Habitat linkages: the effect of intertidal saltmarshes and adjacent subtidal habitats on abundance, movement, and growth of an estuarine fish. Oecologia 110:222–230
Irlandi EA, Ambrose WG, Orlando BA (1995) Landscape ecology and the marine-environment: how spatial configuration of seagrass habitat influences growth and survival of the bay scallop. Oikos 72:307–313
Kendall MS, Christensen JD, Hillis-Starr Z (2003) Multi-scale data used to analyze the spatial distribution of French grunts, Haemulon flavolineatum, relative to hard and soft bottom in a benthic landscape. Environ Biol Fish 66:19–26
Kirsch KD, Valentine JF, Heck KL (2002) Parrotfish grazing on turtlegrass Thalassia testudinum: evidence for the importance of seagrass consumption in food web dynamics of the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 227:71–85
Kraan C, van der Meer J, Dekinga A, Piersma T (2009) Patchiness of macrobenthic invertebrates in homogenized intertidal habitats: hidden spatial structure at a landscape scale. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 383:211–224
Layman CA, Silliman BR (2002) Preliminary survey and diet analysis of juvenile fishes of an estuarine creek on Andros Island, Bahamas. Bull Mar Sci 70:199–210
Layman CA, Arrington DA, Langerhans RB, Silliman BR (2004) Degree of fragmentation affects fish assemblage structure in Andros Island (Bahamas) estuaries. Caribb J Sci 40:232–244
Layman CA, Quattrochi JP, Peyer CM, Allgeier JE (2007) Niche width collapse in a resilient top predator following ecosystem fragmentation. Ecol Lett 10:937–944
Levin SA (1992) The problem of pattern and scale in ecology. Ecology 73:1943–1967
Lirman D, Cropper WP Jr (2003) The influence of salinity on seagrass growth, survivorship and distribution within Biscayne Bay, Florida: field, experimental and modeling studies. Estuaries 26:131–141
Lotze HK et al (2006) Depletion, degradation, and recovery potential of estuaries and coastal seas. Science 312:1806–1809
Luo JG, Serafy JE, Sponaugle S, Teare PB, Kieckbusch D (2009) Movement of gray snapper Lutjanus griseus among subtropical seagrass, mangrove, and coral reef habitats. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 380:255–269
McGarigal K, Cushman SA, MNeel MC, Ene E (2002) FRAGSTATS: spatital pattern analysis program for categorical maps, 3.3 edn. University of Massachusetts, Amherst
Mellin C, Andrefouet S, Kulbicki M, Dalleau M, Vigliola L (2009) Remote sensing and fish-habitat relationships in coral reef ecosystems: review and pathways for systematic multi-scale hierarchical research. Mar Pollut Bull 58:11–19
Miller MW (2002) Using ecological processes to advance artificial reef goals. Ices J Mar Sci 59:S27–S31
Montefalcone M et al (2010) Human influence on seagrass habitat fragmentation in NW Mediterranean Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 86:292–298
Montgomery J, Tolimieri N, Haine O (2001) Active habitat selection by pre-settlement reef fishes. Fish Fish 2:261–277
Mumby PJ (2006) Connectivity of reef fish between mangroves and coral reefs: algorithms for the design of marine reserves at seascape scales. Biol Conserv 128:215–222
Nagelkerken I, Dorenbosch M, Verberk WCEP, de la Moriniere EC, van der Velde G (2000a) Day–night shifts of fishes between shallow-water biotopes of a Caribbean bay, with emphasis on the nocturnal feeding of Haemulidae and Lutjanidae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 194:55–64
Nagelkerken I, van der Velde G, Gorissen MW, Meijer GJ, van’t Hof T, den Hartog C (2000b) Importance of mangroves, seagrass beds and the shallow coral reef as a nursery for important coral reef fishes, using a visual census technique. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 51:31–44
Nakamura Y, Sano M (2005) Comparison of invertebrate abundance in a seagrass bed and adjacent coral and sand areas at Amitori Bay, Iriomote Island, Japan. Fish Sci 71:543–550
Ogden JC, Ehrlich PR (1977) Behavior of heterotypic resting schools of juvenile grunts (Pomadasyidae). Mar Biol 42:273–280
Orth RJ et al (2006) A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 56:987–996
Pickett STA, Cadenasso ML (1995) Landscape ecology: spatial heterogeneity in ecological-systems. Science 269:331–334
Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J Theor Biol 13:131–144
Pittman SJ, McAlpine CA, Pittman KM (2004) Linking fish and prawns to their environment: a hierarchical landscape approach. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 283:233–254
Pittman SJ, Caldow C, Hile SD, Monaco ME (2007) Using seascape types to explain the spatial patterns of fish in the mangroves of SW Puerto Rico. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 348:273–284
Randall JE (1967) Food habitat of reef fishes of the West Indies. Stud Trop Oceanogr 5:665–847
Robbins BD, Bell SS (1994) Seagrass landscapes: a terrestrial approach to the marine subtidal environment. Trends Ecol Evol 9:301–304
Sale PF, Douglas WA (1984) Temporal variability in the community structure of fish on coral patch reefs and the relation of community structure to reef structure. Ecology 65:409–422
Sandel B, Smith AB (2009) Scale as a lurking factor: incorporating scale-dependence in experimental ecology. Oikos 118:1284–1291
SAS Institute (2007) SAS v.9.2. Cary, USA
Schneider DC (2001) The rise of concept of scale in ecology. Bioscience 51:545–553
Shulman MJ (1985) Recruitment of coral reef fishes: effects of distribution of predators and shelter. Ecology 66:1056–1066
Shulman MJ, Ogden JC (1987) What controls tropical reef fish populations: recruitment or bethic mortality? An example in the Caribbean reef fish Haemulon flavolineatum. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 39:233–242
Shulman MJ, Ogden JC, Ebersole JP, McFarland WN, Miller SL, Wolf NG (1983) Priority effects in the recruitment of juvenile coral reef fishes. Ecology 64:1508–1513
SPSS (2005) SPSS v.14.0. Chicago, USA
Syms C, Jones GP (2000) Disturbance, habitat structure, and the dynamics of a coral-reef fish community. Ecology 81:2714–2729
Turner MG (1989) Landscape ecology—the effect of pattern on process. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 20:171–197
Velleman P, Welsch R (1981) Efficient computing of regression diagnostics. Am Stat 35:234–242
Wu JG, Hobbs R (2002) Key issues and research priorities in landscape ecology: an idiosyncratic synthesis. Landsc Ecol 17:355–365
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by National Science Foundation OCE #0746164, a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship, and a Florida International University Presidential Fellowship. We thank Friends of the Environment, D. Haines and F. DeRosa on Abaco for their logistical support and the Department of Marine Resources of The Bahamas for research permits. Field assistance and help with data management was provided by A. Anton, C. Acevedo, D. Chacin, G. Mineau, L. Pierre, M. Seese, M. Simpson and E. Stoner. Also, we thank J. Trexler for advice on data analysis, M. Donnelly, members of the Layman Lab, J. Fodrie and an anonymous reviewer for their valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jeff Shima.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeager, L.A., Layman, C.A. & Allgeier, J.E. Effects of habitat heterogeneity at multiple spatial scales on fish community assembly. Oecologia 167, 157–168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-011-1959-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-011-1959-3