Abstract
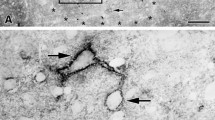
Although the tissue plasminogen activator/plasminogen system contributes to numerous brain functions, such as learning, memory, and anxiety behavior, little attention has as yet been given to the localization of plasminogen in the brain. We have investigated the localization of plasminogen in the adult mouse brain by using immunohistochemistry. In the hippocampus, plasminogen immunoreactivity was seen in the pyramidal cell layer as numerous punctate structures in neuronal somata. An electron-microscopic study further demonstrated that the plasminogen-immunoreactive punctate structures represented secretory vesicles and/or vesicle clusters. In the cerebral cortex, plasminogen immunoreactivity was evident in the somata of the layer II/III and V neurons. A quantitative analysis revealed that parvalbumin (PV)-positive neurons had more plasminogen-immunoreactive puncta compared with those of PV-negative neurons in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. Plasminogen immunoreactivity was present throughout the hypothalamus, being particularly prominent in the neuronal somata of the organum vasculosum laminae terminalis, ventromedial preoptic nucleus, supraoptic nucleus, subfornical organ, medial part of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN), posterior part of the PVN, and arcuate hypothalamic nucleus. Thus, plasminogen is highly expressed in specific populations of hippocampal, cortical, and hypothalamic neurons, and plasminogen-containing vesicles are mainly observed at neuronal somata.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asp L, Kartberg F, Fernandez-Rodriguez J, Smedh M, Elsner M, Laporte F, Bárcena M, Jansen KA, Valentijn JA, Koster AJ, Bergeron JJM, Nilsson T (2009) Early stages of Golgi vesicles and tubule formation require diacylglycerol. Mol Biol 20:780–790
Baranes D, LopezGarcia JC, Chen M, Bailey CH, Kandel ER (1996) Reconstitution of the hippocampal mossy fiber and associational-commissural pathways in a novel dissociated cell culture system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:4706–4711
Baranes D, Lederfein D, Huang YY, Chen M, Bailey CH, Kandel ER (1998) Tissue plasminogen activator contributes to the late phase of LTP and to synaptic growth in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway. Neuron 21:813–825
Basham ME, Seeds NW (2001) Plasminogen expression in the neonatal and adult mouse brain. J Neurochem 77:318–325
Brigadski T, Hartmann M, Lessmann V (2005) Differential vesicular targeting and time course of synaptic secretion of the mammalian neurotrophins. J Neurosci 25:7601–7614
Burgoyne RD, Morgan A (2003) Secretory granule exocytosis. Physiol Rev 83:581–632
Carmeliet P, Schoonjans L, Kieckens L, Ream B, Degen J, Bronson R, De Vos R, Van den Oord JJ, Collen D, Mulligan RC (1994) Physiological consequences of loss of plasminogen activator gene function in mice. Nature 368:419–424
Celio MR, Spreafico R, De Biasi S, Vittelaro-Zuccarello L (1998) Perineuronal nets: past and present. Trend Neurosci 21:510–515
Chen Z-L, Strickland S (1997) Neuronal death in the hippocampus is promoted by plasmin-catalyzed degradation of laminin. Cell 91:917–925
Chen Z-L, Yu H, Yu WM, Pawlak R, Strickland S (2008) Proteolytic fragments of laminin promote excitotoxic neurodegeneration by upregulation of the KA1 subunit of the kainite receptor. J Cell Biol 183:1299–1313
Conde H (1992) Organization and physiology of the substantia nigra. Exp Brain Res 88:233–248
Dityatev A, Schachner M (2003) Extracellular matrix molecules and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:456–486
Gualandris TP, Jones TE, Strickland S, Tsirka SE (1996) Membrane depolarization induces calcium-dependent secretion of tissue plasminogen activator. J Neurosci 16:2220–2225
Hu K, Yang J, Tanaka S, Gonias SL, Mars WM, Liu Y (2006) Tissue-type plasminogen activator acts as a cytokine that triggers intracellular signal transduction and induces matrix metalloprotease-9 gene expression. J Biol Chem 281:2120–2127
Imamura Y, Morita S, Nakatani Y, Okada K, Ueshima S, Matsuo O, Miyata S (2010) Tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen are critical for osmotic homeostasis by regulating vasopressin secretion. J Neurosci Res 88:1995–2006
Kuczewski N, Porcher C, Lessmann V, Medina I, Gaiarsa J-L (2009) Activity-dependent dendritic release of BDNF and biological consequences. Mol Neurobiol 39:37–49
Lochner JE, Kingma M, Kuhn S, Meliza CD, Cutler B, Scalettar BA (1998) Real-time imaging of the axonal transport of granules containing a tissue plasminogen activator/green fluorescent protein hybrid. Mol Biol Cell 9:2463–2476
Ludwig M, Sabatler N, Landgraft R, Dayanithi G, Leng G (2002) Intracellular calcium stores regulate activity-dependent neuropeptide release from dendrites. Nature 418:85–89
Madani R, Hulo S, Toni N, Madani H, Steiner T, Muller D, Vassali J-D (1999) Enhanced hippocampal long-term potentiation and learning by increased neuronal expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator in transgenic mice. EMBO J 18:3007–3012
Mataga N, Nagai N, Hensch TK (2002) Permissive proteolytic activity for visual cortical plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7717–7721
Mataga N, Mizuguchi Y, Hensch T (2004) Experience-dependent pruning of dendritic spines in visual cortex by tissue plasminogen activator. Neuron 44:1031–1041
Matys T, Pawlak R, Matys E, Pavlides C, McEwen BS, Strickland S (2004) Tissue plasminogen activator promotes the effects of corticotrophin-releasing factor on the amygdala and anxiety-like behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:16345–16350
Matys T, Pawlak R, Strickland S (2005) Tissue plasminogen activator in the bed nucleus of stria terminals regulates acoustic startle. Neuroscience 135:715–722
Melchor JP, Strickland S (2005) The tissue plasminogen activator in central nervous system physiology and pathology. Thromb Haemost 93:665–660
Melchor JP, Pawlak R, Strickland S (2003) The tissue plasminogen activator-plasminogen proteolytic cascade accelerates amyloid-beta (Abeta) degradation and inhibits Abeta-induced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 23:8867–8871
Miyata S, Takamatsu H, Maekawa S, Matsumoto N, Watanabe K, Kiyohara T, Hatton GI (2001) Plasticity of neurohypophysial terminals with increased hormonal release during dehydration: ultrastructural and biochemical analyses. J Comp Neurol 434:413–427
Miyata S, Nakatani Y, Hayashi N, Nakashima T (2005) Matrix-degrading enzymes tissue plasminogen activator and matrix metalloprotease-3 in the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Brain Res 1058:1–9
Mou X, Peterson CB, Prosser RA (2009) Tissue-type plasminogen activator-plasmin-BDNF modulate glutamate-induced phase-shifts of the mouse suprachiasmatic circadian clock in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 30:1451–1460
Mowla SJ, Pareek S, Farhadi HF, Petrecca K, Fawcett JP, Seidah NG, Morris SJ, Sossin WS, Murphy RA (1999) Differential sorting of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 19:2069–2080
Müller CM, Griesinger CB (1998) Tissue plasminogen activator mediates reverse occlusion plasticity in visual cortex. Nat Neurosci 1:47–53
Nagai T, Ito M, Nakamichi N, Mizoguchi H, Kamei H, Fukakusa A, Nabeshima T, Takuma K, Yamada K (2006) The rewards of nicotine regulation by tissue plasminogen activator-plasmin system through protease activated receptor-1. J Neurosci 26:12374–12383
Nakagami Y, Abe K, Nishiyama N, Matsuki N (2000) Laminin degradation by plasmin regulates long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 20:2003–2010
Neuhoff H, Roeper J, Schweizer M (1999) Activity-dependent formation of perforated synapses in cultured hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 11:4241–4250
Nicole O, Docagne F, Ali C, Margaill I, Carmeliet P, MacKenzie ET, Vivien D, Buisson A (2001) The proteolytic activity of tissue-plasminogen activator enhances NMDA receptor-mediated signaling. Nat Med 7:59–64
Oray S, Majewska A, Sur A (2004) Dendritic spine dynamics are regulated by monocular deprivation and extracellular matrix degradation. Neuron 44:1021–1030
Panda S, Antoch MP, Miller BH, Su AI, Schook AB, Straume M, Schultz PG, Kay SA, Takahashi JS, Hogenesch JB (2002) Coordinated transcription of key pathways in the mouse by the circadian clock. Cell 109:307–320
Pang PT, Lu B (2004) Regulation of late-phase LTP and long-term memory in normal and aging hippocampus: role of secreted proteins tPA and BDNF. Aging Res Rev 3:407–430
Pang PT, Ten HK, Zaitsev E, Woo NT, Sakata K, Zhen S, Teng KK, Yung W-H, Hempstead BL, Lu B (2004) Cleavage of proBDNF by tPA/plasmin is essential for long-term hippocampal plasticity. Science 306:487–491
Park L, Gallo EF, Anrather J, Wang G, Norris E, Paul J, Strickland S, Iadecola C (2008) Key role of tissue plasminogen activator in neurovascular coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:1073–1078
Parmer RJ, Mahata M, Mahata S, Sebald MT, O’Connor DT, Miles LA (1997) Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) is targeted to the regulated secretory pathway: catecholamine storage vesicles as a reservoir for the rapid release of tPA. J Biol Chem 272:1976–1982
Pawlak R, Magarinos AM, Melchor JP, McEwen B, Strickland S (2003) Tissue plasminogen activator in the amygdala is critical for stress-induced anxiety-like behaviors. Nat Neurosci 6:168–174
Pawlak R, Rao BSS, Melchor JP, Chattarji S, McEwen B, Strickland S (2005) Tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen mediate stress-induced decline of neuronal and cognitive functions in the mouse hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18201–18206
Pittman RN, Ivins JK, Buettner HM (1989) Neuronal plasminogen activators: cell surface binding sites and involvement in neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci 9:4269–4286
Pizzorusso T, Medini P, Berardi N, Chierzi S, Fawcett JW, Maffei L (2002) Reactivation of ocular dominance plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Science 898:1248–1251
Pow DV, Morris JF (1989) Dendrites of hypothalamic magnocellular neurons release neurohypophysial peptides by exocytosis. Neuroscience 32:435–439
Powell EM, Cambell DB, Stanwood GD, Davis C, Naebels JL, Levitt P (2003) Genetic disruption of cortical interneuron development causes region- and GABA cell type-specific deficits: epilepsy and hormonal dysfunction. J Neurosci 21:622–631
Pucak ML, Grace AA (1994) Regulation of substantia nigra dopamine neurons. Crit Rev Neurobiol 9:67–89
Qian Z, Gilbert ME, Colicos MA, Kandel ER, Kuhl D (1993) Tissue-plasminogen activator is induced as an immediate-early gene during seizure, kindling and long-term potentiation. Nature 361:453–457
Reinhard C, Schweikert M, Wieland FT, Nickel W (2003) Functional reconstitution of COPI coat assembly using chemically defined components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8253–8257
Rhodes KE, Fawcett JW (2004) Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans: preventing plasticity or protecting the CNS. J Anat 204:33–48
Sallés FJ, Strickland S (2002) Localization and regulation of the tissue plasminogen activator-plasmin system in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 22:2125–2134
Sappino A, Madani R, Huarte J, Belin D, Kiss J, Wohlwend A, Vassalli J-D (1993) Extracellular proteolysis in the adult murine brain. J Clin Invest 92:679–685
Seeds NW, Williams BL, Bickford PC (1995) Tissue plasminogen activator induction in Purkinje neurons after cerebellar motor learning. Science 270:1992–1994
Seeds NW, Basham ME, Haffke SP (1999) Neuronal migration is retarded in mice lacking the tissue plasminogen activator gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14118–14123
Shin CY, Kundel M, Wells DG (2004) Rapid, activity-induced increase in tissue plasminogen activator is mediated by metabotrophic glutamate receptor-dependent mRNA translation. J Neurosci 24:9425–9433
Silverman M, Johnson S, Gurkins D, Farmer M, Lochner JE, Rosa P, Scalettar BA (2005) Mechanisms of transport and exocytosis of dense-core granules containing tissue plasminogen activator in developing hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 25:3095–3106
Skrzypiec AE, Buczko W, Pawlak R (2008) Tissue plasminogen activator in the amygdala: a new role for an old protease. J Physiol Pharmacol S8:135–146
Tsirka SE, Gualandris A, Amaral DG, Strickland S (1995) Excitation-induced neuronal degeneration and seizure are mediated by tissue plasminogen activator. Nature 377:340–344
Tsirka SE, Rogove AD, Bugge TH, Degen JL, Strickland S (1997) An extracellular proteolytic cascade promotes neuronal degeneration in the mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci 17:543–552
Wang YF, Tsirka SE, Strickland S, Stieg PE, Soriano SG, Lipton SA (1998) Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) increases neuronal damage after focal cerebral ischemia in wild-type and tPA-deficient mice. Nat Med 4:228–231
Wu YP, Siao CJ, Lu W, Sung TC, Frohman MA, Milev P, Bugen TH, Degen JL, Levine JM, Margolis RU, Tsirka SE (2000) The tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)/plasmin extracellular proteolytic system regulates seizure-induced hippocampal mossy fiber outgrowth through a proteoglycan substrate. J Cell Biol 148:1295–1304
Xu X, Roby KD, Callaway EM (2010) Immunochemical characterization of inhibitory mouse cortical neurons: three chemically distinct classes of inhibitory cells. J Comp Neurol 518:389–404
Yepes M, Lawrence DL (2004) New functions for an old enzyme: nonhomeostatic roles for tissue-type plasminogen activator in the central nervous system. Exp Biol Med 229:1097–1104
Zhang Y, Kanaho Y, Frohman MA, Tsirka SE (2005) Phospholipase D1-promoted release of tissue plasminogen activator facilitates neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci 25:1797–1805
Zhuo M, Holtzman DM, Li Y, Osaka H, DeMaro J, Jacquin M, Bu G (2000) Role of tissue plasminogen activator receptor LRP in hippocampal long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 20:542–549
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yuki Taniguchi and Naoko Inoue contributed equally to this work.
This work was supported in part by Scientific Research Grants from the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (no. 21500323). The authors express their gratitude to the “High-Tech Research Center” Project for Private Universities.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taniguchi, Y., Inoue, N., Morita, S. et al. Localization of plasminogen in mouse hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and hypothalamus. Cell Tissue Res 343, 303–317 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-1110-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-1110-5