Abstract
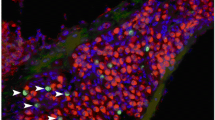
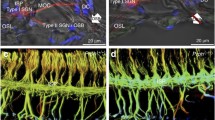
The organ of Corti contains two different types of auditory receptors; the inner (IHCs) and outer (OHCs) hair cells. This dualism is further represented in their innervation, IHCs being innervated by type I neurons, and OHCs by type II neurons (in man, named small ganglion cells). Two efferent systems are also present. Here, we have analyzed the expression of the 57-kDa neuron-specific intermediate filament protein peripherin (PP) in human cochlea. In the human organ of Corti, PP seems to be specifically expressed in OHC afferents. Small or type II spiral ganglion cell bodies also intensely express PP. Thus, PP can be used as a marker for the characterization of the innervation of the OHC system in man.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barclay M, Julien JP, Ryanc AF, Housleya GD (2010) Type III intermediate filament peripherin inhibits neuritogenesis in type II spiral ganglion neurons in vitro. Neurosci Lett 478:51–55
Beaulieu JM, Nguyen MD, Julien JP (1999) Late onset of motor neurons in mice overexpressing wild-type peripherin. J Cell Biol 147:531–544
Benson TE, Brown MC (2004) Postsynaptic targets of type II auditory nerve fibers in the cochlear nucleus. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 5:111–125
Berglund AM, Brown MC (1994) Central trajectories of type II spiral ganglion cells from various cochlear regions in mice. Hear Res 75:121–130
Berglund AM, Ryugo DK (1987) Hair cell innervation by spiral ganglion neurons in the mouse. J Comp Neurol 255:560–570
Berglund AM, Ryugo DK (1991) Neurofilament antibodies and spiral ganglion neurons of the mammalian cochlea. J Comp Neurol 306:393–408
Brown MC, Ledwith JV III (1990) Projections of thin (type-II) and thick (type-I) auditory-nerve fibers into the cochlear nucleus of the mouse. Hear Res 49:105–118
Brown MC, Berglund AM, Kiang NY, Ryugo DK (1988) Central trajectories of type II spiral ganglion neurons. J Comp Neurol 278:581–590
Chadan S, Le Gall JY, Di Giamberardino L, Filliatreau G (1994) Axonal transport of type III intermediate filament protein peripherin in intact and regenerating motor axons of the rat sciatic nerve. J Neurosci Res 39:127–139
Després G, Leger GP, Dahl D, Romand R (1994) Distribution of cytoskeletal proteins (neurofilaments, peripherin and MAP-tau) in the cochlea of the human fetus. Acta Otolaryngol 114:377–381
Fritzsch B, Dillard M, Lavado A, Harvey NL, Jahan I (2010) Canal cristae growth and fiber extension to the outer hair cells of the mouse ear require Prox1 activity. PLoS One 23 5:e9377
Gorham JD, Baker H, Kegler D, ZiV EB (1990) The expression of the neuronal intermediate filament protein peripherin in the rat embryo. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 57:235–248
Hafidi A (1998) Peripherin-like immunoreactivity in type II spiral ganglion cell body and projections. Brain Res 805:181–190
Helfand BT, Mendez MG, Pugh J, Delsert C, Goldman RD (2003) A role for intermediate filaments in determining and maintaining the shape of nerve cells. Mol Biol Cell 14:5069–5081
Huang LC, Thorne PR, Housley GD, Montgomery JM (2007) Spatiotemporal definition of neurite outgrowth, refinement and retraction in the developing mouse cochlea. Development 134:2925–2933
Hurd LB, Hutson KA, Morest DK (1999) Cochlear nerve projections to the small cell shell of the cochlear nucleus: the neuroanatomy of extremely thin sensory axons. Synapse 33:83–117
Keithley EM, Truong T, Chandronait B, Billings PB (2000) Immunohistochemistry and microwave decalcification of human temporal bones. Hear Res 148:192–196
Kuijpers W, Tonnaer EL, Peters TA, Ramaekers FC (1991) Expression of intermediate filament proteins in the mature inner ear of the rat and guinea pig. Hear Res 52:133–146
Lallemend F, Vandenbosch R, Hadjab S, Bodson M, Breuskin I, Moonen G, Lefebvre PP, Malgrange B (2007) New insights into peripherin expression in cochlear neurons. Neuroscience 150:212–222
Lecomte MJ, Basseville M, Landon F, Karpov V, Fauquet M (1998) Transcriptional activation of the mouse peripherin gene by leukemia inhibitory factor: involvement of STAT proteins. J Neurochem 70:971–982
Leonard DG, Gorham JD, Cole P, Greene LA, Ziff EB (1988) A nerve growth factor-regulated messenger RNA encodes a new intermediate filament protein. J Cell Biol 106:181–193
Liu W, Boström M, Kinnefors A, Rask-Andersen H (2009a) Unique expression of connexins in the human cochlea. Hear Res 250:55–62
Liu W, Boström M, Rask-Andersen H (2009b) Expression of peripherin in the pig spiral ganglion—aspects of nerve injury and regeneration. Acta Otolaryngol 129:608–614
Mathew JS, Westmoreland SV, Alvarez X, Simon MA, Pauley DR, MacKey JJ, Lackner AA (2001) Expression of peripherin in the brain of macaques (Macaca mulatta and Macaca fascicularis) occurs in astrocytes rather than neurones and is associated with encephalitis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 27:434–443
Oblinger MM, Wong J, Parysek LM (1989) Axotomy-induced changes in the expression of a type III neuronal intermediate filament gene. J Neurosci 9:3766–3775
Parysek LM, Chisholm RL, Ley CA, Goldman RD (1988) A type III intermediate filament gene is expressed in mature neurons. Neuron 1:395–401
Romand R, Sobkowicz H, Emmerling M, Whitlon D, Dahl D (1990) Patterns of neurofilament stain in the spiral ganglion of the developing and adult mouse. Hear Res 49:119–125
Ryugo DK, Dodds LW, Benson TE, Kiang NY (1991) Unmyelinated axons of the auditory nerve in cats. J Comp Neurol 308:209–223
Schimmang T, Tan J, Müller M, Zimmermann U, Rohbock K, Kôpschall I, Limberger A, Minichiello L, Knipper M (2003) Lack of Bdnf and TrkB signalling in the postnatal cochlea leads to a spatial reshaping of innervation along the tonotopic axis and hearing loss. Development 130:4741–4750
Thompson MA, Ziff EB (1989) Structure of the gene encoding peripherin, an NGF-regulated neuronal-specific type III intermediate filament protein. Neuron 2:1043–1053
Troy CM, Brown K, Greene LA, Shelanski ML (1990a) Ontogeny of the neuronal intermediate filament protein, peripherin, in the mouse embryo. Neuroscience 36:217–237
Troy CM, Muma NA, Greene LA, Price DL, Shelanski ML (1990b) Regulation of peripherin and neurofilament expression in regenerating rat motor neurons. Brain Res 529:232–238
Terao E, Janssens S, Bosch de Aguilar P van den, Portier M, Klosen P (2000) In vivo expression of the intermediate filament peripherin in rat motoneurons: modulation by inhibitory and stimulatory signals. Neuroscience 101:679–688
Wong J, Oblinger MM (1990) Differential regulation of peripherin and neurofilament gene expression in regenerating rat DRG neurons. J Neurosci Res 27:332–341
Ylikoski J, Pirvola U, Häppölä O (1993) Characterization of the vestibular and spiral ganglion cell somata of the rat by distribution of neurofilament proteins. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 503:121–126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This study was supported by ALF grants from Uppsala University Hospital and Uppsala University and by the Foundation “Tysta Skolan”, the Sellander Foundation, and the Swedish Deafness Foundation (HRF). Our research is a part of the European Community 6th Framework Programme on Research, Technological Development and Demonstration (Nanotechnology-based Targeted Drug Delivery; contract number: NMP-2004–3.4.1.5-1-1, project acronym: NANOEAR; NINDC[NIH] 1 R 24 DC 008625).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Kinnefors, A., Boström, M. et al. Expression of peripherin in human cochlea. Cell Tissue Res 342, 345–351 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-1081-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-1081-6