Abstract
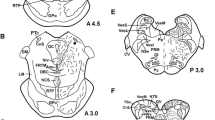
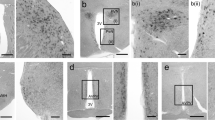
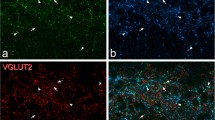
The GLW-amide family is a neuropeptide family found in cnidarian species and is characterized by the C-terminal amino acid sequence -Gly-Leu-Trp-NH2. To detect mammalian peptides structurally related to the GLW-amide family, we examined rat brain by immunohistochemistry with an anti-GLW-amide antibody. GLW-amide-like immunoreactivity (GLW-amide-LI) was observed in thin varicose fibers in some regions of the brain. Most neurons showing GLW-amide-LI were observed in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus, pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus, and trigeminal/spinal ganglia. These results strongly suggest that the rat nervous system contains as yet unidentified GLW-amide-like peptides, and that GLW-amide-LI in the brain is a good marker for ascending projections from mesopontine cholinergic neurons.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boer HH, Schot LP, Veenstra JA, Reichelt D (1980) Immunocytochemical identification of neural elements in the central nervous systems of a snail, some insects, a fish, and a mammal with an antiserum to the molluscan cardio-excitatory tetrapeptide FMRF-amide. Cell Tissue Res 213:21–27
Butcher LL, Woolf NJ (2003) Cholinergic neurons and networks revisited. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, New York, pp 1257-1268
Cao YQ, Mantyh PW, Carlson EJ, Gillespie AM, Epstein CJ, Basbaum AI (1998) Primary afferent tachykinins are required to experience moderate to intense pain. Nature 392:390–394
Cornwall J, Cooper JD, Phillipson OT (1990) Afferent and efferent connections of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus in the rat. Brain Res Bull 25:271–284
Cuello AC, Kanazawa I (1978) The distribution of substance P immunoreactive fibers in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 178:129–156
De Felipe C, Herrero JF, O'Brien JA, Palmer JA, Doyle CA, Smith AJ, Laird JM, Belmonte C, Cervero F, Hunt SP (1998) Altered nociception, analgesia and aggression in mice lacking the receptor for substance P. Nature 392:394–397
Gajewski M, Leitz T, Schloßherr J, Plickert G (1996) LWamides from Cnidaria constitute a novel family of neuropeptides with morphogenetic activity. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 205:232–242
Grimmelikhuijzen CJ, Sundler F, Rehfeld JF (1980) Gastrin/CCK-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of coelenterates. Histochemistry 69:61–68
Grimmelikhuijzen CJ, Dierickx K, Boer GJ (1982) Oxytocin/vasopressin-like immunoreactivity is present in the nervous system of hydra. Neuroscience 7:3191–3199
Hallanger AE, Wainer BH (1988) Ascending projections from the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus and the adjacent mesopontine tegmentum in the rat. J Comp Neurol 274:483–515
Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl A, Terenius L, Elde R, Nilsson G (1977) Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:3081–3085
Kapuscinski M, Green M, Sinha SN, Shepherd JJ, Shulkes A (1993) Peptide alpha-amidation activity in human plasma: relationship to gastrin processing. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 39:51–58
Leitz T, Lay M (1995) Metamorphosin A is a neuropeptide. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 204:276–279
Leitz T, Morand K, Mann M (1994) Metamorphosin A: a novel peptide controlling development of the lower metazoan Hydractinia echinata (Coelenterata, Hydrozoa). Dev Biol 163:440–446
Leviev I, Grimmelikhuijzen CJ (1995) Molecular cloning of preprohormone from sea anemones containing numerous copies of a metamorphosis-inducing neuropeptide: a likely role for dipeptidyl aminopeptidase in neuropeptide precursor processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:11647–11651
Leviev I, Williamson M, Grimmelikhuijzen CJ (1997) Molecular cloning of a preprohormone from Hydra magnipapillata containing multiple copies of Hydra-LWamide (Leu-Trp-NH2) neuropeptides: evidence for processing at Ser and Asn residues. J Neurochem 68:1319–1325
Liang P, Pardee AB (1992) Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science 257:967–971
Ljungdahl A, Hökfelt T, Nilsson G (1978) Distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat-I. Cell bodies and nerve terminals. Neuroscience 3:861–943
Paxinos G, Watson C (1996) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Powell JF, Reska-Skinner SM, Prakash MO, Fischer WH, Park M, Rivier JE, Craig AG, Mackie GO, Sherwood NM (1996) Two new forms of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in a protochordate and the evolutionary implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10461–10464
Rexed B (1954) A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the spinal cord in the cat. J Comp Neurol 100:297–379
Sasek CA, Elde RP (1985) Distribution of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity and its relationship to FMRF-amide-like immunoreactivity in the sixth lumbar and first sacral spinal cord segments of the rat. J Neurosci 5:1729–1739
Satoh K, Fibiger HC (1986) Cholinergic neurons of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus: efferent and afferent connections. J Comp Neurol 253:277–302
Schot LP, Boer HH, Swaab DF, Van Noorden S (1981) Immunocytochemical demonstration of peptidergic neurons in the central nervous system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis with antisera raised to biologically active peptides of vertebrates. Cell Tissue Res 216:273–291
Siegel J (2004) Brain mechanisms that control sleep and waking. Naturwissenschaften 91:355–365
Strand FL (1999) Neuropeptides: regulators of physiological processes. MIT Press, Cambridge (Mass.)
Takahashi T, Muneoka Y, Lohmann J, Lopez de Haro MS, Solleder G, Bosch TC, David CN, Bode HR, Koizumi O, Shimizu H, Hatta M, Fujisawa T, Sugiyama T (1997) Systematic isolation of peptide signal molecules regulating development in hydra: LWamide and PW families. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1241–1246
Takahashi T, Kobayakawa Y, Muneoka Y, Fujisawa Y, Mohri S, Hatta M, Shimizu H, Fujisawa T, Sugiyama T, Takahara M, Yanagi K, Koizumi O (2003) Identification of a new member of the GLW-amide peptide family: physiological activity and cellular localization in cnidarian polyps. Comp Biochem Physiol [B] Biochem Mol Biol 135:309–324
Wand GS, Ney RL, Mains RE, Eipper BA (1985) Characterization of peptide alpha-amidation activity in human cerebrospinal fluid and central nervous system tissue. Neuroendocrinology 41:482–489
Woolf NJ, Butcher LL (1986) Cholinergic systems in the rat brain. III. Projections from the pontomesencephalic tegmentum to the thalamus, tectum, basal ganglia, and basal forebrain. Brain Res Bull 16:603–637
Yang HY, Fratta W, Majane EA, Costa E (1985) Isolation, sequencing, synthesis, and pharmacological characterization of two brain neuropeptides that modulate the action of morphine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7757–7761
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Toshitaka Fujisawa (National Institute of Genetics) and Dr. Toshio Takahashi (Suntory Institute for Bioorganic Research) for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Sports, and Culture, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamaguchi-Hamada, K., Fujisawa, Y., Koizumi, O. et al. Immunohistochemical evidence for the existence of novel mammalian neuropeptides related to the Hydra GLW-amide neuropeptide family. Cell Tissue Res 337, 15–25 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0808-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0808-8