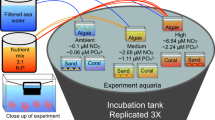
Abstract
Restoration of degraded coral reef communities is dependent on successful recruitment and survival of new coral planulae. Degraded reefs are often characterized by high cover of fleshy algae and high microbial densities, complemented by low abundance of coral and coral recruits. Here, we investigated how the presence and abundance of macroalgae and microbes affected recruitment success of a common Hawaiian coral. We found that the presence of algae reduced survivorship and settlement success of planulae. With the addition of the broad-spectrum antibiotic, ampicillin, these negative effects were reversed, suggesting that algae indirectly cause planular mortality by enhancing microbial concentrations or by weakening the coral’s resistance to microbial infections. Algae further reduced recruitment success of corals as planulae preferentially settled on algal surfaces, but later suffered 100% mortality. In contrast to survival, settlement was unsuccessful in treatments containing antibiotics, suggesting that benthic microbes may be necessary to induce settlement. These experiments highlight potential complex interactions that govern the relationships between microbes, algae and corals and emphasize the importance of microbial dynamics in coral reef ecology and restoration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aluwihare LI, Repeta DJ (1999) A comparison of the chemical characteristics of oceanic DOM and extracellular DOM produced by marine algae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 186:105–117
Aluwihare LI, Repeta DJ, Chen RF (1997) A major biopolymeric component to dissolved organic carbon in surface sea water. Nature 387:166–169
Babcock RC, Baird AH, Piromvaragorn S, Thomson DP, Willis BL (2003) Identification of scleractinian coral recruits from Indo-Pacific reefs. Zool Stud 42:211–226
Baird AH, Morse ANC (2004) Induction of metamorphosis in larvae of the brooding corals Acropora palifera and Stylophora pistillata. Mar Fresh Res 55:469–472
Bak RPM, Borsboom JLA (1984) Allelopathic interaction between a reef coelenterate and benthic algae. Oecologia 63:194–198
Bhadury P, Wright PC (2004) Exploitation of marine algae: biogenic compounds for potential antifouling applications. Planta 219:561–578
Birkeland C (1977) The importance of rate of biomass accumulation in early successional stages of benthic communities to the survival of coral recruits. Proc. 3rd Int. Coral Reef Symp. Miami 1:331–336
Birrell CL, McCook LJ, Willis BL (2005) Effects of algal turfs and sediment on coral settlement. Mar Pollut Bull 51:408–414
Box SJ, Mumby PJ (2007) Effect of macroalgal competition on growth and survival of juvenile. Caribb Corals 342:139–149
Brun FG, Vergara JJ, Navarro G, Hernández I, Pérez-Lloréns JL (2003) Effect of shading by Ulva rigida canopies on growth and carbon balance of the seagrass Zostera noltii. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 265:85–96
Brylinsky M (1977) Release of dissolved organic matter by some marine macrophytes. Mar Biol 3:213–220
Caley MJ, Carr MH, Hixon MA, Hughes TP, Jones GP, Menge BA (1996) Recruitment and the local dynamics of open marine populations. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 27:477–500
Cole JJ, Likens GE, Strayer DL (1982) Photosynthetically produced dissolved organic carbon: an important carbon source for planktonic bacteria. Limnol Oceanogr 27:1080–1090
Cumming RL (1999) Predation on reef-building corals: multiscale variation in the density of three corallivorous gastropods, Drupella sp. Coral Reefs 18:147–157
Dayton PK (1971) Competition, disturbance, and community organization: the provision and subsequent utilization of space in a rocky intertidal community. Ecol Monogr 41:351–389
Dobson AP, Hudson PJ (1986) Parasites, disease and the structure of ecological communities. Trends Ecol Evol 1:11–15
Done TJ (1992) Phase shifts in coral reef communities and their ecological significance. Hydrobiologia 247:121–132
Edmunds PJ, Carpenter RC (2001) Recovery of Diadema antillarum reduces macroalgal cover and increases abundance of juvenile corals on a Caribbean reef. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5067–5071
Frias-Lopez J, Zerkle AL, Bonheyo GT, Fouke BW (2002) Partitioning of bacterial communities between seawater and healthy, black band diseased, and dead coral surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2214–2228
Gardner TA, Côté IM, Gill JA, Grant A, Watkinson AR (2003) Long-term region-wide declines in Caribbean corals. Science 301:958–960
Golbuu Y, Robson B, Hunter RH (1995) Settlement preference by larvae of the coral Stylaraea punctata. Seventh International Conference on Invertebrate Reproduction, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA, USA (abstract)
Grant WS (1977) High intertidal community structure on a rocky headland in Maine, USA. Mar Biol 44:15–25
Grizzle RE, Short FT, Newell CR, Hoven H, Kindblom L (1996) Hydrodynamically induced synchronous waving of seagrasses: ‘monami’ and its possible effects on larval mussel settlement. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 206:165–177
Gross EM (2003) Allelopathy of aquatic autotrophs. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:313–339
Harrington L, Fabricius K, De’ath G, Negri A (2004) Recognition and selection of settlement substrata determine post-settlement survival in corals. Ecology 85:3428–3437
Harvell CD, Kim K, Burkholder JM, Colwell RR, Epstein PR, Grimes DJ, Hofmann EE, Lipp EK, Osterhaus ADME, Overstreet RM, Porter JW, Smith GW, Vasta GR (1999) Emerging marine diseases—climate links and anthropogenic factors. Science 285:1505–1510
Heyward AJ, Negri AP (1999) Natural inducers for coral larval metamorphosis. Coral Reefs 18:273–279
Hilborn R, Mangel M (1997) The ecological detective: confronting models with data. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Hoegh-Guldberg O (1999) Climate change, coral bleaching and the future of the world’s coral reefs. Mar Fresh Res 50:839–866
Horn HS (1975) Markovian properties of forest succession. In: Cody ML, Diamond JM (eds) Ecology and evolution of communities. Belknap Press, Cambridge, pp 196–211
Hudson P, Greenman J (1998) Competition mediated by parasites: biological and theoretical progress. Trends Ecol Evol 13:387–390
Hughes TP (1989) Community structure and diversity of coral reefs: the role of history. Ecology 70:275–279
Hughes TP (1996) Demographic approaches to community dynamics: a coral reef example. Ecology 77:2256–2260
Hughes TP (1994) Catastrophes, phase shifts, and large-scale degradation of a Caribbean coral reef. Science 265:1547–1551
Hughes TP, Jackson JBC (1985) Population dynamics and life histories of foliaceous corals. Ecol Monogr 55:141–166
Hughes TP, Rodrigues MJ, Bellwood DR, Ceccarelli D, Hoegh-Guldberg O, McCook L, Moltschaniwskyj N, Pratchett MS, Steneck RS, Willis B (2007) Phase shifts, herbivory, and the resilience of coral reefs to climate change. Curr Biol 17:360–365
Hunter CL, Evans CW (1995) Coral reefs in Kaneohe Bay, Hawai’i: two centuries of western influence and two decades of data. Bull Mar Sci 57:501–515
Jackson JBC (1977) Competition on marine hard substrata: the adaptive significance of solitary and colonial strategies. Am Nat 111:743–767
Jackson JBC, Kirby MX, Berger WH, Bjorndal KA, Botsford LW, Bourque BJ, Bradbury RH, Cooke R, Erlandson J, Estes JA, Hughes TP, Kidwell S, Lange CB, Lenihan HS, Pandolfi JM, Peterson CH, Steneck RS, Tegner MJ, Warner RR (2001) Historical overfishing and the recent collapse of coastal ecosystems. Science 293:629–637
Johnson D, Welsh B (1985) Detrimental effects of Ulva lactuca (L.) exudates and low oxygen on estuarine crab larvae. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 86:73–83
Jompa J, McCook LJ (2003) Coral–algal competition: macroalgae with different properties have different effects on corals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 258:87–95
Kelman D, Kushmaro A, Loya Y, Kashman Y, Benayahu Y (1998) Antimicrobial activity of a red sea soft coral, Parerythropodium fulvum fulvum: reproductive and developmental considerations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 169:87–95
Khailov KM, Burlakova ZP (1969) Release of dissolved organic matter by marine seaweeds and distribution of their total organic production to inshore communities. Limnol Oceanogr 14:521–527
Kline DI, Kuntz NM, Breitbart M, Knowlton N, Rohwer F (2006) Role of elevated organic carbon and microbial activity in coral mortality. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 314:119–125
Koh EGL (1997) Do scleractinian corals engage in chemical warfare against microbes? J Chem Ecol 23:379–398
Kuffner IB, Paul VJ (2004) Effects of the benthic cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula on larval recruitment of the reef corals Acropora surculosa and Pocillopora damicornis. Coral Reefs 23:455–458
Kuffner IB, Walters LJ, Becerro MA, Paul VJ, Ritson-Williams R, Beach KS (2006) Inhibition of coral recruitment by macroalgae and cyanobacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 323:107–117
Kuntz NM, Kline DI, Sandin SA, Rohwer F (2005) Pathologies and mortality rates caused by organic carbon and nutrient stressors in three Caribbean coral species. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 294:173–180
Ledlie MH, Graham NAJ, Bythell JC, Wilson SK, Jennings S, Polunin NVC, Hardcastle J (2007) Phase shifts and the role of herbivory in the resilience of coral reefs. Coral Reefs 26:641–653
Leitz T (1997) Induction of settlement and metamorphosis of cnidarian larvae: signals and signal transduction. Invert Reprod Dev 31:109–122
Lesser MP, Bythell JC, Gates RD, Johnstone RW, Hoegh-Guldberg O (2007) Are infectious diseases really killing corals? Alternative interpretations of the experimental and ecological data. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 346:36–44
Lindquist N (2002) Chemical defense of early life stages of benthic marine invertebrates. J Chem Ecol 28:1987–2000
Lindquist N, May ME, Fenical W (1992) Defenses of ascidians and their conspicuous larvae: adult versus larval chemical defenses. Ecol Monogr 62:547–568
Magre EJ (1974) Ulva lactuca L. negatively affects Balanus balanoides (L.) (Cirripedia: Thoracica) in tidepools. Crustaceana 27:231–234
Maida M, Sammarco PW, Coll JC (2001) Effects of soft corals on scleractinian coral recruitment. II: Allelopathy, spat survivorship and reef community structure. Mar Ecol 22:397–414
McCook LJ (2001) Competition between coral and algal turfs along a gradient of terrestrial runoff in the nearshore central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 19:419–425
McCook LJ, Jompa J, Diaz-Pulido G (2001) Competition between corals and algae on coral reefs: a review of evidence and mechanisms. Coral Reefs 19:400–417
Miller MW, Hay ME (1996) Coral-seaweed-grazer-nutrient interactions on temperate reefs. Ecol Monogr 66:323–344
Mitchell R, Chet I (1975) Bacterial attack of corals in polluted seawater. Microb Ecol 2:227–233
Morse DE, Hooker N, Morse ANC, Jensen RA (1988) Control of larval metamorphosis and recruitment in sympatric agariciid corals. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 116:193–217
Mumby PJ, Harborne AR, Williams J, Cappel CV, Brumbaugh DR, Micheli F, Holmes KE, Dahlgren CP, Paris CB, Blackwell PG (2007) Trophic cascade facilitates coral recruitment in a marine reserve. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8362–8367
Negri AP, Webster NS, Hill RT, Heyward AJ (2001) Metamorphosis of broadcast spawning corals in response to bacteria isolated from crustose algae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 223:121–131
Neumann R (1979) Bacterial induction of settlement and metamorphosis in the planulae larvae Cassiopea andromeda (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa, Rhizostomeae). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 1:21–28
Nugues MM (2002) Impact of a coral disease outbreak on coral communities in St Lucia: what and how much has been lost? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 229:61–71
Nugues MM, Delvoye L, Bak RPM (2004a) Coral defence against macroalgae: differential effects of mesenterial filaments on the green alga Halimeda opuntia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 278:103–114
Nugues MM, Smith GW, van Hooidonk RJ, Seabra MI, Bak RPM (2004b) Algal contact as a trigger for coral disease. Ecol Lett 7:919–923
Nugues MM, Szmant AM (2006) Coral settlement onto Halimeda opuntia: a fatal attraction to an ephemeral substrate? Coral Reefs 25:585–591
Paine RT (1984) Ecological determinism in the competition for space: the Robert H. MacArthur Award Lecture. Ecology 65:1339–1348
Paul VJ, Puglisi MP (2004) Chemical mediation of interactions among marine organisms. Nat Prod Rep 21:189–209
Richmond RH (1987) Energetics, competency, and long-distance dispersal of planula larvae of the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Mar Biol 93:527–533
Rogers CS, Fitz HC, Gilnack M, Beets J, Hardin J (1984) Scleractinian coral recruitment patterns at Salt River submarine canyon, St Croix, US Virgin Islands. Coral Reefs 3:69–76
Sebens KP (1989) Competition for space: growth rate, reproductive output, and escape in size. Am Nat 120:189–197
Slattery M, Hines GA, Starmer J, Paul VJ (1999) Chemical signals in gametogenesis, spawning, and larval settlement and defense of the soft coral Sinularia polydactyla. Coral Reefs 18:75–84
Smith JE, Shaw M, Edwards RA, Obura D, Pantos O, Sala E, Sandin SA, Smriga S, Hatay M, Rohwer FL (2006) Indirect effects of algae on coral: algae-mediated, microbe-induced coral mortality. Ecol Lett 9:835–845
Stanley EH, Johnson MD, Ward AK (2003) Evaluating the influence of macrophytes on algal and bacterial production in multiple habitats of a freshwater wetland. Limnol Oceanogr 48:1101–1111
Vermeij MJA (2005) Substrate characteristics and adult density determine recruitment patterns in a Caribbean brooding coral. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 295:123–133
Vermeij MJA (2006) Early life-history dynamics of Caribbean coral species on artificial substratum: the importance of competition, growth and variation in life-history strategy. Coral Reefs 25:59–71
Vermeij MJA, Fogarty ND, Miller MW (2006) Variable planktonic conditions affect larval behavior, survival, and settlement patterns in the Caribbean coral Montastraea faveolata. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 310:119–128
Vermeij MJA, Sandin SA (2008) Density-dependent settlement and mortality structure the earliest life phases of a coral population. Ecology (in press)
Webster NS, Smith LD, Heyward AJ, Watts JE, Webb RI, Blackall LL, Negri AP (2004) Metamorphosis of a scleractinian coral in response to microbial biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1213–1221
Wetzel RG (1982) Limnology, 2nd edn. Saunder College Publishing, Philadelphia
Wilkinson C (2002) Status of coral reefs of the world. Australian Institute of Marine Sciences, Townsville, Australia
Zaslow RBD, Benayahu Y (1996) Longevity, competence and energetic content in planulae of the soft coral Heteroxenia fuscescens. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 206:55–68
Acknowledgments
We thank Heather Spalding, Meghan Dailer and Christine Huffard for help with the collections of gametes during the coral spawning. Dave Gulko and the Hawai’i Department of Aquatic Resources (DAR) assisted with permitting procedures. We thank F.L. Rohwer for intellectual support and comments. This research was supported by a grant to CMS, no. NA03NOS4780020, from the Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research, National Ocean Service, NOAA. This ECOHAB publication #294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jeff Shima.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vermeij, M.J.A., Smith, J.E., Smith, C.M. et al. Survival and settlement success of coral planulae: independent and synergistic effects of macroalgae and microbes. Oecologia 159, 325–336 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-008-1223-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-008-1223-7