Abstract
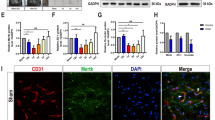
Transplantation of human umbilical cord blood (hucb) cells in a model of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury led to the amelioration of lesion-impaired neurological and motor functions. However, the mechanisms by which transplanted cells mediate functional recovery after brain injury are largely unknown. In this study, the effects of hucb cell transplantation were investigated in this experimental paradigm at the cellular and molecular level. As the pathological cascade in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury includes inflammation, reduced blood flow, and neuronal cell death, we analyzed the effects of peripherally administered hucb cells on these detrimental processes, investigating the expression of characteristic marker proteins. Application of hucb cells after perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury correlated with an increased expression of the proteins Tie-2 and occludin, which are associated with angiogenesis. Lesion-induced apoptosis, determined by expression of cleaved caspase-3, decreased, whereas the number of vital neurons, identified by counting of NeuN-positive cells, increased. In addition, we observed an increase in the expression of neurotrophic and pro-angiogenic growth factors, namely BDNF and VEGF, in the lesioned brain upon hucb cell transplantation. The release of neurotrophic factors mediated by transplanted hucb cells might cause a lower number of neurons to undergo apoptosis and result in a higher number of living neurons. In parallel, the increase of VEGF might cause growth of blood vessels. Thus, hucb transplantation might contribute to functional recovery after brain injury mediated by systemic or local effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV, Gomes JR, Mendes CS, Graos MM, Carvalho RF, Carvalho AP, Duarte CB (2005) Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ 12:1329–1343
Asai N, Abe T, Saito T, Sato H, Ishiguro S, Nishida K (2007) Temporal and spatial differences in expression of TrkB isoforms in rat retina during constant light exposure. Exp Eye Res 85:346–355
Bai XF, Zhu J, Zhang GX, Kaponides G, Hojeberg B, van der Meide PH, Link H (1997) IL-10 suppresses experimental autoimmune neuritis and down-regulates TH1-type immune responses. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 83:117–126
Balda MS, Whitney JA, Flores C, Gonzalez S, Cereijido M, Matter K (1996) Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J Cell Biol 134:1031–1049
Berger R, Garnier Y (2000) Perinatal brain injury. J Perinat Med 28:261–285
Bolton SJ, Anthony DC, Perry VH (1998) Loss of the tight junction proteins occludin and zonula occludens-1 from cerebral vascular endothelium during neutrophil-induced blood-brain barrier breakdown in vivo. Neuroscience 86:1245–1257
Bona E, Aden U, Gilland E, Fredholm BB, Hagberg H (1997) Neonatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia: the effect of adenosine receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 36:1327–1338
Buzanska L, Machaj EK, Zablocka B, Pojda Z, Domanska-Janik K (2002) Human cord blood-derived cells attain neuronal and glial features in vitro. J Cell Sci 115:2131–2138
Chen J, Li Y, Katakowski M, Chen X, Wang L, Lu D, Lu M, Gautam SC, Chopp M (2003a) Intravenous bone marrow stromal cell therapy reduces apoptosis and promotes endogenous cell proliferation after stroke in female rat. J Neurosci Res 73:778–786
Chen J, Zhang ZG, Li Y, Wang L, Xu YX, Gautam SC, Lu M, Zhu Z, Chopp M (2003b) Intravenous administration of human bone marrow stromal cells induces angiogenesis in the ischemic boundary zone after stroke in rats. Circ Res 92:692–699
Donovan MJ, Lin MI, Wiegn P, Ringstedt T, Kraemer R, Hahn R, Wang S, Ibanez CF, Rafii S, Hempstead BL (2000) Brain derived neurotrophic factor is an endothelial cell survival factor required for intramyocardial vessel stabilization. Development 127:4531–4540
Fukuhara S, Sako K, Minami T, Noda K, Kim HZ, Kodama T, Shibuya M, Takakura N, Koh GY, Mochizuki N (2008) Differential function of Tie2 at cell-cell contacts and cell-substratum contacts regulated by angiopoietin-1. Nat Cell Biol 10:513–526
Garbuzova-Davis S, Willing AE, Zigova T, Saporta S, Justen EB, Lane JC, Hudson JE, Chen N, Davis CD, Sanberg PR (2003) Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood cells in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: distribution, migration, and differentiation. J Hematother Stem Cell Res 12:255–270
Geissler M, Dinse HR, Kumbruch S, Kreikemeier K, Meier C (2011) Human umbilical cord blood cells restore brain damage induced changes in rat somatosensory cortex. PLoS One 6:e20194
Ha Y, Choi JU, Yoon DH, Yeon DS, Lee JJ, Kim HO, Cho YE (2001) Neural phenotype expression of cultured human cord blood cells in vitro. NeuroReport 12:3523–3527
Hagberg H, Mallard C, Rousset CI, Xiaoyang W (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms in the immature brain: involvement of mitochondria. J Child Neurol 24:1141–1146
Han BH, Holtzman DM (2000) BDNF protects the neonatal brain from hypoxic-ischemic injury in vivo via the ERK pathway. J Neurosci 20:5775–5781
Han BH, D'Costa A, Back SA, Parsadanian M, Patel S, Shah AR, Gidday JM, Srinivasan A, Deshmukh M, Holtzman DM (2000) BDNF blocks caspase-3 activation in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 7:38–53
Hossain MA (2008) Hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal brain: involvement of a novel neuronal molecule in neuronal cell death and potential target for neuroprotection. Int J Dev Neurosci 26:93–101
Jensen A, Berger R (1991) Fetal circulatory responses to oxygen lack. J Dev Physiol 16:181–207
Jin K, Zhu Y, Sun Y, Mao XO, Xie L, Greenberg DA (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) stimulates neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11946–11950
Kim SU, de Vellis J (2009) Stem cell-based cell therapy in neurological diseases: a review. J Neurosci Res 87:2183–2200
Lee HJ, Kim KS, Park IH, Kim SU (2007) Human neural stem cells over-expressing VEGF provide neuroprotection, angiogenesis and functional recovery in mouse stroke model. PLoS One 2:e156
Levine S (1960) Anoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in rats. Am J Pathol 36:1–17
Li A, Varney ML, Valasek J, Godfrey M, Dave BJ, Singh RK (2005) Autocrine role of interleukin-8 in induction of endothelial cell proliferation, survival, migration and MMP-2 production and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 8:63–71
Liu W, Hendren J, Qin XJ, Shen J, Liu KJ (2009) Normobaric hyperoxia attenuates early blood-brain barrier disruption by inhibiting MMP-9-mediated occludin degradation in focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 108:811–820
Makar TK, Trisler D, Sura KT, Sultana S, Patel N, Bever CT (2008) Brain derived neurotrophic factor treatment reduces inflammation and apoptosis in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neurol Sci 270:70–76
Marti HH (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor. Adv Exp Med Biol 513:375–394
Meier C, Middelanis J, Wasielewski B, Neuhoff S, Roth-Haerer A, Gantert M, Dinse HR, Dermietzel R, Jensen A (2006) Spastic paresis after perinatal brain damage in rats is reduced by human cord blood mononuclear cells. Pediatr Res 59:244–249
Nakajima W, Ishida A, Lange MS, Gabrielson KL, Wilson MA, Martin LJ, Blue ME, Johnston MV (2000) Apoptosis has a prolonged role in the neurodegeneration after hypoxic ischemia in the newborn rat. J Neurosci 20:7994–8004
Neuhoff S, Moers J, Rieks M, Grunwald T, Jensen A, Dermietzel R, Meier C (2007) Proliferation, differentiation, and cytokine secretion of human umbilical cord blood-derived mononuclear cells in vitro. Exp Hematol 35:1119–1131
Newman MB, Willing AE, Manresa JJ, Sanberg CD, Sanberg PR (2006) Cytokines produced by cultured human umbilical cord blood (HUCB) cells: implications for brain repair. Exp Neurol 199:201–208
Nikkhah G, Odin P, Smits A, Tingstrom A, Othberg A, Brundin P, Funa K, Lindvall O (1993) Platelet-derived growth factor promotes survival of rat and human mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons in culture. Exp Brain Res 92:516–523
Park CW, Kim HW, Lim JH, Yoo KD, Chung S, Shin SJ, Chung HW, Lee SJ, Chae CB, Kim YS, Chang YS (2009a) Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition by dRK6 causes endothelial apoptosis, fibrosis, and inflammation in the heart via the Akt/eNOS axis in db/db mice. Diabetes 58:2666–2676
Park DH, Eve DJ, Musso J 3rd, Klasko SK, Cruz E, Borlongan CV, Sanberg PR (2009b) Inflammation and stem cell migration to the injured brain in higher organisms. Stem Cells Dev 18:693–702
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e36
Pimentel-Coelho PM, Magalhaes ES, Lopes LM, Deazevedo LC, Santiago MF, Mendez-Otero R (2010) Human cord blood transplantation in a neonatal rat model of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: functional outcome related to neuroprotection in the striatum. Stem Cells Dev 19:351–358
Plate KH, Beck H, Danner S, Allegrini PR, Wiessner C (1999) Cell type specific upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in an MCA-occlusion model of cerebral infarct. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:654–666
Ramakers C, Ruijter JM, Deprez RH, Moorman AF (2003) Assumption-free analysis of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) data. Neurosci Lett 339:62–66
Rice JE 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB (1981) The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9:131–141
Rosenkranz K, Meier C (2011) Umbilical cord blood cell transplantation after brain ischemia-From recovery of function to cellular mechanisms. Ann Anat 193:371–379
Rosenkranz K, Kumbruch S, Lebermann K, Marschner K, Jensen A, Dermietzel R, Meier C (2010) The chemokine SDF-1 / CXCL12 contributes to the 'homing' of umbilical cord blood cells to a hypoxic-ischemic lesion in the rat brain. J Neurosci Res 88:1223–1233
Sanchez-Ramos JR, Song S, Kamath SG, Zigova T, Willing A, Cardozo-Pelaez F, Stedeford T, Chopp M, Sanberg PR (2001) Expression of neural markers in human umbilical cord blood. Exp Neurol 171:109–115
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest 111:1843–1851
Unal-Cevik I, Kilinc M, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Gurer G, Dalkara T (2004) Loss of NeuN immunoreactivity after cerebral ischemia does not indicate neuronal cell loss: a cautionary note. Brain Res 1015:169–174
Volpe JJ (2008) Neurology of the newborn. Elsevier, Philadelphia
Volpe JJ (2009) Brain injury in premature infants: a complex amalgam of destructive and developmental disturbances. Lancet Neurol 8:110–124
Wakabayashi K, Nagai A, Sheikh AM, Shiota Y, Narantuya D, Watanabe T, Masuda J, Kobayashi S, Kim SU, Yamaguchi S (2010) Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem cells promotes functional improvement and increased expression of neurotrophic factors in a rat focal cerebral ischemia model. J Neurosci Res 88:1017–1025
Wang X, Karlsson JO, Zhu C, Bahr BA, Hagberg H, Blomgren K (2001) Caspase-3 activation after neonatal rat cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. Biol Neonate 79:172–179
Yasuhara T, Hara K, Maki M, Xu L, Yu G, Ali MM, Masuda T, Yu SJ, Bae EK, Hayashi T, Matsukawa N, Kaneko Y, Kuzmin-Nichols N, Ellovitch S, Cruz EL, Klasko SK, Sanberg CD, Sanberg PR, Borlongan CV (2010) Mannitol facilitates neurotrophic factor upregulation and behavioral recovery in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic rats with human umbilical cord blood grafts. J Cell Mol Med 14:914–921
Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Jiang Q, Zhang R, Davies K, Powers C, Bruggen N, Chopp M (2000) VEGF enhances angiogenesis and promotes blood-brain barrier leakage in the ischemic brain. J Clin Invest 106:829–838
Zigova T, Song S, Willing AE, Hudson JE, Newman MB, Saporta S, Sanchez-Ramos J, Sanberg PR (2002) Human umbilical cord blood cells express neural antigens after transplantation into the developing rat brain. Cell Transplant 11:265–274
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Janet Moers, Lidia Janota, Heike Groth and Jennifer Heinz for their excellent technical assistance and Helga Schulze for expert drawing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding: This study was supported by a grant of the Stem Cell Network North Rhine Westphalia, Germany (to C.M.), and by the Medical Faculty of Ruhr-University Bochum, Germany (FoRUM)
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Expression of occludin in rat brains assessed by immunohistochemistry. Representative images of immunhistochemical staining of occludin (green), on P21 rat brains of animals of the following groups a sham, b lesion and c lesion+hucb (lesion plus additional application of hucb cells). Nuclei are labeled in blue (Hoechst staining a–c). Scale bar in (a) for (a–c) 50 μm (PDF 2484 kb)
Fig. S2
Quantitative real time PCR analysis of rat VEGF mRNA expression. For determination of species origin of VEGF, quantitative real time PCR was performed with primers specific for rat VEGF. Analysis was performed at P9 and P21 in left hemispheres of rat brains of the following experimental groups: sham, sham+hucb, lesion and lesion+hucb. Significant differences of p < 0.05 are indicated by *** (PDF 5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenkranz, K., Kumbruch, S., Tenbusch, M. et al. Transplantation of human umbilical cord blood cells mediated beneficial effects on apoptosis, angiogenesis and neuronal survival after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats. Cell Tissue Res 348, 429–438 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-012-1401-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-012-1401-0